| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
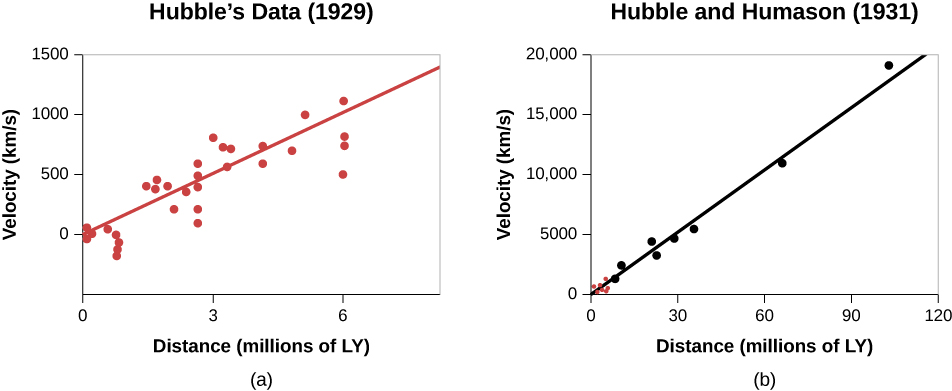
We now know that this relationship holds for every galaxy except a few of the nearest ones. Nearly all of the galaxies that are approaching us turn out to be part of the Milky Way’s own group of galaxies, which have their own individual motions, just as birds flying in a group may fly in slightly different directions at slightly different speeds even though the entire flock travels through space together.
Written as a formula, the relationship between velocity and distance is
where v is the recession speed, d is the distance, and H is a number called the Hubble constant . This equation is now known as Hubble’s law .
Mathematical relationships such as Hubble’s law are pretty common in life. To take a simple example, suppose your college or university hires you to call rich alumni and ask for donations. You are paid $2.50 for each call; the more calls you can squeeze in between studying astronomy and other courses, the more money you take home. We can set up a formula that connects p , your pay, and n , the number of calls
where A is the alumni constant, with a value of $2.50. If you make 20 calls, you will earn $2.50 times 20, or $50.
Suppose your boss forgets to tell you what you will get paid for each call. You can calculate the alumni constant that governs your pay by keeping track of how many calls you make and noting your gross pay each week. If you make 100 calls the first week and are paid $250, you can deduce that the constant is $2.50 (in units of dollars per call). Hubble, of course, had no “boss” to tell him what his constant would be—he had to calculate its value from the measurements of distance and velocity.
Astronomers express the value of Hubble’s constant in units that relate to how they measure speed and velocity for galaxies. In this book, we will use kilometers per second per million light-years as that unit. For many years, estimates of the value of the Hubble constant have been in the range of 15 to 30 kilometers per second per million light-years The most recent work appears to be converging on a value near 22 kilometers per second per million light-years If H is 22 kilometers per second per million light-years, a galaxy moves away from us at a speed of 22 kilometers per second for every million light-years of its distance. As an example, a galaxy 100 million light-years away is moving away from us at a speed of 2200 kilometers per second.
Hubble’s law tells us something fundamental about the universe. Since all but the nearest galaxies appear to be in motion away from us, with the most distant ones moving the fastest, we must be living in an expanding universe. We will explore the implications of this idea shortly, as well as in the final chapters of this text. For now, we will just say that Hubble’s observation underlies all our theories about the origin and evolution of the universe.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?