| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
In addition to visible and infrared radiation, radio waves from astronomical objects can also be detected from the surface of Earth. In the early 1930s, Karl G. Jansky , an engineer at Bell Telephone Laboratories, was experimenting with antennas for long-range radio communication when he encountered some mysterious static—radio radiation coming from an unknown source ( [link] ). He discovered that this radiation came in strongest about four minutes earlier on each successive day and correctly concluded that since Earth’s sidereal rotation period (how long it takes us to rotate relative to the stars) is four minutes shorter than a solar day, the radiation must be originating from some region fixed on the celestial sphere. Subsequent investigation showed that the source of this radiation was part of the Milky Way Galaxy ; Jansky had discovered the first source of cosmic radio waves.
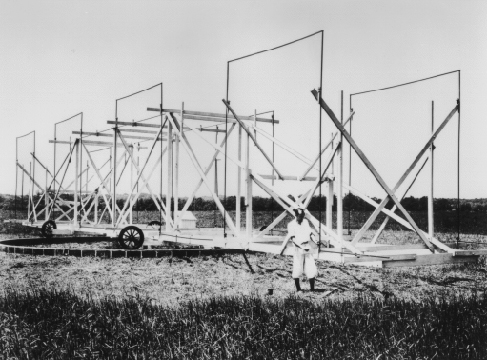
In 1936, Grote Reber , who was an amateur astronomer interested in radio communications, used galvanized iron and wood to build the first antenna specifically designed to receive cosmic radio waves. Over the years, Reber built several such antennas and used them to carry out pioneering surveys of the sky for celestial radio sources; he remained active in radio astronomy for more than 30 years. During the first decade, he worked practically alone because professional astronomers had not yet recognized the vast potential of radio astronomy.
It is important to understand that radio waves cannot be “heard”: they are not the sound waves you hear coming out of the radio receiver in your home or car. Like light, radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, but unlike light, we cannot detect them with our senses—we must rely on electronic equipment to pick them up. In commercial radio broadcasting, we encode sound information (music or a newscaster’s voice) into radio waves. These must be decoded at the other end and then turned back into sound by speakers or headphones.
The radio waves we receive from space do not, of course, have music or other program information encoded in them. If cosmic radio signals were translated into sound, they would sound like the static you hear when scanning between stations. Nevertheless, there is information in the radio waves we receive—information that can tell us about the chemistry and physical conditions of the sources of the waves.
Just as vibrating charged particles can produce electromagnetic waves (see the Radiation and Spectra chapter), electromagnetic waves can make charged particles move back and forth. Radio waves can produce a current in conductors of electricity such as metals. An antenna is such a conductor: it intercepts radio waves, which create a feeble current in it. The current is then amplified in a radio receiver until it is strong enough to measure or record. Like your television or radio, receivers can be tuned to select a single frequency (channel). In astronomy, however, it is more common to use sophisticated data-processing techniques that allow thousands of separate frequency bands to be detected simultaneously. Thus, the astronomical radio receiver operates much like a spectrometer on a visible-light or infrared telescope, providing information about how much radiation we receive at each wavelength or frequency. After computer processing, the radio signals are recorded on magnetic disks for further analysis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?