| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
If what we have described so far were the whole story of the evolution of stars and elements, we would have a big problem on our hands. We will see in later chapters that in our best models of the first few minutes of the universe, everything starts with the two simplest elements—hydrogen and helium (plus a tiny bit of lithium). All the predictions of the models imply that no heavier elements were produced at the beginning of the universe. Yet when we look around us on Earth, we see lots of other elements besides hydrogen and helium. These elements must have been made (fused) somewhere in the universe, and the only place hot enough to make them is inside stars . One of the fundamental discoveries of twentieth-century astronomy is that the stars are the source of most of the chemical richness that characterizes our world and our lives.
We have already seen that carbon and some oxygen are manufactured inside the lower-mass stars that become red giants. But where do the heavier elements we know and love (such as the silicon and iron inside Earth, and the gold and silver in our jewelry) come from? The kinds of stars we have been discussing so far never get hot enough at their centers to make these elements. It turns out that such heavier elements can be formed only late in the lives of more massive stars.
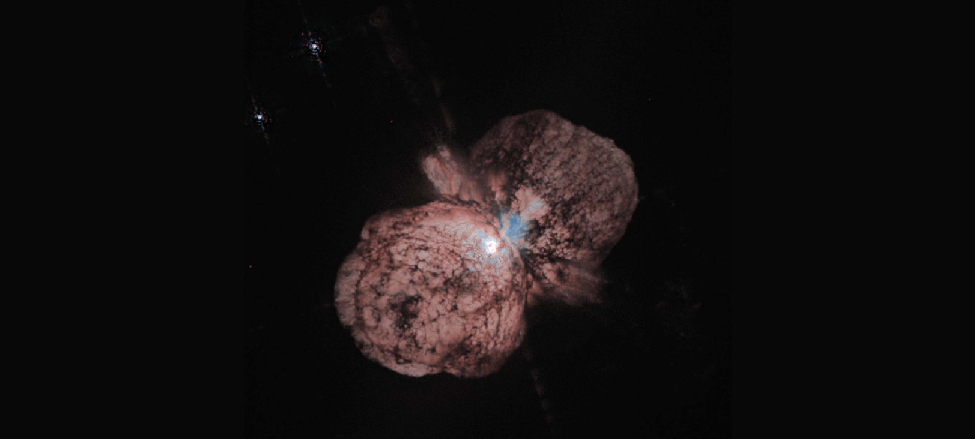
Massive stars evolve in much the same way that the Sun does (but always more quickly)—up to the formation of a carbon-oxygen core. One difference is that for stars with more than about twice the mass of the Sun, helium begins fusion more gradually, rather than with a sudden flash. Also, when more massive stars become red giants, they become so bright and large that we call them supergiants . Such stars can expand until their outer regions become as large as the orbit of Jupiter, which is precisely what the Hubble Space Telescope has shown for the star Betelgeuse (see [link] ). They also lose mass very effectively, producing dramatic winds and outbursts as they age. [link] shows a wonderful image of the very massive star Eta Carinae , with a great deal of ejected material clearly visible.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?