| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Before the discovery of exoplanets, most astronomers expected that other planetary systems would be much like our own—planets following roughly circular orbits, with the most massive planets several AU from their parent star. Such systems do exist in large numbers, but many exoplanets and planetary systems are very different from those in our solar system. Another surprise is the existence of whole classes of exoplanets that we simply don’t have in our solar system: planets with masses between the mass of Earth and Neptune, and planets that are several times more massive than Jupiter.
The Kepler telescope has been responsible for the discovery of most exoplanets, especially at smaller sizes, as illustrated in [link] , where the Kepler discoveries are plotted in yellow. You can see the wide range of sizes, including planets substantially larger than Jupiter and smaller than Earth. The absence of Kepler-discovered exoplanets with orbital periods longer than a few hundred days is a consequence of the 4-year lifetime of the mission. (Remember that three evenly spaced transits must be observed to register a discovery.) At the smaller sizes, the absence of planets much smaller than one earth radius is due to the difficulty of detecting transits by very small planets. In effect, the “discovery space” for Kepler was limited to planets with orbital periods less than 400 days and sizes larger than Mars.
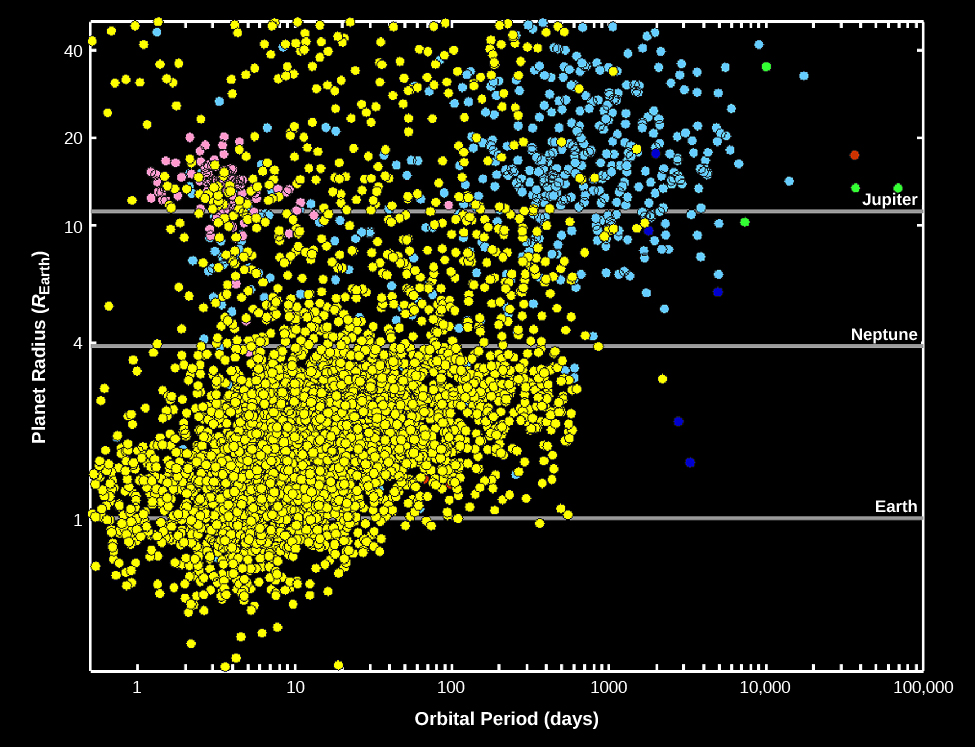
One of the primary objectives of the Kepler mission was to find out how many stars hosted planets and especially to estimate the frequency of earthlike planets. Although Kepler looked at only a very tiny fraction of the stars in the Galaxy, the sample size was large enough to draw some interesting conclusions. While the observations apply only to the stars observed by Kepler, those stars are reasonably representative, and so astronomers can extrapolate to the entire Galaxy.
[link] shows that the Kepler discoveries include many rocky, Earth-size planets, far more than Jupiter-size gas planets. This immediately tells us that the initial Doppler discovery of many hot Jupiters was a biased sample, in effect, finding the odd planetary systems because they were the easiest to detect. However, there is one huge difference between this observed size distribution and that of planets in our solar system. The most common planets have radii between 1.4 and 2.8 that of Earth, sizes for which we have no examples in the solar system. These have been nicknamed super-Earths , while the other large group with sizes between 2.8 and 4 that of Earth are often called mini-Neptunes .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?