| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
At the beginning of this chapter, we hinted that the core of our Galaxy contains a large concentration of mass. In fact, we now have evidence that the very center contains a black hole with a mass equivalent to 4.6 million Suns and that all this mass fits within a sphere that has less than the diameter of Mercury’s orbit. Such monster black holes are called supermassive black holes by astronomers, to indicate that the mass they contain is far greater than that of the typical black hole created by the death of a single star. It is amazing that we have very convincing evidence that this black hole really does exist. After all, recall from the chapter on Black Holes and Curved Spacetime that we cannot see a black hole directly because by definition it radiates no energy. And we cannot even see into the center of the Galaxy in visible light because of absorption by the interstellar dust that lies between us and the galactic center. Light from the central region of the Galaxy is dimmed by a factor of a trillion (10 12 ) by all this dust.
Fortunately, we are not so blind at other wavelengths. Infrared and radio radiation, which have long wavelengths compared to the sizes of the interstellar dust grains, flow unimpeded past the dust particles and so reach our telescopes with hardly any dimming. In fact, the very bright radio source in the nucleus of the Galaxy, now known as Sagittarius A* (pronounced “Sagittarius A-star” and abbreviated Sgr A*), was the first cosmic radio source astronomers discovered.
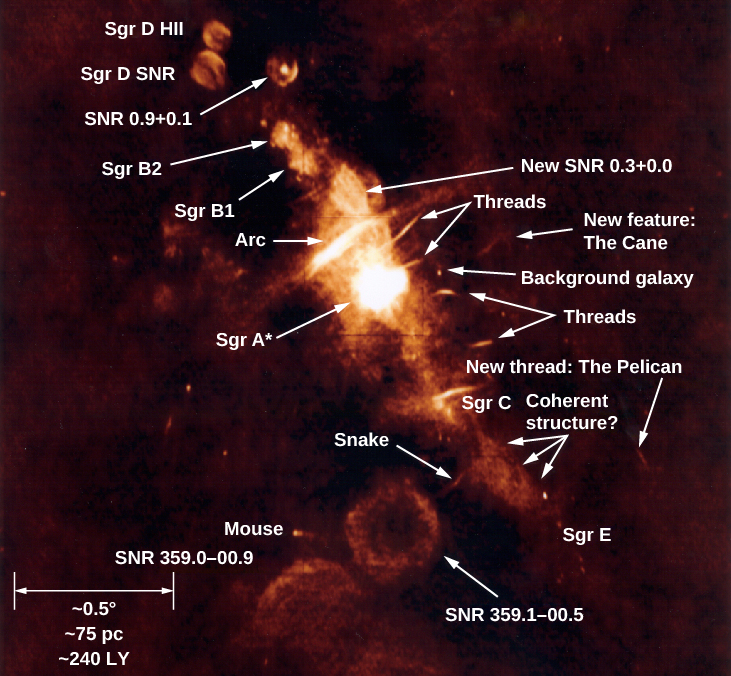
Let’s take a voyage to the mysterious heart of our Galaxy and see what’s there. [link] is a radio image of a region about 1500 light-years across, centered on Sagittarius A , a bright radio source that contains the smaller Sagittarius A * . Much of the radio emission comes from hot gas heated either by clusters of hot stars (the stars themselves do not produce radio emission and can’t be seen in the image) or by supernova blast waves. Most of the hollow circles visible on the radio image are supernova remnants. The other main source of radio emission is from electrons moving at high speed in regions with strong magnetic fields. The bright thin arcs and “threads” on the figure show us where this type of emission is produced.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?