| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
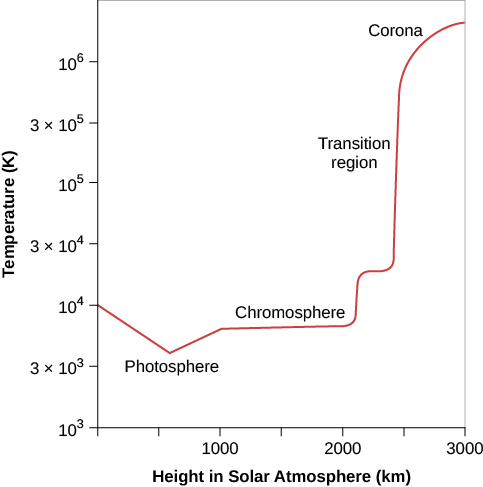
The temperature of the chromosphere is about 10,000 K. This means that the chromosphere is hotter than the photosphere, which should seem surprising. In all the situations we are familiar with, temperatures fall as one moves away from the source of heat, and the chromosphere is farther from the center of the Sun than the photosphere is.
The increase in temperature does not stop with the chromosphere. Above it is a region in the solar atmosphere where the temperature changes from 10,000 K (typical of the chromosphere) to nearly a million degrees. The hottest part of the solar atmosphere, which has a temperature of a million degrees or more, is called the corona . Appropriately, the part of the Sun where the rapid temperature rise occurs is called the transition region . It is probably only a few tens of kilometers thick. [link] summarizes how the temperature of the solar atmosphere changes from the photosphere outward.
In 2013, NASA launched the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) to study the transition region to understand better how and why this sharp temperature increase occurs. IRIS is the first space mission that is able to obtain high spatial resolution images of the different features produced over this wide temperature range and to see how they change with time and location ( [link] ).
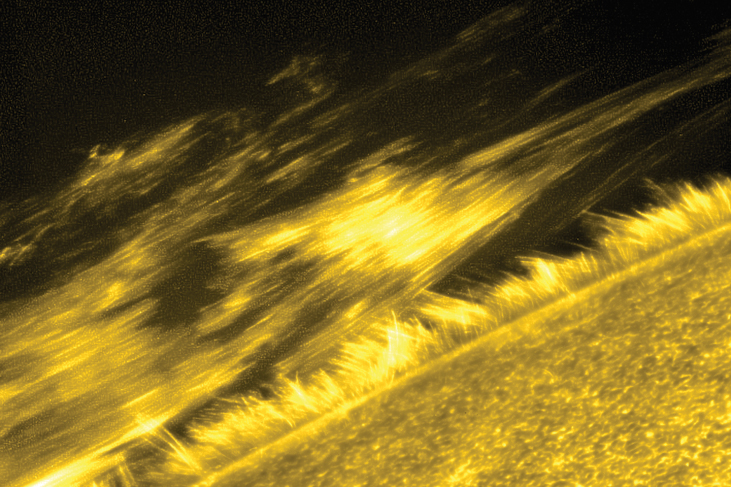
[link] and the red graph in [link] make the Sun seem rather like an onion, with smooth spherical shells, each one with a different temperature. For a long time, astronomers did indeed think of the Sun this way. However, we now know that while this idea of layers—photosphere, chromosphere, transition region, corona—describes the big picture fairly well, the Sun’s atmosphere is really more complicated, with hot and cool regions intermixed. For example, clouds of carbon monoxide gas with temperatures colder than 4000 K have now been found at the same height above the photosphere as the much hotter gas of the chromosphere.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?