| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Mechanoreceptors of Somatosensation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Historical (eponymous) name | Location(s) | Stimuli |
| Free nerve endings | * | Dermis, cornea, tongue, joint capsules, visceral organs | Pain, temperature, mechanical deformation |
| Mechanoreceptors | Merkel’s discs | Epidermal–dermal junction, mucosal membranes | Low frequency vibration (5–15 Hz) |
| Bulbous corpuscle | Ruffini’s corpuscle | Dermis, joint capsules | Stretch |
| Tactile corpuscle | Meissner’s corpuscle | Papillary dermis, especially in the fingertips and lips | Light touch, vibrations below 50 Hz |
| Lamellated corpuscle | Pacinian corpuscle | Deep dermis, subcutaneous tissue | Deep pressure, high-frequency vibration (around 250 Hz) |
| Hair follicle plexus | * | Wrapped around hair follicles in the dermis | Movement of hair |
| Muscle spindle | * | In line with skeletal muscle fibers | Muscle contraction and stretch |
| Tendon stretch organ | Golgi tendon organ | In line with tendons | Stretch of tendons |
Vision is the special sense of sight that is based on the transduction of light stimuli received through the eyes. The eyes are located within either orbit in the skull. The bony orbits surround the eyeballs, protecting them and anchoring the soft tissues of the eye ( [link] ). The eyelids, with lashes at their leading edges, help to protect the eye from abrasions by blocking particles that may land on the surface of the eye. The inner surface of each lid is a thin membrane known as the palpebral conjunctiva . The conjunctiva extends over the white areas of the eye (the sclera), connecting the eyelids to the eyeball. Tears are produced by the lacrimal gland , located beneath the lateral edges of the nose. Tears produced by this gland flow through the lacrimal duct to the medial corner of the eye, where the tears flow over the conjunctiva, washing away foreign particles.
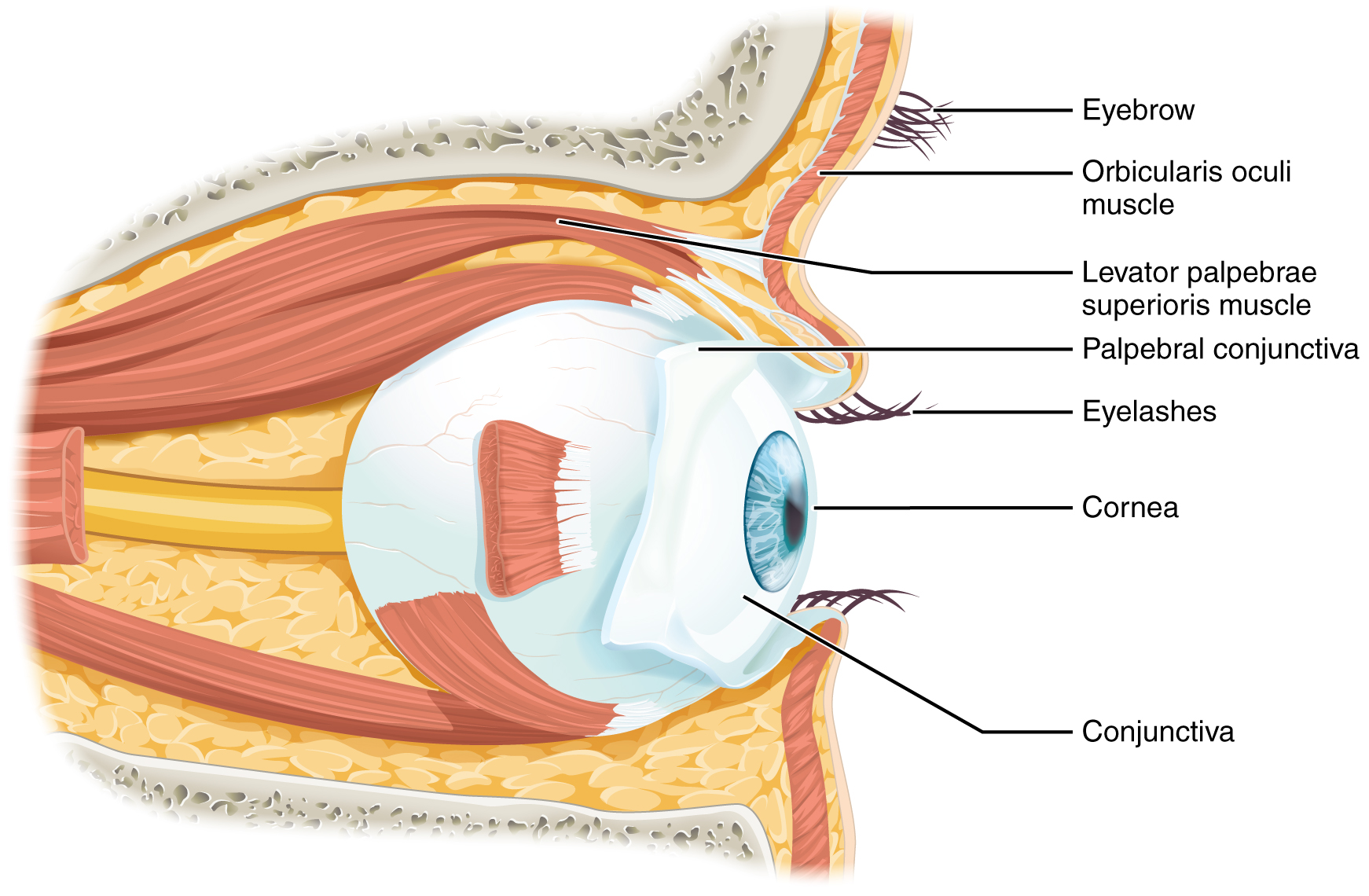
Movement of the eye within the orbit is accomplished by the contraction of six extraocular muscles that originate from the bones of the orbit and insert into the surface of the eyeball ( [link] ). Four of the muscles are arranged at the cardinal points around the eye and are named for those locations. They are the superior rectus , medial rectus , inferior rectus , and lateral rectus . When each of these muscles contract, the eye to moves toward the contracting muscle. For example, when the superior rectus contracts, the eye rotates to look up. The superior oblique originates at the posterior orbit, near the origin of the four rectus muscles. However, the tendon of the oblique muscles threads through a pulley-like piece of cartilage known as the trochlea . The tendon inserts obliquely into the superior surface of the eye. The angle of the tendon through the trochlea means that contraction of the superior oblique rotates the eye medially. The inferior oblique muscle originates from the floor of the orbit and inserts into the inferolateral surface of the eye. When it contracts, it laterally rotates the eye, in opposition to the superior oblique. Rotation of the eye by the two oblique muscles is necessary because the eye is not perfectly aligned on the sagittal plane. When the eye looks up or down, the eye must also rotate slightly to compensate for the superior rectus pulling at approximately a 20-degree angle, rather than straight up. The same is true for the inferior rectus, which is compensated by contraction of the inferior oblique. A seventh muscle in the orbit is the levator palpebrae superioris , which is responsible for elevating and retracting the upper eyelid, a movement that usually occurs in concert with elevation of the eye by the superior rectus (see [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?