| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
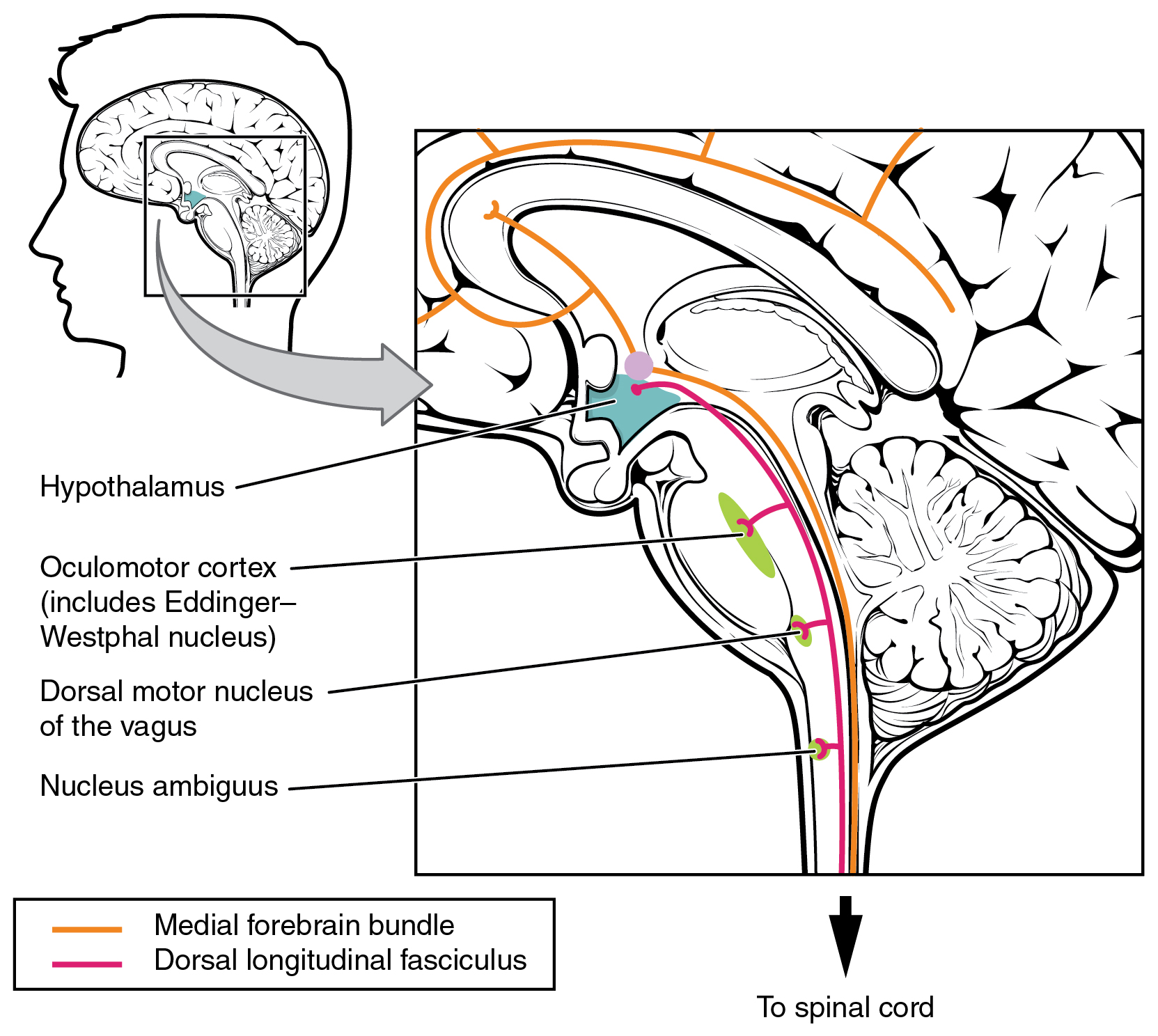
These two tracts connect the hypothalamus with the major parasympathetic nuclei in the brain stem and the preganglionic (central) neurons of the thoracolumbar spinal cord. The hypothalamus also receives input from other areas of the forebrain through the medial forebrain bundle. The olfactory cortex, the septal nuclei of the basal forebrain, and the amygdala project into the hypothalamus through the medial forebrain bundle. These forebrain structures inform the hypothalamus about the state of the nervous system and can influence the regulatory processes of homeostasis. A good example of this is found in the amygdala, which is found beneath the cerebral cortex of the temporal lobe and plays a role in our ability to remember and feel emotions.
