| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
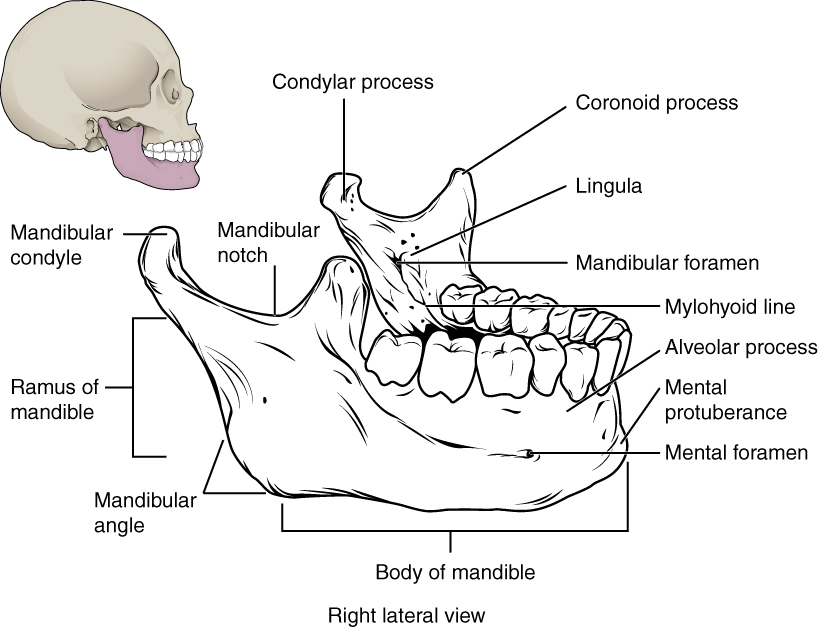
Important landmarks for the mandible include the following:
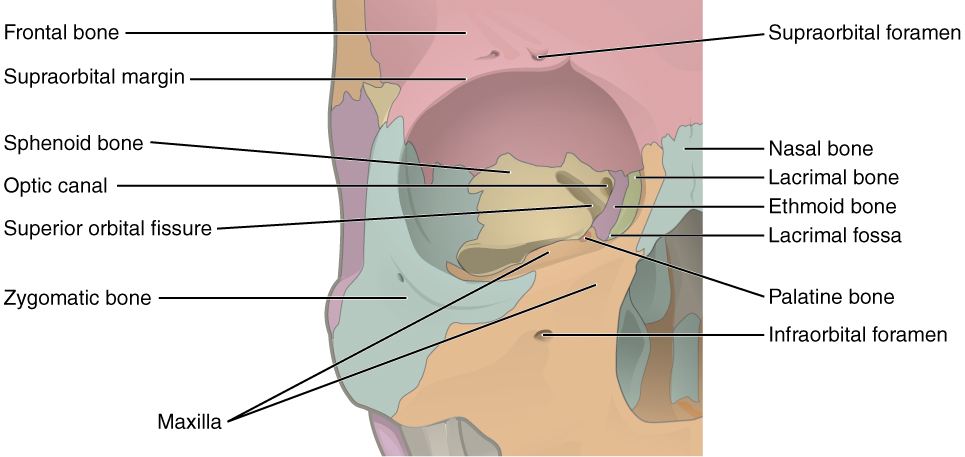
The orbit is the bony socket that houses the eyeball and contains the muscles that move the eyeball or open the upper eyelid. Each orbit is cone-shaped, with a narrow posterior region that widens toward the large anterior opening. To help protect the eye, the bony margins of the anterior opening are thickened and somewhat constricted. The medial walls of the two orbits are parallel to each other but each lateral wall diverges away from the midline at a 45° angle. This divergence provides greater lateral peripheral vision.
The walls of each orbit include contributions from seven skull bones ( [link] ). The frontal bone forms the roof and the zygomatic bone forms the lateral wall and lateral floor. The medial floor is primarily formed by the maxilla, with a small contribution from the palatine bone. The ethmoid bone and lacrimal bone make up much of the medial wall and the sphenoid bone forms the posterior orbit.
At the posterior apex of the orbit is the opening of the optic canal , which allows for passage of the optic nerve from the retina to the brain. Lateral to this is the elongated and irregularly shaped superior orbital fissure, which provides passage for the artery that supplies the eyeball, sensory nerves, and the nerves that supply the muscles involved in eye movements.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?