| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Some physicists suggested that these fundamental characteristics of the cosmos—its flatness and uniformity—can be explained if shortly after the Big Bang (and before the emission of the CMB), the universe experienced a sudden increase in size. A model universe in which this rapid, early expansion occurs is called an inflationary universe . The inflationary universe is identical to the Big Bang universe for all time after the first 10 –30 second. Prior to that, the model suggests that there was a brief period of extraordinarily rapid expansion or inflation, during which the scale of the universe increased by a factor of about 10 50 times more than predicted by standard Big Bang models ( [link] ).
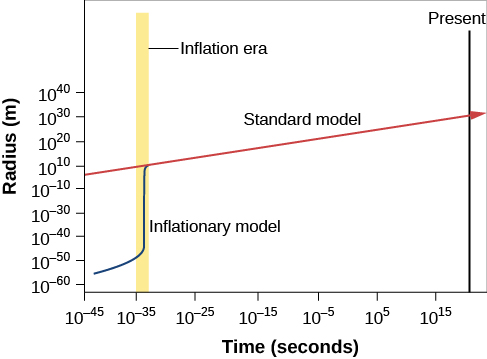
Prior to (and during) inflation, all the parts of the universe that we can now see were so small and close to each other that they could exchange information, that is, the horizon distance included all of the universe that we can now observe. Before (and during) inflation, there was adequate time for the observable universe to homogenize itself and come to the same temperature. Then, inflation expanded those regions tremendously, so that many parts of the universe are now beyond each other’s horizon.
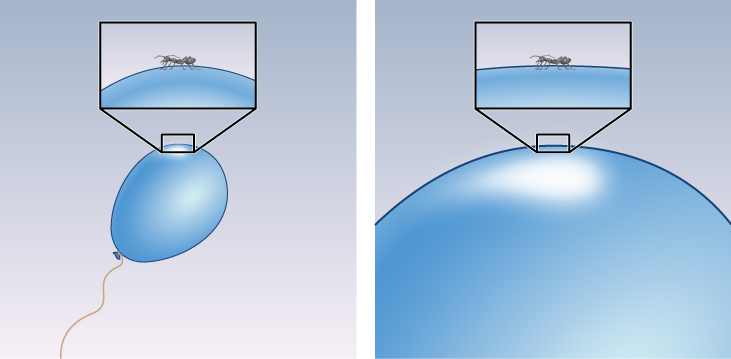
Another appeal of the inflationary model is its prediction that the density of the universe should be exactly equal to the critical density. To see why this is so, remember that curvature of spacetime is intimately linked to the density of matter. If the universe began with some curvature of its spacetime, one analogy for it might be the skin of a balloon. The period of inflation was equivalent to blowing up the balloon to a tremendous size. The universe became so big that from our vantage point, no curvature should be visible ( [link] ). In the same way, Earth’s surface is so big that it looks flat to us no matter where we are. Calculations show that a universe with no curvature is one that is at critical density. Universes with densities either higher or lower than the critical density would show marked curvature. But we saw that the observations of the CMB in [link] , which show that the universe has critical density, rule out the possibility that space is significantly curved.
While inflation is an intriguing idea and widely accepted by researchers, we cannot directly observe events so early in the universe. The conditions at the time of inflation were so extreme that we cannot reproduce them in our laboratories or high-energy accelerators, but scientists have some ideas about what the universe might have been like. These ideas are called grand unified theories or GUTs.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?