| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
What Einstein proposed was nothing less than a major revolution in our understanding of space and time. It was a new theory of gravity, in which mass determines the curvature of spacetime and that curvature, in turn, controls how objects move. Like all new ideas in science, no matter who advances them, Einstein’s theory had to be tested by comparing its predictions against the experimental evidence. This was quite a challenge because the effects of the new theory were apparent only when the mass was quite large. (For smaller masses, it required measuring techniques that would not become available until decades later.)
When the distorting mass is small, the predictions of general relativity must agree with those resulting from Newton’s law of universal gravitation, which, after all, has served us admirably in our technology and in guiding space probes to the other planets. In familiar territory, therefore, the differences between the predictions of the two models are subtle and difficult to detect. Nevertheless, Einstein was able to demonstrate one proof of his theory that could be found in existing data and to suggest another one that would be tested just a few years later.
Of the planets in our solar system, Mercury orbits closest to the Sun and is thus most affected by the distortion of spacetime produced by the Sun’s mass. Einstein wondered if the distortion might produce a noticeable difference in the motion of Mercury that was not predicted by Newton’s law. It turned out that the difference was subtle, but it was definitely there. Most importantly, it had already been measured.
Mercury has a highly elliptical orbit, so that it is only about two-thirds as far from the Sun at perihelion as it is at aphelion. (These terms were defined in the chapter on Orbits and Gravity .) The gravitational effects (perturbations) of the other planets on Mercury produce a calculable advance of Mercury’s perihelion. What this means is that each successive perihelion occurs in a slightly different direction as seen from the Sun ( [link] ).
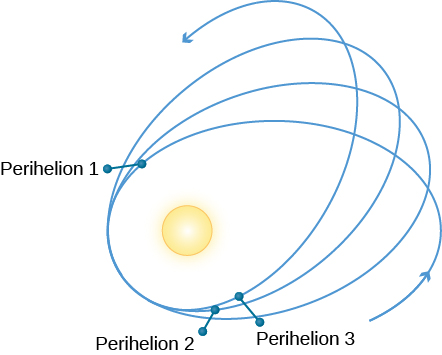
According to Newtonian gravitation, the gravitational forces exerted by the planets will cause Mercury’s perihelion to advance by about 531 seconds of arc (arcsec) per century. In the nineteenth century, however, it was observed that the actual advance is 574 arcsec per century. The discrepancy was first pointed out in 1859 by Urbain Le Verrier, the codiscoverer of Neptune. Just as discrepancies in the motion of Uranus allowed astronomers to discover the presence of Neptune, so it was thought that the discrepancy in the motion of Mercury could mean the presence of an undiscovered inner planet. Astronomers searched for this planet near the Sun, even giving it a name: Vulcan, after the Roman god of fire. (The name would later be used for the home planet of a famous character on a popular television show about future space travel.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?