| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The thick atmosphere of Venus produces the high surface temperature and shrouds the surface in a perpetual red twilight. Sunlight does not penetrate directly through the heavy clouds, but the surface is fairly well lit by diffuse light (about the same as the light on Earth under a heavy overcast). The weather at the bottom of this deep atmosphere remains perpetually hot and dry, with calm winds. Because of the heavy blanket of clouds and atmosphere, one spot on the surface of Venus is similar to any other as far as weather is concerned.
The most abundant gas on Venus is carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), which accounts for 96% of the atmosphere. The second most common gas is nitrogen. The predominance of carbon dioxide over nitrogen is not surprising when you recall that Earth’s atmosphere would also be mostly carbon dioxide if this gas were not locked up in marine sediments (see the discussion of Earth’s atmosphere in Earth as a Planet ).
[link] compares the compositions of the atmospheres of Venus, Mars, and Earth. Expressed in this way, as percentages, the proportions of the major gases are very similar for Venus and Mars, but in total quantity, their atmospheres are dramatically different. With its surface pressure of 90 bars, the venusian atmosphere is more than 10,000 times more massive than its martian counterpart. Overall, the atmosphere of Venus is very dry; the absence of water is one of the important ways that Venus differs from Earth.
| Atmospheric Composition of Earth, Venus, and Mars | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Earth | Venus | Mars |
| Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) | 0.03% | 96% | 95.3% |
| Nitrogen (N 2 ) | 78.1% | 3.5% | 2.7% |
| Argon (Ar) | 0.93% | 0.006% | 1.6% |
| Oxygen (O 2 ) | 21.0% | 0.003% | 0.15% |
| Neon (Ne) | 0.002% | 0.001% | 0.0003% |
The atmosphere of Venus has a huge troposphere (region of convection) that extends up to at least 50 kilometers above the surface ( [link] ). Within the troposphere, the gas is heated from below and circulates slowly, rising near the equator and descending over the poles. Being at the base of the atmosphere of Venus is something like being a kilometer or more below the ocean surface on Earth. There, the mass of water evens out temperature variations and results in a uniform environment—the same effect the thick atmosphere has on Venus.
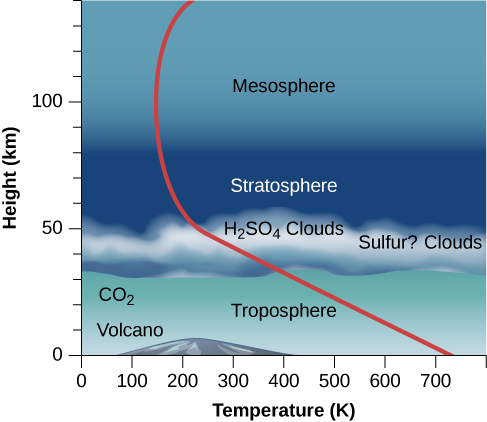
In the upper troposphere, between 30 and 60 kilometers above the surface, a thick cloud layer is composed primarily of sulfuric acid droplets. Sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ) is formed from the chemical combination of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) and water (H 2 O). In the atmosphere of Earth, sulfur dioxide is one of the primary gases emitted by volcanoes, but it is quickly diluted and washed out by rainfall. In the dry atmosphere of Venus, this unpleasant substance is apparently stable. Below 30 kilometers, the Venus atmosphere is clear of clouds.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Astronomy' conversation and receive update notifications?