| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The idea that energy could turn into matter in the universe at large is a new one for many students, since it is not part of our everyday experience. That’s because, when we compare the universe today to what it was like right after the Big Bang, we live in cold, hard times. The photons in the universe today typically have far-less energy than the amount required to make new matter. In the discussion on the source of the Sun’s energy in The Sun: A Nuclear Powerhouse , we briefly mentioned that when subatomic particles of matter and antimatter collide, they turn into pure energy. But the reverse, energy turning into matter and antimatter , is equally possible. This process has been observed in particle accelerators around the world. If we have enough energy, under the right circumstances, new particles of matter (and antimatter) are indeed created —and the conditions were right during the first few minutes after the expansion of the universe began.
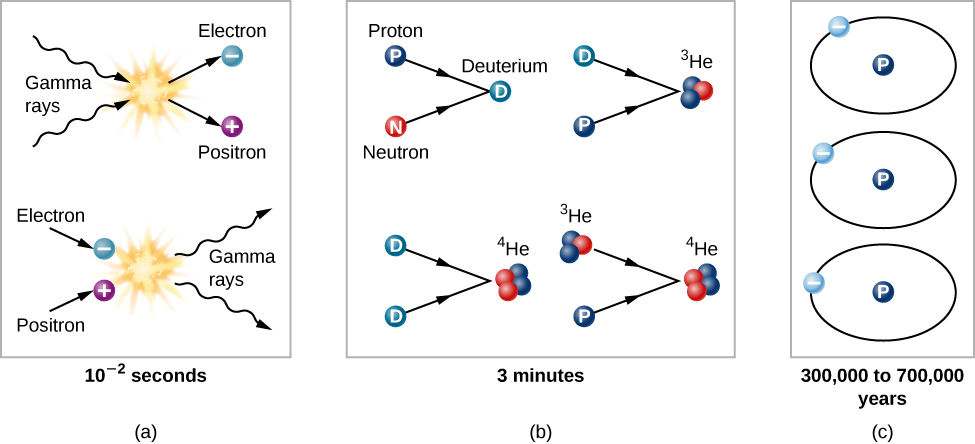
Our third key point is that the hotter the universe was, the more energetic were the photons available to make matter and antimatter (see [link] ). To take a specific example, at a temperature of 6 billion (6 × 10 9 ) K, the collision of two typical photons can create an electron and its antimatter counterpart, a positron. If the temperature exceeds 10 14 K, much more massive protons and antiprotons can be created.
Keeping these three ideas in mind, we can trace the evolution of the universe from the time it was about 0.01 second old and had a temperature of about 100 billion K. Why not begin at the very beginning? There are as yet no theories that allow us penetrate to a time before about 10 –43 second (this number is a decimal point followed by 42 zeros and then a one). It is so small that we cannot relate it to anything in our everyday experience. When the universe was that young, its density was so high that the theory of general relativity is not adequate to describe it, and even the concept of time breaks down.
Scientists, by the way, have been somewhat more successful in describing the universe when it was older than 10 –43 second but still less than about 0.01 second old. We will take a look at some of these ideas later in this chapter, but for now, we want to start with somewhat more familiar situations.
By the time the universe was 0.01 second old, it consisted of a soup of matter and radiation; the matter included protons and neutrons, leftovers from an even younger and hotter universe. Each particle collided rapidly with other particles. The temperature was no longer high enough to allow colliding photons to produce neutrons or protons, but it was sufficient for the production of electrons and positrons ( [link] ). There was probably also a sea of exotic subatomic particles that would later play a role as dark matter. All the particles jiggled about on their own; it was still much too hot for protons and neutrons to combine to form the nuclei of atoms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?