| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
After the Sun, the Moon is the brightest and most obvious object in the sky. Unlike the Sun, it does not shine under its own power, but merely glows with reflected sunlight. If you were to follow its progress in the sky for a month, you would observe a cycle of phases (different appearances), with the Moon starting dark and getting more and more illuminated by sunlight over the course of about two weeks. After the Moon’s disk becomes fully bright, it begins to fade, returning to dark about two weeks later.
These changes fascinated and mystified many early cultures, which came up with marvelous stories and legends to explain the cycle of the Moon. Even in the modern world, many people don’t understand what causes the phases, thinking that they are somehow related to the shadow of Earth. Let us see how the phases can be explained by the motion of the Moon relative to the bright light source in the solar system, the Sun.
Although we know that the Sun moves 1/12 of its path around the sky each month, for purposes of explaining the phases, we can assume that the Sun’s light comes from roughly the same direction during the course of a four-week lunar cycle. The Moon, on the other hand, moves completely around Earth in that time. As we watch the Moon from our vantage point on Earth, how much of its face we see illuminated by sunlight depends on the angle the Sun makes with the Moon.
Here is a simple experiment to show you what we mean: stand about 6 feet in front of a bright electric light in a completely dark room (or outdoors at night) and hold in your hand a small round object such as a tennis ball or an orange. Your head can then represent Earth, the light represents the Sun, and the ball the Moon. Move the ball around your head (making sure you don’t cause an eclipse by blocking the light with your head). You will see phases just like those of the Moon on the ball. (Another good way to get acquainted with the phases and motions of the Moon is to follow our satellite in the sky for a month or two, recording its shape, its direction from the Sun, and when it rises and sets.)
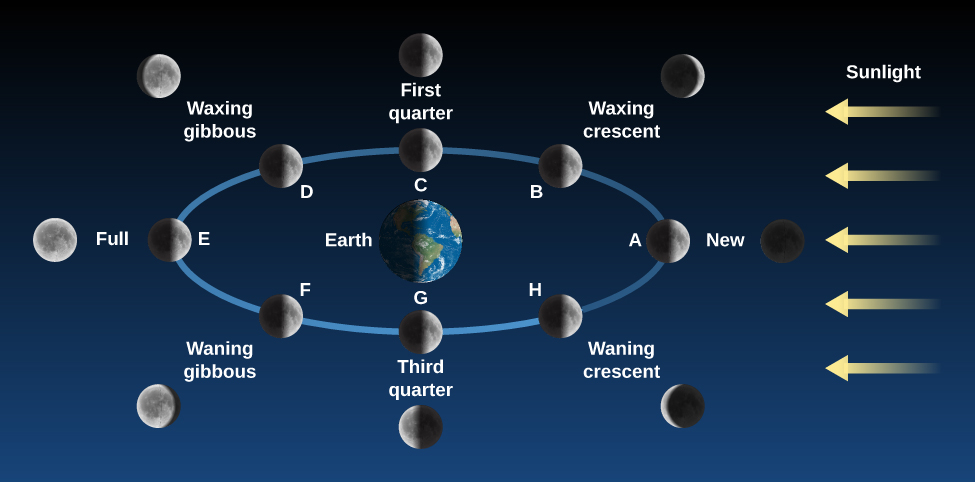
Let’s examine the Moon’s cycle of phases using [link] , which depicts the Moon’s behavior for the entire month. The trick to this figure is that you must imagine yourself standing on Earth, facing the Moon in each of its phases. So, for the position labeled “New,” you are on the right side of Earth and it’s the middle of the day; for the position “Full,” you are on the left side of Earth in the middle of the night. Note that in every position on [link] , the Moon is half illuminated and half dark (as a ball in sunlight should be). The difference at each position has to do with what part of the Moon faces Earth.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?