| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
RNA is transcribed, but must be processed into a mature form before translation can begin. This processing after an RNA molecule has been transcribed, but before it is translated into a protein, is called post-transcriptional modification. As with the epigenetic and transcriptional stages of processing, this post-transcriptional step can also be regulated to control gene expression in the cell. If the RNA is not processed, shuttled, or translated, then no protein will be synthesized.
In eukaryotic cells, the RNA transcript often contains regions, called introns, that are removed prior to translation. The regions of RNA that code for protein are called exons ( [link] ). After an RNA molecule has been transcribed, but prior to its departure from the nucleus to be translated, the RNA is processed and the introns are removed by splicing.

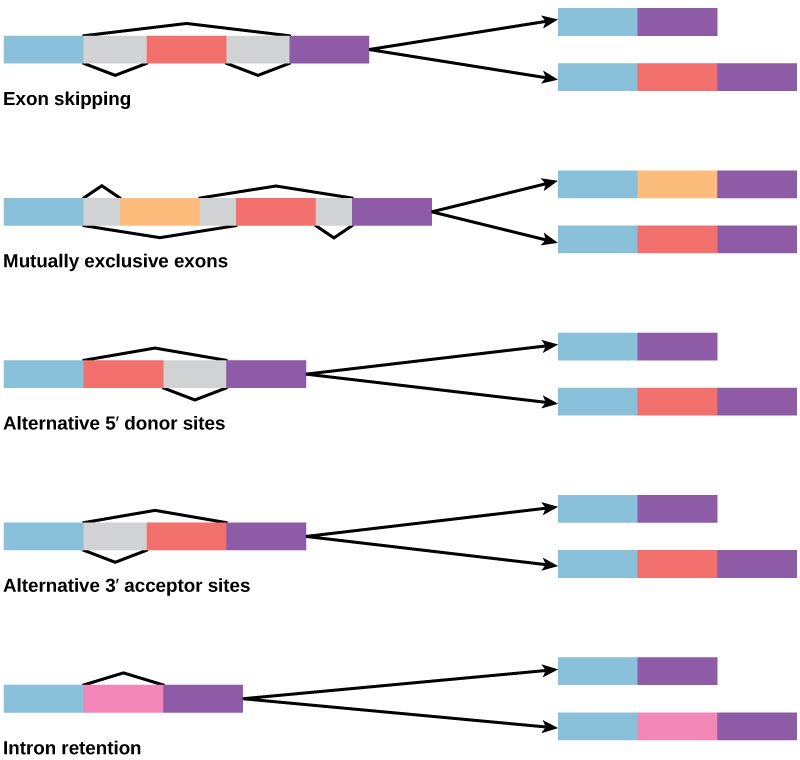
How could alternative splicing evolve? Introns have a beginning and ending recognition sequence; it is easy to imagine the failure of the splicing mechanism to identify the end of an intron and instead find the end of the next intron, thus removing two introns and the intervening exon. In fact, there are mechanisms in place to prevent such intron skipping, but mutations are likely to lead to their failure. Such “mistakes” would more than likely produce a nonfunctional protein. Indeed, the cause of many genetic diseases is alternative splicing rather than mutations in a sequence. However, alternative splicing would create a protein variant without the loss of the original protein, opening up possibilities for adaptation of the new variant to new functions. Gene duplication has played an important role in the evolution of new functions in a similar way by providing genes that may evolve without eliminating the original, functional protein.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?