| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
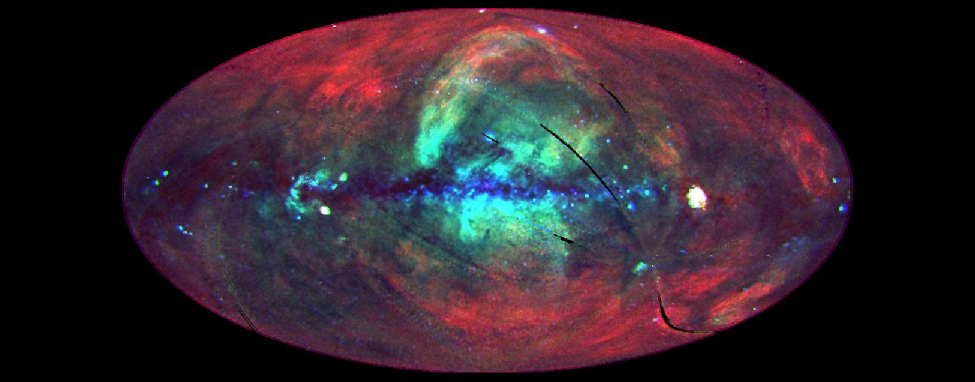
We want to conclude our discussion of interstellar matter by asking how this material is organized in our immediate neighborhood. As we discussed above, orbiting X-ray observatories have shown that the Galaxy is full of bubbles of hot, X-ray-emitting gas. They also revealed a diffuse background of X-rays that appears to fill the entire sky from our perspective ( [link] ). While some of this emission comes from the interaction of the solar wind with the interstellar medium, a majority of it comes from beyond the solar system. The natural explanation for why there is X-ray-emitting gas all around us is that the Sun is itself inside one of the bubbles. We therefore call our “neighborhood” the Local Hot Bubble, or Local Bubble for short. The Local Bubble is much less dense—an average of approximately 0.01 atoms per cm 3 —than the average interstellar density of about 1 atom per cm 3 . This local gas has a temperature of about a million degrees, just like the gas in the other superbubbles that spread throughout our Galaxy, but because there is so little hot material, this high temperature does not affect the stars or planets in the area in any way.
What caused the Local Bubble to form? Scientists are not entirely sure, but the leading candidate is winds from stars and supernova explosions. In a nearby region in the direction of the constellations Scorpius and Centaurus, a lot of star formation took place about 15 million years ago. The most massive of these stars evolved very quickly until they produced strong winds, and some ended their lives by exploding. These processes filled the region around the Sun with hot gas, driving away cooler, denser gas. The rim of this expanding superbubble reached the Sun about 7.6 million years ago and now lies more than 200 light-years past the Sun in the general direction of the constellations of Orion, Perseus, and Auriga.
A few clouds of interstellar matter do exist within the Local Bubble. The Sun itself seems to have entered a cloud about 10,000 years ago. This cloud is warm (with a temperature of about 7000 K) and has a density of 0.3 hydrogen atom per cm 3 —higher than most of the Local Bubble but still so tenuous that it is also referred to as Local Fluff ( [link] ). (Aren’t these astronomical names fun sometimes?)
While this is a pretty thin cloud, we estimate that it contributes 50 to 100 times more particles than the solar wind to the diffuse material between the planets in our solar system. These interstellar particles have been detected and their numbers counted by the spacecraft traveling between the planets. Perhaps someday, scientists will devise a way to collect them without destroying them and to return them to Earth, so that we can touch—or at least study in our laboratories—these messengers from distant stars.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?