| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
We live at the bottom of the ocean of air that envelops our planet. The atmosphere, weighing down upon Earth ’s surface under the force of gravity, exerts a pressure at sea level that scientists define as 1 bar (a term that comes from the same root as barometer , an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure). A bar of pressure means that each square centimeter of Earth’s surface has a weight equivalent to 1.03 kilograms pressing down on it. Humans have evolved to live at this pressure; make the pressure a lot lower or higher and we do not function well.
The total mass of Earth’s atmosphere is about 5 × 10 18 kilograms. This sounds like a large number, but it is only about a millionth of the total mass of Earth. The atmosphere represents a smaller fraction of Earth than the fraction of your mass represented by the hair on your head.
The structure of the atmosphere is illustrated in [link] . Most of the atmosphere is concentrated near the surface of Earth, within about the bottom 10 kilometers where clouds form and airplanes fly. Within this region—called the troposphere —warm air, heated by the surface, rises and is replaced by descending currents of cooler air; this is an example of convection. This circulation generates clouds and wind. Within the troposphere, temperature decreases rapidly with increasing elevation to values near 50 °C below freezing at its upper boundary, where the stratosphere begins. Most of the stratosphere, which extends to about 50 kilometers above the surface, is cold and free of clouds.
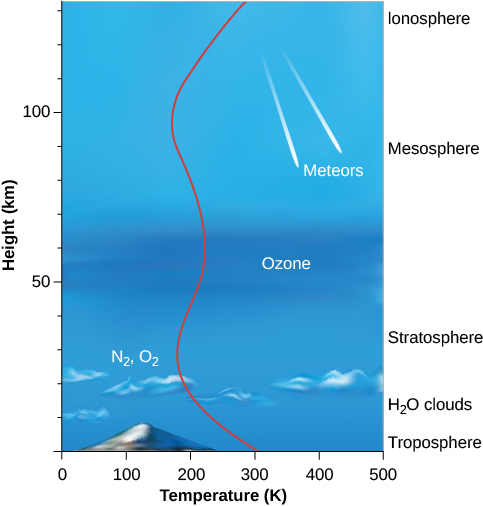
Near the top of the stratosphere is a layer of ozone (O 3 ), a heavy form of oxygen with three atoms per molecule instead of the usual two. Because ozone is a good absorber of ultraviolet light, it protects the surface from some of the Sun’s dangerous ultraviolet radiation, making it possible for life to exist on Earth. The breakup of ozone adds heat to the stratosphere, reversing the decreasing temperature trend in the troposphere. Because ozone is essential to our survival, we reacted with justifiable concern to evidence that became clear in the 1980s that atmospheric ozone was being destroyed by human activities. By international agreement, the production of industrial chemicals that cause ozone depletion, called chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs, has been phased out. As a result, ozone loss has stopped and the “ozone hole” over the Antarctic is shrinking gradually. This is an example of how concerted international action can help maintain the habitability of Earth.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?