| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The comets we notice when they come near Earth (especially the ones coming for the first time) are probably the most primitive objects we can study, preserved unchanged for billions of years in the deep freeze of the outer solar system. However, astronomers have discovered many other objects that orbit the Sun beyond the planets.
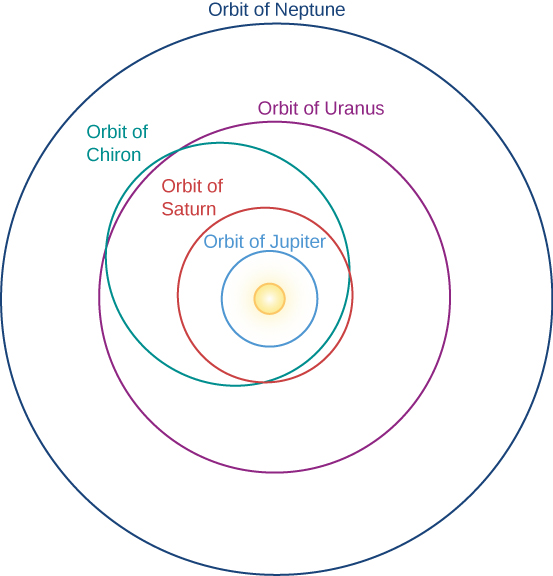
In the outer solar system, where most objects contain large amounts of water ice, the distinction between asteroids and comets breaks down. Astronomers initially still used the name “asteroids” for new objects discovered going around the Sun with orbits that carry them far beyond Jupiter. The first of these objects is Chiron , found in 1977 on a path that carries it from just inside the orbit of Saturn at its closest approach to the Sun out to almost the distance of Uranus ( [link] ). The diameter of Chiron is estimated to be about 200 kilometers, much larger than any known comet.
In 1992, a still-more-distant object named Pholus was discovered with an orbit that takes it 33 AU from the Sun, beyond the orbit of Neptune. Pholus has the reddest surface of any object in the solar system, indicating a strange (and still unknown) surface composition. As more objects are discovered in these distant reaches, astronomers decided that they will be given the names of centaurs from classical mythology; this is because the centaurs were half human, half horse, and these new objects display some of the properties of both asteroids and comets.
Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies a cold, dark realm populated by objects called simply trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs). The first discovered, and best known, of these TNOs is the dwarf planet Pluto . We discussed Pluto and the New Horizons spacecraft encounter with it in Rings, Moons, and Pluto . The second TNO was discovered in 1992, and now more than a thousand are known, most of them smaller than Pluto.
The largest ones after Pluto—named Eris , Makemake , and Haumea —are also classed as dwarf planets. Except for their small size, dwarf planets have many properties in common with the larger planets. Pluto has five moons, and two moons have been discovered orbiting Haumea and one each circling Eris and Makemake.
TNOs are a part of what is called the Kuiper belt , a large area of space beyond Neptune that is also the source of many comets. Astronomers study the Kuiper belt in two ways. New, more powerful telescopes allow us to discover many of the larger members of the Kuiper belt directly. We can also measure the composition of comets that come from the Kuiper belt. More than a thousand Kuiper belt objects have been discovered, and astronomers estimate that there are more than 100,000 with diameters large than 100 kilometers, in a disk extending out to about 50 AU from the Sun.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?