| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Recall that the path of an object under the influence of gravity through space is called its orbit, whether that object is a spacecraft, planet, star, or galaxy. An orbit, once determined, allows the future positions of the object to be calculated.
Two points in any orbit in our solar system have been given special names. The place where the planet is closest to the Sun ( helios in Greek) and moves the fastest is called the perihelion of its orbit, and the place where it is farthest away and moves the most slowly is the aphelion . For the Moon or a satellite orbiting Earth ( gee in Greek), the corresponding terms are perigee and apogee . (In this book, we use the word moon for a natural object that goes around a planet and the word satellite to mean a human-made object that revolves around a planet.)
Today, Newton’s work enables us to calculate and predict the orbits of the planets with marvelous precision. We know eight planets, beginning with Mercury closest to the Sun and extending outward to Neptune. The average orbital data for the planets are summarized in [link] . (Ceres is the largest of the asteroids, now considered a dwarf planet.)
According to Kepler’s laws, Mercury must have the shortest orbital period (88 Earth-days); thus, it has the highest orbital speed, averaging 48 kilometers per second. At the opposite extreme, Neptune has a period of 165 years and an average orbital speed of just 5 kilometers per second.
All the planets have orbits of rather low eccentricity. The most eccentric orbit is that of Mercury (0.21); the rest have eccentricities smaller than 0.1. It is fortunate that among the rest, Mars has an eccentricity greater than that of many of the other planets. Otherwise the pre-telescopic observations of Brahe would not have been sufficient for Kepler to deduce that its orbit had the shape of an ellipse rather than a circle.
The planetary orbits are also confined close to a common plane, which is near the plane of Earth’s orbit (called the ecliptic). The strange orbit of the dwarf planet Pluto is inclined about 17° to the ecliptic, and that of the dwarf planet Eris (orbiting even farther away from the Sun than Pluto) by 44°, but all the major planets lie within 10° of the common plane of the solar system.
You can use an orbital simulator to design your own mini solar system with up to four bodies. Adjust masses, velocities, and positions of the planets, and see what happens to their orbits as a result.
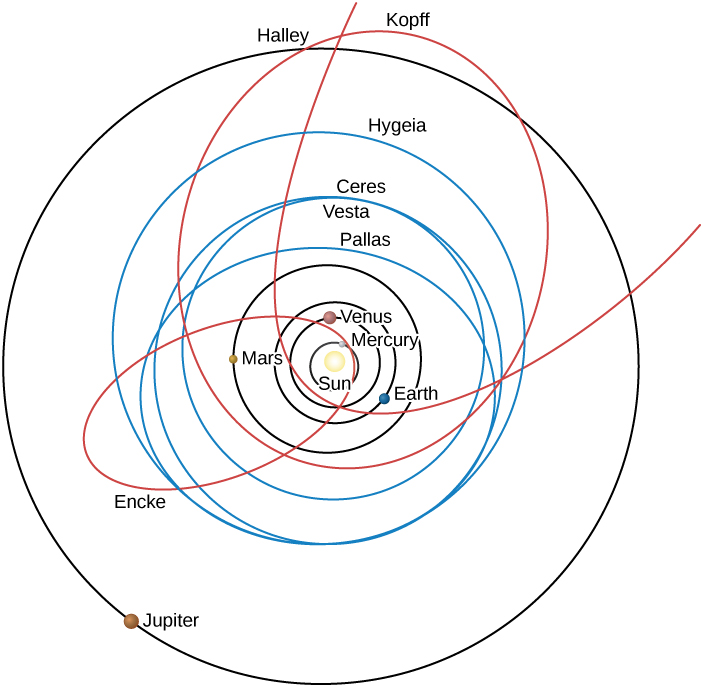
In addition to the eight planets, there are many smaller objects in the solar system. Some of these are moons (natural satellites) that orbit all the planets except Mercury and Venus. In addition, there are two classes of smaller objects in heliocentric orbits: asteroids and comets . Both asteroids and comets are believed to be small chunks of material left over from the formation process of the solar system.
In general, asteroids have orbits with smaller semimajor axes than do comets ( [link] ). The majority of them lie between 2.2 and 3.3 AU, in the region known as the asteroid belt (see Comets and Asteroids: Debris of the Solar System ). As you can see in [link] , the asteroid belt (represented by its largest member, Ceres) is in the middle of a gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is because these two planets are so far apart that stable orbits of small bodies can exist in the region between them.
| Orbital Data for the Planets | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Planet | Semimajor Axis (AU) | Period (y) | Eccentricity |
| Mercury | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| Venus | 0.72 | 0.6 | 0.01 |
| Earth | 1 | 1.00 | 0.02 |
| Mars | 1.52 | 1.88 | 0.09 |
| ( Ceres ) | 2.77 | 4.6 | 0.08 |
| Jupiter | 5.20 | 11.86 | 0.05 |
| Saturn | 9.54 | 29.46 | 0.06 |
| Uranus | 19.19 | 84.01 | 0.05 |
| Neptune | 30.06 | 164.82 | 0.01 |
Comets generally have orbits of larger size and greater eccentricity than those of the asteroids. Typically, the eccentricity of their orbits is 0.8 or higher. According to Kepler’s second law, therefore, they spend most of their time far from the Sun, moving very slowly. As they approach perihelion, the comets speed up and whip through the inner parts of their orbits more rapidly.
The closest point in a satellite orbit around Earth is its perigee, and the farthest point is its apogee (corresponding to perihelion and aphelion for an orbit around the Sun). The planets follow orbits around the Sun that are nearly circular and in the same plane. Most asteroids are found between Mars and Jupiter in the asteroid belt, whereas comets generally follow orbits of high eccentricity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?