| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
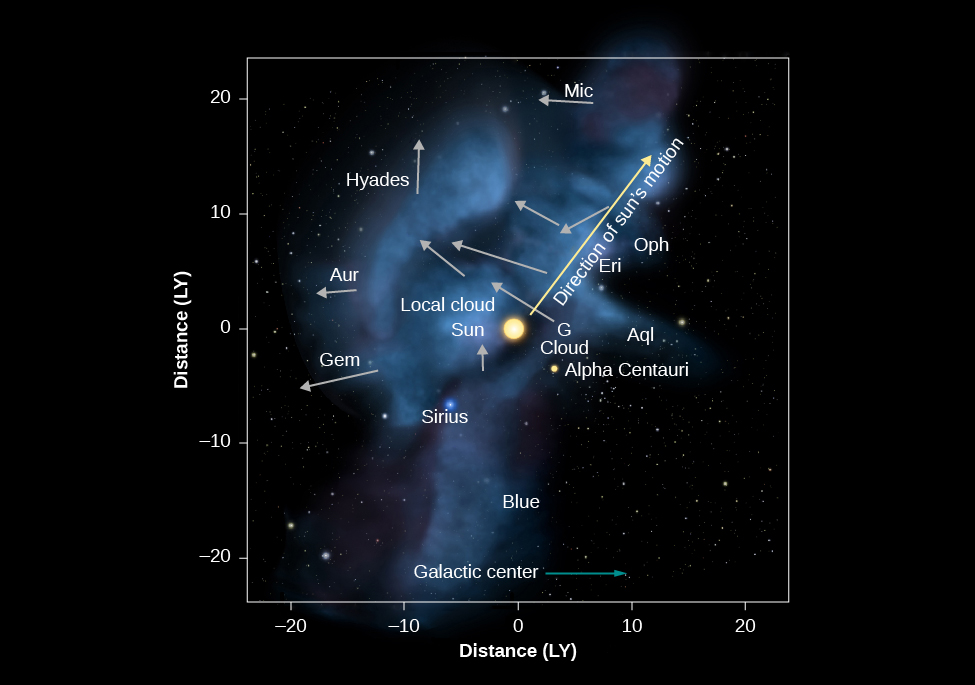
The Sun is located at the edge of a low-density cloud called the Local Fluff. The Sun and this cloud are located within the Local Bubble, a region extending to at least 300 light-years from the Sun, within which the density of interstellar material is extremely low. Astronomers think this bubble was blown by some nearby stars that experienced a strong wind and some supernova explosions.
Goodman, A. “Recycling the Universe.” Sky&Telescope November (2000): 44. Review of how stellar evolution, the interstellar medium, and supernovae all work together to recycle cosmic material.
Greenberg, J. “The Secrets of Stardust.” Scientific American December (2000): 70. The makeup and evolutionary role of solid particles between the stars.
Knapp, G. “The Stuff between the Stars.” Sky&Telescope May (1995): 20. An introduction to the interstellar medium.
Nadis, S. “Searching for the Molecules of Life in Space.” Sky&Telescope January (2002): 32. Recent observations of water in the interstellar medium by satellite telescopes.
Olinto, A. “Solving the Mystery of Cosmic Rays.” Astronomy April (2014): 30. What accelerates them to such high energies.
Reynolds, R. “The Gas between the Stars.” Scientific American January (2002): 34. On the interstellar medium.
Barnard, E. E., Biographical Memoir: http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/barnard-edward.pdf.
Cosmicopia: http://helios.gsfc.nasa.gov/cosmic.html. NASA’s learning site explains about the history and modern understanding of cosmic rays.
DECO: https://wipac.wisc.edu/deco. A smart-phone app for turning your phone into a cosmic-ray detector.
Hubble Space Telescope Images of Nebulae: http://hubblesite.org/gallery/album/nebula/. Click on any of the beautiful images in this collection, and you are taken to a page with more information; while looking at these images, you may also want to browse through the slide sequence on the meaning of colors in the Hubble pictures (http://hubblesite.org/gallery/behind_the_pictures/meaning_of_color/).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?