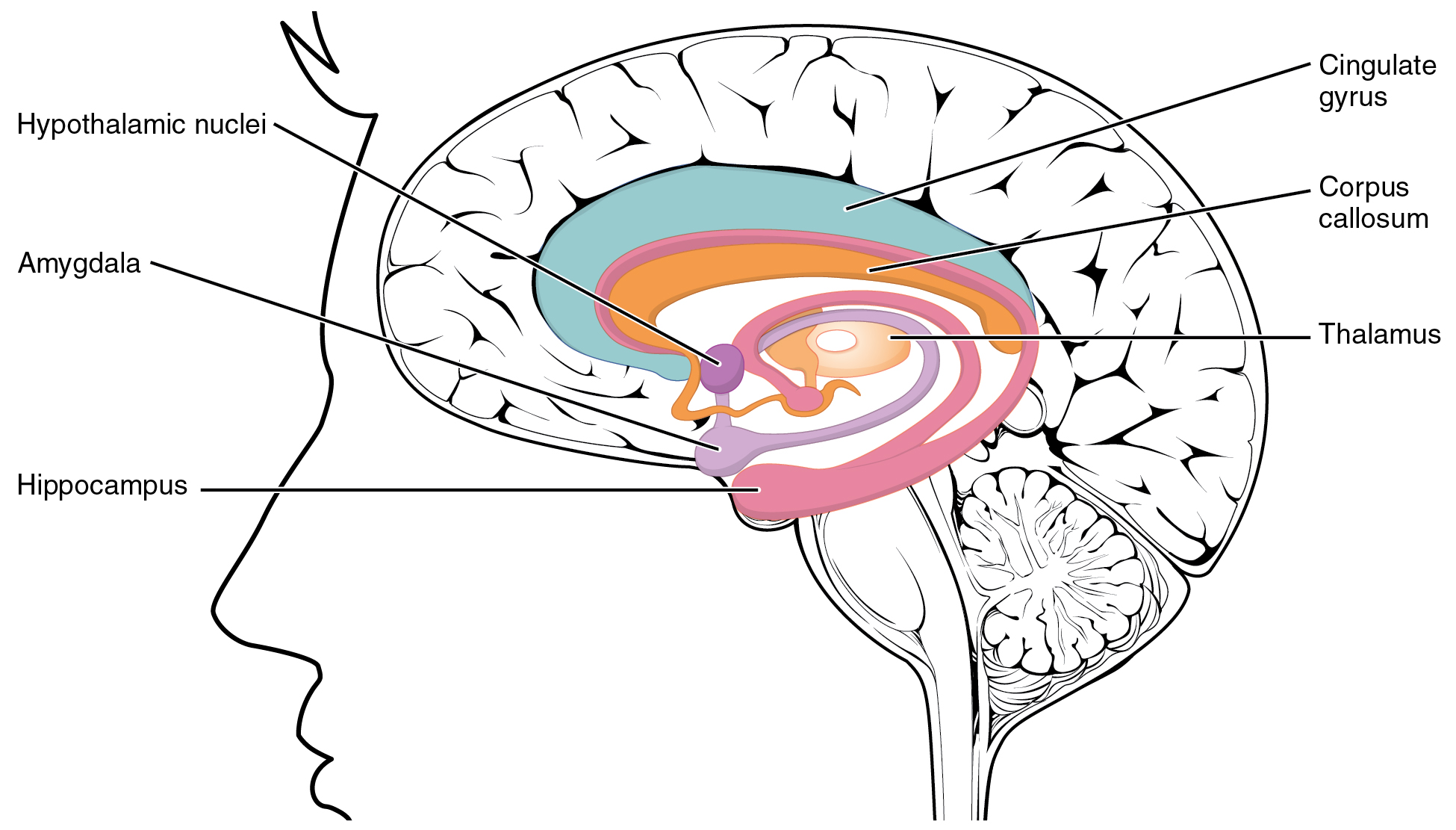
The amygdala is a group of nuclei in the medial region of the temporal lobe that is part of the limbic lobe ( [link] ). The limbic lobe includes structures that are involved in emotional responses, as well as structures that contribute to memory function. The limbic lobe has strong connections with the hypothalamus and influences the state of its activity on the basis of emotional state. For example, when you are anxious or scared, the amygdala will send signals to the hypothalamus along the medial forebrain bundle that will stimulate the sympathetic fight-or-flight response. The hypothalamus will also stimulate the release of stress hormones through its control of the endocrine system in response to amygdala input.
The medulla contains nuclei referred to as the cardiovascular center , which controls the smooth and cardiac muscle of the cardiovascular system through autonomic connections. When the homeostasis of the cardiovascular system shifts, such as when blood pressure changes, the coordination of the autonomic system can be accomplished within this region. Furthermore, when descending inputs from the hypothalamus stimulate this area, the sympathetic system can increase activity in the cardiovascular system, such as in response to anxiety or stress. The preganglionic sympathetic fibers that are responsible for increasing heart rate are referred to as the cardiac accelerator nerves , whereas the preganglionic sympathetic fibers responsible for constricting blood vessels compose the vasomotor nerves .
Several brain stem nuclei are important for the visceral control of major organ systems. One brain stem nucleus involved in cardiovascular function is the solitary nucleus. It receives sensory input about blood pressure and cardiac function from the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, and its output will activate sympathetic stimulation of the heart or blood vessels through the upper thoracic lateral horn. Another brain stem nucleus important for visceral control is the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, which is the motor nucleus for the parasympathetic functions ascribed to the vagus nerve, including decreasing the heart rate, relaxing bronchial tubes in the lungs, and activating digestive function through the enteric nervous system. The nucleus ambiguus, which is named for its ambiguous histology, also contributes to the parasympathetic output of the vagus nerve and targets muscles in the pharynx and larynx for swallowing and speech, as well as contributing to the parasympathetic tone of the heart along with the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?