| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The brain case consists of eight bones. These include the paired parietal and temporal bones, plus the unpaired frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
The parietal bone forms most of the upper lateral side of the skull (see [link] ). These are paired bones, with the right and left parietal bones joining together at the top of the skull. Each parietal bone is also bounded anteriorly by the frontal bone, inferiorly by the temporal bone, and posteriorly by the occipital bone.
The temporal bone forms the lower lateral side of the skull (see [link] ). Common wisdom has it that the temporal bone (temporal = “time”) is so named because this area of the head (the temple) is where hair typically first turns gray, indicating the passage of time.
The temporal bone is subdivided into several regions ( [link] ). The flattened, upper portion is the squamous portion of the temporal bone. Below this area and projecting anteriorly is the zygomatic process of the temporal bone, which forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch. Posteriorly is the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. Projecting inferiorly from this region is a large prominence, the mastoid process , which serves as a muscle attachment site. The mastoid process can easily be felt on the side of the head just behind your earlobe. On the interior of the skull, the petrous portion of each temporal bone forms the prominent, diagonally oriented petrous ridge in the floor of the cranial cavity. Located inside each petrous ridge are small cavities that house the structures of the middle and inner ears.
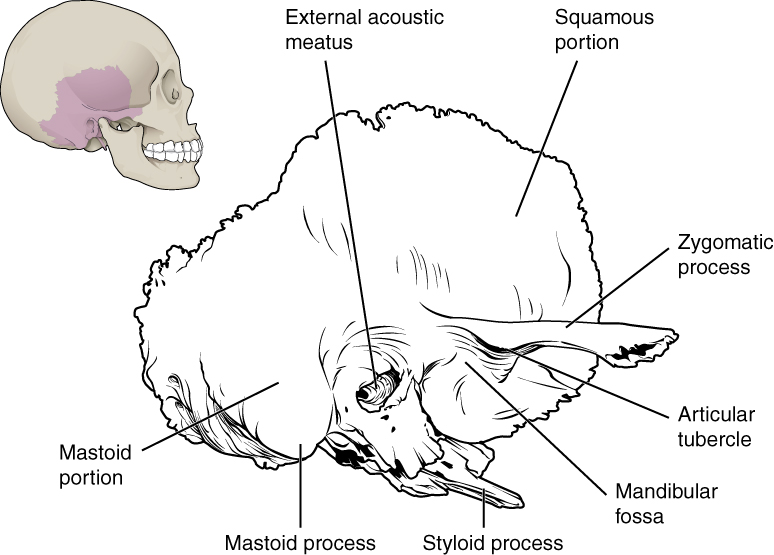
Important landmarks of the temporal bone, as shown in [link] , include the following:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?