| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we noted in The Milky Way Galaxy chapter, our Galaxy has a modest bar too (see [link] ). The spiral arms usually begin from the ends of the bar. The fact that bars are so common suggests that they are long lived; it may be that most spiral galaxies form a bar at some point during their evolution.
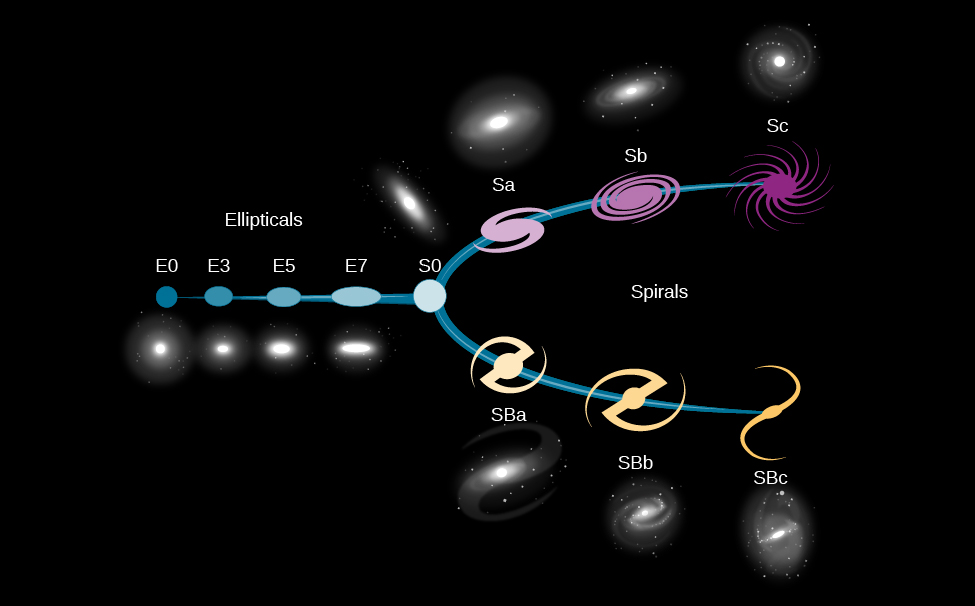
In both barred and unbarred spiral galaxies, we observe a range of different shapes. At one extreme, the central bulge is large and luminous, the arms are faint and tightly coiled, and bright emission nebulae and supergiant stars are inconspicuous. Hubble, who developed a system of classifying galaxies by shape, gave these galaxies the designation Sa. Galaxies at this extreme may have no clear spiral arm structure, resulting in a lens-like appearance (they are sometimes referred to as lenticular galaxies). These galaxies seem to share as many properties with elliptical galaxies as they do with spiral galaxies
At the other extreme, the central bulge is small and the arms are loosely wound. In these Sc galaxies, luminous stars and emission nebulae are very prominent. Our Galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy are both intermediate between the two extremes. Photographs of spiral galaxies , illustrating the different types, are shown in [link] , along with elliptical galaxies for comparison.
The luminous parts of spiral galaxies appear to range in diameter from about 20,000 to more than 100,000 light-years. Recent studies have found that there is probably a large amount of galactic material that extends well beyond the apparent edge of galaxies. This material appears to be thin, cold gas that is difficult to detect in most observations.
From the observational data available, the masses of the visible portions of spiral galaxies are estimated to range from 1 billion to 1 trillion Suns (10 9 to 10 12 M Sun ). The total luminosities of most spirals fall in the range of 100 million to 100 billion times the luminosity of our Sun (10 8 to 10 11 L Sun ). Our Galaxy and M31 are relatively large and massive, as spirals go. There is also considerable dark matter in and around the galaxies, just as there is in the Milky Way; we deduce its presence from how fast stars in the outer parts of the Galaxy are moving in their orbits.
Elliptical galaxies consist almost entirely of old stars and have shapes that are spheres or ellipsoids (somewhat squashed spheres) ( [link] ). They contain no trace of spiral arms. Their light is dominated by older reddish stars (the population II stars discussed in The Milky Way Galaxy ). In the larger nearby ellipticals, many globular clusters can be identified. Dust and emission nebulae are not conspicuous in elliptical galaxies, but many do contain a small amount of interstellar matter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?