| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The skeletal system includes all of the bones, cartilages, and ligaments of the body that support and give shape to the body and body structures. The skeleton consists of the bones of the body. For adults, there are 206 bones in the skeleton. Younger individuals have higher numbers of bones because some bones fuse together during childhood and adolescence to form an adult bone. The primary functions of the skeleton are to provide a rigid, internal structure that can support the weight of the body against the force of gravity, and to provide a structure upon which muscles can act to produce movements of the body. The lower portion of the skeleton is specialized for stability during walking or running. In contrast, the upper skeleton has greater mobility and ranges of motion, features that allow you to lift and carry objects or turn your head and trunk.
In addition to providing for support and movements of the body, the skeleton has protective and storage functions. It protects the internal organs, including the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, and pelvic organs. The bones of the skeleton serve as the primary storage site for important minerals such as calcium and phosphate. The bone marrow found within bones stores fat and houses the blood-cell producing tissue of the body.
The skeleton is subdivided into two major divisions—the axial and appendicular.
The skeleton is subdivided into two major divisions—the axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton forms the vertical, central axis of the body and includes all bones of the head, neck, chest, and back ( [link] ). It serves to protect the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. It also serves as the attachment site for muscles that move the head, neck, and back, and for muscles that act across the shoulder and hip joints to move their corresponding limbs.
The axial skeleton of the adult consists of 80 bones, including the skull , the vertebral column , and the thoracic cage . The skull is formed by 22 bones. Also associated with the head are an additional seven bones, including the hyoid bone and the ear ossicles (three small bones found in each middle ear). The vertebral column consists of 24 bones, each called a vertebra , plus the sacrum and coccyx . The thoracic cage includes the 12 pairs of ribs , and the sternum , the flattened bone of the anterior chest.
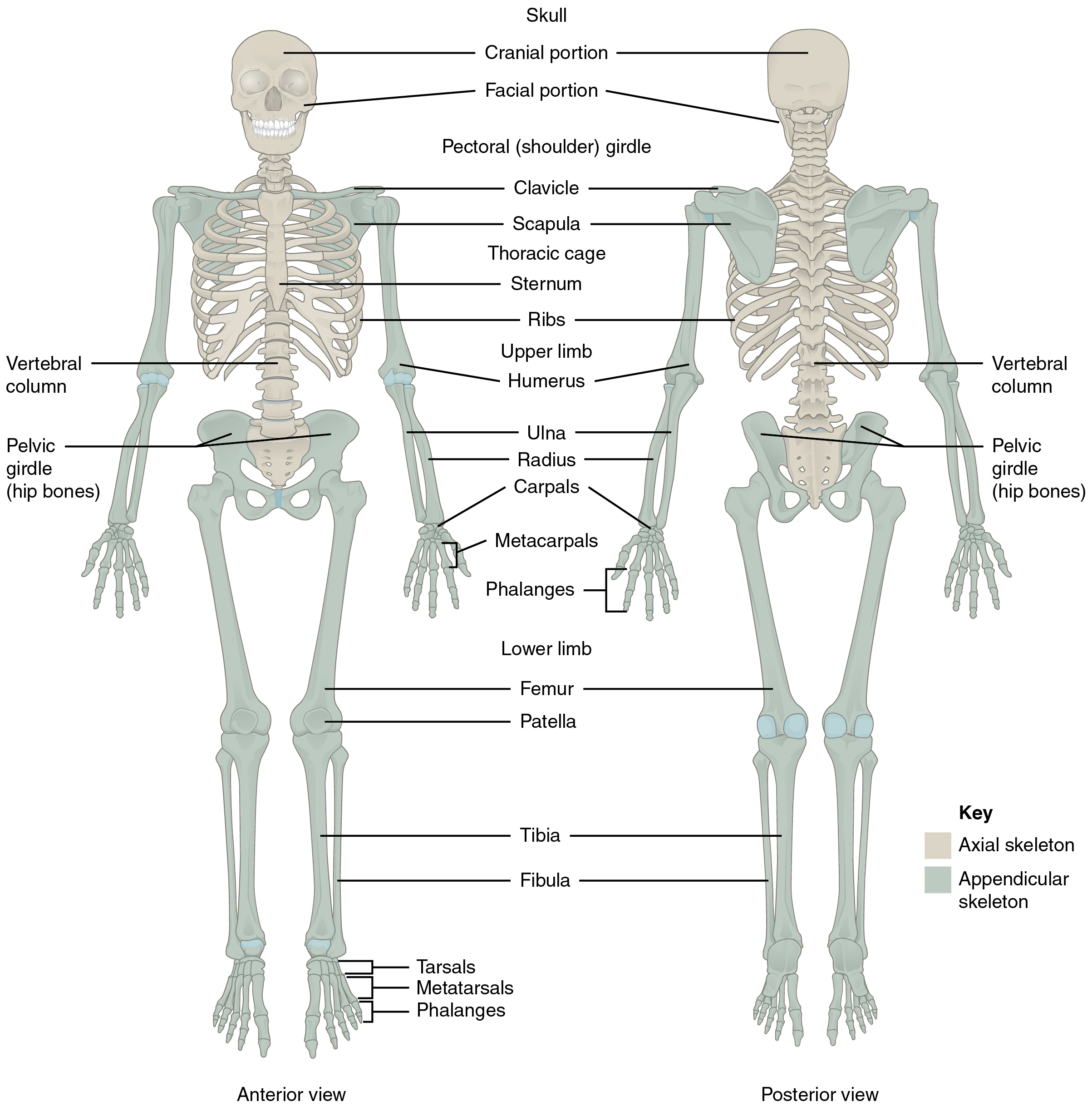
The appendicular skeleton includes all bones of the upper and lower limbs, plus the bones that attach each limb to the axial skeleton. There are 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton of an adult. The bones of the appendicular skeleton are covered in a separate chapter.
The skeletal system includes all of the bones, cartilages, and ligaments of the body. It serves to support the body, protect the brain and other internal organs, and provides a rigid structure upon which muscles can pull to generate body movements. It also stores fat and the tissue responsible for the production of blood cells. The skeleton is subdivided into two parts. The axial skeleton forms a vertical axis that includes the head, neck, back, and chest. It has 80 bones and consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The adult vertebral column consists of 24 vertebrae plus the sacrum and coccyx. The thoracic cage is formed by 12 pairs of ribs and the sternum. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones in the adult and includes all of the bones of the upper and lower limbs plus the bones that anchor each limb to the axial skeleton.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?