| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Information about stellar populations holds vital clues to how our Galaxy was built up over time. The flattened disk shape of the Galaxy suggests that it formed through a process similar to the one that leads to the formation of a protostar (see The Birth of Stars and the Discovery of Planets outside the Solar System ). Building on this idea, astronomers first developed models that assumed the Galaxy formed from a single rotating cloud. But, as we shall see, this turns out to be only part of the story.
Because the oldest stars—those in the halo and in globular clusters—are distributed in a sphere centered on the nucleus of the Galaxy, it makes sense to assume that the protogalactic cloud that gave birth to our Galaxy was roughly spherical. The oldest stars in the halo have ages of 12 to 13 billion years, so we estimate that the formation of the Galaxy began about that long ago. (See the chapter on The Big Bang for other evidence that galaxies in general began forming a little more than 13 billion years ago.) Then, just as in the case of star formation, the protogalactic cloud collapsed and formed a thin rotating disk. Stars born before the cloud collapsed did not participate in the collapse, but have continued to orbit in the halo to the present day ( [link] ).
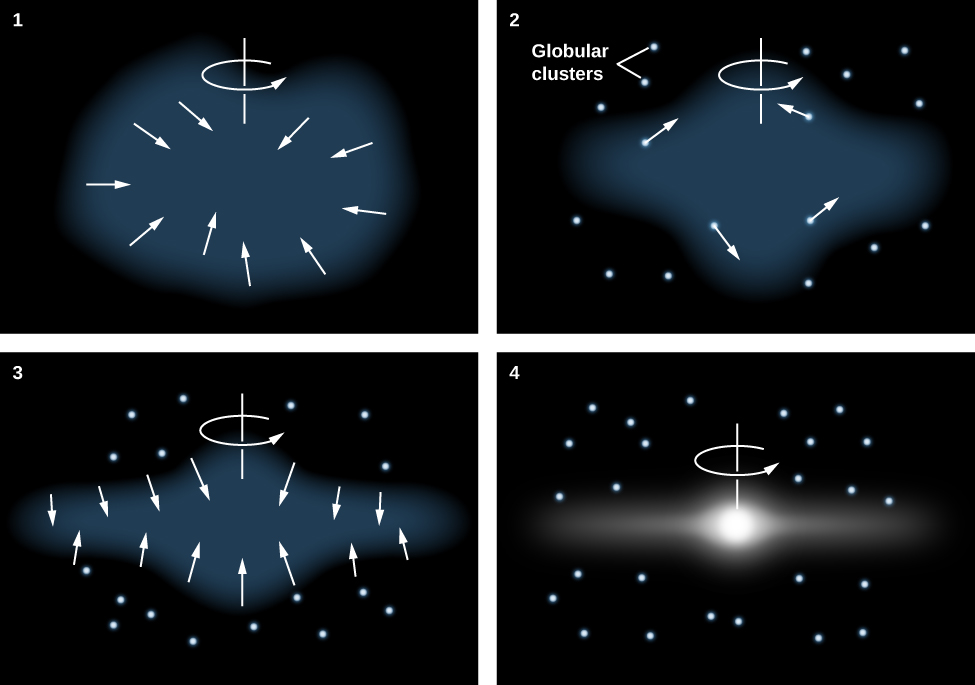
Gravitational forces caused the gas in the thin disk to fragment into clouds or clumps with masses like those of star clusters. These individual clouds then fragmented further to form stars. Since the oldest stars in the disk are nearly as old as the youngest stars in the halo, the collapse must have been rapid (astronomically speaking), requiring perhaps no more than a few hundred million years.
In past decades, astronomers have learned that the evolution of the Galaxy has not been quite as peaceful as this monolithic collapse model suggests. In 1994, astronomers discovered a small new galaxy in the direction of the constellation of Sagittarius. The Sagittarius dwarf galaxy is currently about 70,000 light-years away from Earth and 50,000 light-years from the center of the Galaxy. It is the closest galaxy known ( [link] ). It is very elongated, and its shape indicates that it is being torn apart by our Galaxy’s gravitational tides—just as Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 was torn apart when it passed too close to Jupiter in 1992.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?