| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
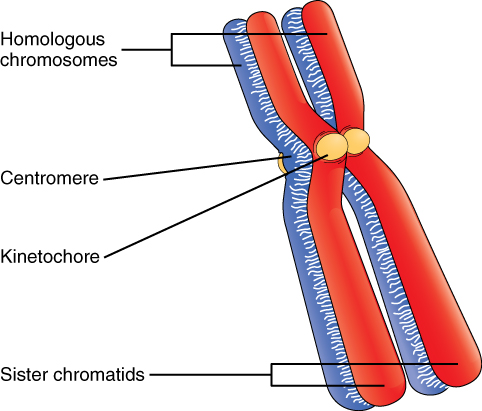
Billions of cells in the human body divide every day. During the synthesis phase (S, for DNA synthesis) of interphase, the amount of DNA within the cell precisely doubles. Therefore, after DNA replication but before cell division, each cell actually contains two copies of each chromosome. Each copy of the chromosome is referred to as a sister chromatid and is physically bound to the other copy. The centromere is the structure that attaches one sister chromatid to another. Because a human cell has 46 chromosomes, during this phase, there are 92 chromatids (46 × 2) in the cell. Make sure not to confuse the concept of a pair of chromatids (one chromosome and its exact copy attached during mitosis) and a homologous pair of chromosomes (two paired chromosomes which were inherited separately, one from each parent) ( [link] ).
The mitotic phase of the cell typically takes between 1 and 2 hours. During this phase, a cell undergoes two major processes. First, it completes mitosis, during which the contents of the nucleus are equitably pulled apart and distributed between its two halves. Cytokinesis then occurs, dividing the cytoplasm and cell body into two new cells. Mitosis is divided into four major stages that take place after interphase ( [link] ) and in the following order: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The process is then followed by cytokinesis.
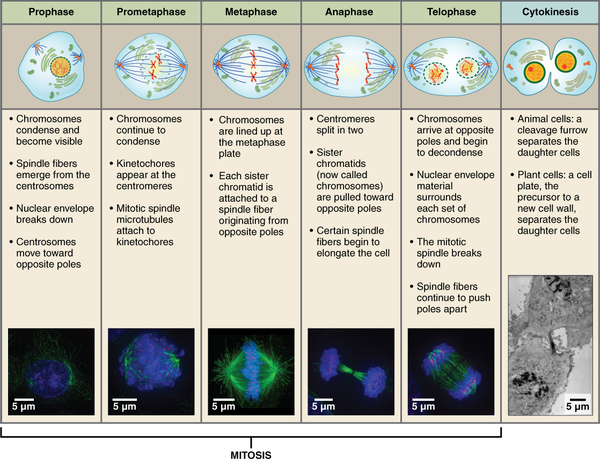
Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, during which the loosely packed chromatin coils and condenses into visible chromosomes. During prophase, each chromosome becomes visible with its identical partner attached, forming the familiar X-shape of sister chromatids. The nucleolus disappears early during this phase, and the nuclear envelope also disintegrates.
A major occurrence during prophase concerns a very important structure that contains the origin site for microtubule growth. Recall the cellular structures called centrioles that serve as origin points from which microtubules extend. These tiny structures also play a very important role during mitosis. A centrosome is a pair of centrioles together. The cell contains two centrosomes side-by-side, which begin to move apart during prophase. As the centrosomes migrate to two different sides of the cell, microtubules begin to extend from each like long fingers from two hands extending toward each other. The mitotic spindle is the structure composed of the centrosomes and their emerging microtubules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?