| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Newton’s universal law of gravitation and Kepler’s laws describe the motions of Earth satellite s and interplanetary spacecraft as well as the planets. Sputnik, the first artificial Earth satellite, was launched by what was then called the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Since that time, thousands of satellites have been placed into orbit around Earth, and spacecraft have also orbited the Moon, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and a number of asteroids and comets.
Once an artificial satellite is in orbit, its behavior is no different from that of a natural satellite, such as our Moon. If the satellite is high enough to be free of atmospheric friction, it will remain in orbit forever. However, although there is no difficulty in maintaining a satellite once it is in orbit, a great deal of energy is required to lift the spacecraft off Earth and accelerate it to orbital speed.
To illustrate how a satellite is launched, imagine a gun firing a bullet horizontally from the top of a high mountain, as in [link] , which has been adapted from a similar diagram by Newton. Imagine, further, that the friction of the air could be removed and that nothing gets in the bullet’s way. Then the only force that acts on the bullet after it leaves the muzzle is the gravitational force between the bullet and Earth.
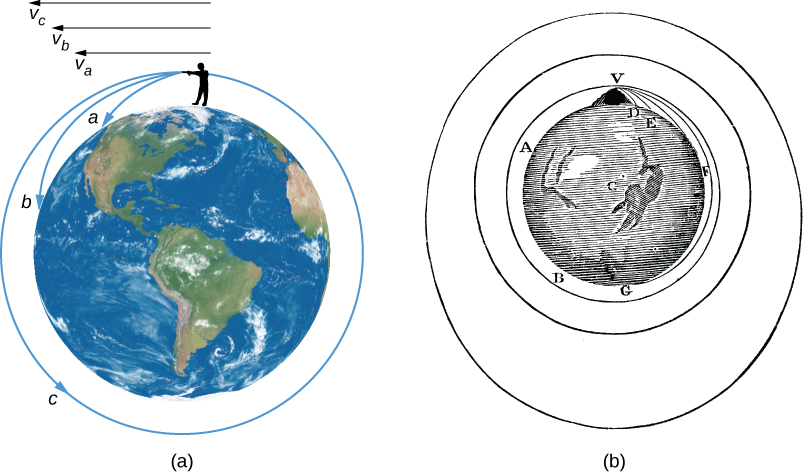
If the bullet is fired with a velocity we can call v a , the gravitational force acting upon it pulls it downward toward Earth, where it strikes the ground at point a . However, if it is given a higher muzzle velocity, v b , its higher speed carries it farther before it hits the ground at point b .
If our bullet is given a high enough muzzle velocity, v c , the curved surface of Earth causes the ground to remain the same distance from the bullet so that the bullet falls around Earth in a complete circle. The speed needed to do this—called the circular satellite velocity—is about 8 kilometers per second, or about 17,500 miles per hour in more familiar units.
Each year, more than 50 new satellites are launched into orbit by such nations as Russia, the United States, China, Japan, India, and Israel, as well as by the European Space Agency (ESA), a consortium of European nations ( [link] ). Today, these satellites are used for weather tracking, ecology, global positioning systems, communications, and military purposes, to name a few uses. Most satellites are launched into low Earth orbit, since this requires the minimum launch energy. At the orbital speed of 8 kilometers per second, they circle the planet in about 90 minutes. Some of the very low Earth orbits are not indefinitely stable because, as Earth’s atmosphere swells from time to time, a frictional drag is generated by the atmosphere on these satellites, eventually leading to a loss of energy and “decay” of the orbit.

The exploration of the solar system has been carried out largely by robot spacecraft sent to the other planets. To escape Earth, these craft must achieve escape speed , the speed needed to move away from Earth forever, which is about 11 kilometers per second (about 25,000 miles per hour). After escaping Earth, these craft coast to their targets, subject only to minor trajectory adjustments provided by small thruster rockets on board. In interplanetary flight, these spacecraft follow orbits around the Sun that are modified only when they pass near one of the planets.
As it comes close to its target, a spacecraft is deflected by the planet’s gravitational force into a modified orbit, either gaining or losing energy in the process. Spacecraft controllers have actually been able to use a planet’s gravity to redirect a flyby spacecraft to a second target. For example, Voyager 2 used a series of gravity-assisted encounters to yield successive flybys of Jupiter (1979), Saturn (1980), Uranus (1986), and Neptune (1989). The Galileo spacecraft, launched in 1989, flew past Venus once and Earth twice to gain the energy required to reach its ultimate goal of orbiting Jupiter.
If we wish to orbit a planet, we must slow the spacecraft with a rocket when the spacecraft is near its destination, allowing it to be captured into an elliptical orbit. Additional rocket thrust is required to bring a vehicle down from orbit for a landing on the surface. Finally, if a return trip to Earth is planned, the landed payload must include enough propulsive power to repeat the entire process in reverse.
The orbit of an artificial satellite depends on the circumstances of its launch. The circular satellite velocity needed to orbit Earth’s surface is 8 kilometers per second, and the escape speed from our planet is 11 kilometers per second. There are many possible interplanetary trajectories, including those that use gravity-assisted flybys of one object to redirect the spacecraft toward its next target.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?