| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
In order to create an accurate map, a mapmaker needs a way to uniquely and simply identify the location of all the major features on the map, such as cities or natural landmarks. Similarly, astronomical mapmakers need a way to uniquely and simply identify the location of stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. On Earth maps, we divide the surface of Earth into a grid, and each location on that grid can easily be found using its latitude and longitude coordinate. Astronomers have a similar system for objects on the sky. Learning about these can help us understand the apparent motion of objects in the sky from various places on Earth.
Let’s begin by fixing our position on the surface of planet Earth . As we discussed in Observing the Sky: The Birth of Astronomy , Earth’s axis of rotation defines the locations of its North and South Poles and of its equator, halfway between. Two other directions are also defined by Earth’s motions: east is the direction toward which Earth rotates, and west is its opposite. At almost any point on Earth, the four directions—north, south, east, and west—are well defined, despite the fact that our planet is round rather that flat. The only exceptions are exactly at the North and South Poles, where the directions east and west are ambiguous (because points exactly at the poles do not turn).
We can use these ideas to define a system of coordinates attached to our planet. Such a system, like the layout of streets and avenues in Manhattan or Salt Lake City, helps us find where we are or want to go. Coordinates on a sphere, however, are a little more complicated than those on a flat surface. We must define circles on the sphere that play the same role as the rectangular grid that you see on city maps.
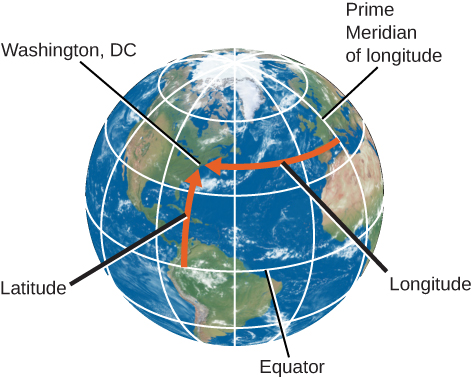
A great circle is any circle on the surface of a sphere whose center is at the center of the sphere. For example, Earth’s equator is a great circle on Earth’s surface, halfway between the North and South Poles. We can also imagine a series of great circles that pass through both the North and South Poles. Each of this circles is called a meridian ; they are each perpendicular to the equator, crossing it at right angles.
Any point on the surface of Earth will have a meridian passing through it ( [link] ). The meridian specifies the east-west location, or longitude, of the place. By international agreement (and it took many meetings for the world’s countries to agree), longitude is defined as the number of degrees of arc along the equator between your meridian and the one passing through Greenwich, England, which has been designated as the Prime Meridian. The longitude of the Prime Meridian is defined as 0°.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?