| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The idea that matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms is at least 25 centuries old. It took until the twentieth century, however, for scientists to invent instruments that permitted them to probe inside an atom and find that it is not, as had been thought, hard and indivisible. Instead, the atom is a complex structure composed of still smaller particles.
The first of these smaller particles was discovered by British physicist James (J. J.) Thomson in 1897. Named the electron , this particle is negatively charged. (It is the flow of these particles that produces currents of electricity, whether in lightning bolts or in the wires leading to your lamp.) Because an atom in its normal state is electrically neutral, each electron in an atom must be balanced by the same amount of positive charge.
The next step was to determine where in the atom the positive and negative charges are located. In 1911, British physicist Ernest Rutherford devised an experiment that provided part of the answer to this question. He bombarded an extremely thin piece of gold foil, only about 400 atoms thick, with a beam of alpha particles ( [link] ). Alpha particles (α particles) are helium atoms that have lost their electrons and thus are positively charged. Most of these particles passed though the gold foil just as if it and the atoms in it were nearly empty space. About 1 in 8000 of the alpha particles, however, completely reversed direction and bounced backward from the foil. Rutherford wrote, “It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you.”
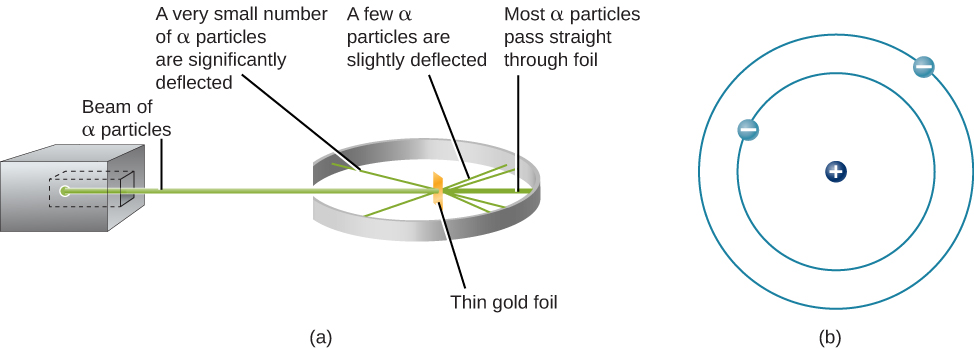
The only way to account for the particles that reversed direction when they hit the gold foil was to assume that nearly all of the mass, as well as all of the positive charge in each individual gold atom, is concentrated in a tiny center or nucleus . When a positively charged alpha particle strikes a nucleus, it reverses direction, much as a cue ball reverses direction when it strikes another billiard ball. Rutherford’s model placed the other type of charge—the negative electrons—in orbit around this nucleus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?