| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The head of the fibula is the small, knob-like, proximal end of the fibula. It articulates with the inferior aspect of the lateral tibial condyle, forming the proximal tibiofibular joint . The thin shaft of the fibula has the interosseous border of the fibula , a narrow ridge running down its medial side for the attachment of the interosseous membrane that spans the fibula and tibia. The distal end of the fibula forms the lateral malleolus , which forms the easily palpated bony bump on the lateral side of the ankle. The deep (medial) side of the lateral malleolus articulates with the talus bone of the foot as part of the ankle joint. The distal fibula also articulates with the fibular notch of the tibia.
The posterior half of the foot is formed by seven tarsal bones ( [link] ). The most superior bone is the talus . This has a relatively square-shaped, upper surface that articulates with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint . Three areas of articulation form the ankle joint: The superomedial surface of the talus bone articulates with the medial malleolus of the tibia, the top of the talus articulates with the distal end of the tibia, and the lateral side of the talus articulates with the lateral malleolus of the fibula. Inferiorly, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone), the largest bone of the foot, which forms the heel. Body weight is transferred from the tibia to the talus to the calcaneus, which rests on the ground. The medial calcaneus has a prominent bony extension called the sustentaculum tali (“support for the talus”) that supports the medial side of the talus bone.
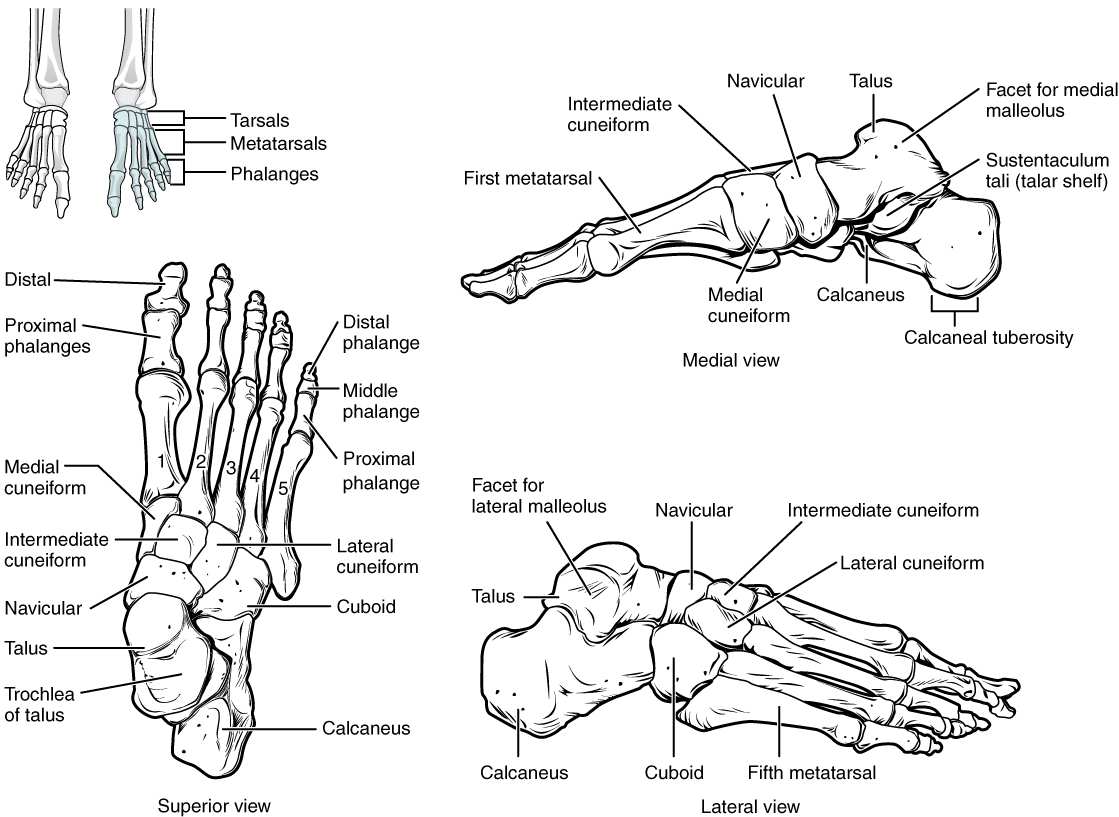
The cuboid bone articulates with the anterior end of the calcaneus bone. The cuboid has a deep groove running across its inferior surface, which provides passage for a muscle tendon. The talus bone articulates anteriorly with the navicular bone, which in turn articulates anteriorly with the three cuneiform (“wedge-shaped”) bones. These bones are the medial cuneiform , the intermediate cuneiform , and the lateral cuneiform . Each of these bones has a broad superior surface and a narrow inferior surface, which together produce the transverse (medial-lateral) curvature of the foot. The navicular and lateral cuneiform bones also articulate with the medial side of the cuboid bone.
Use this tutorial to review the bones of the foot. Which tarsal bones are in the proximal, intermediate, and distal groups?
The anterior half of the foot is formed by the five metatarsal bones, which are located between the tarsal bones of the posterior foot and the phalanges of the toes (see [link] ). These elongated bones are numbered 1–5, starting with the medial side of the foot. The first metatarsal bone is shorter and thicker than the others. The second metatarsal is the longest. The base of the metatarsal bone is the proximal end of each metatarsal bone. These articulate with the cuboid or cuneiform bones. The base of the fifth metatarsal has a large, lateral expansion that provides for muscle attachments. This expanded base of the fifth metatarsal can be felt as a bony bump at the midpoint along the lateral border of the foot. The expanded distal end of each metatarsal is the head of the metatarsal bone . Each metatarsal bone articulates with the proximal phalanx of a toe to form a metatarsophalangeal joint . The heads of the metatarsal bones also rest on the ground and form the ball (anterior end) of the foot.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?