| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
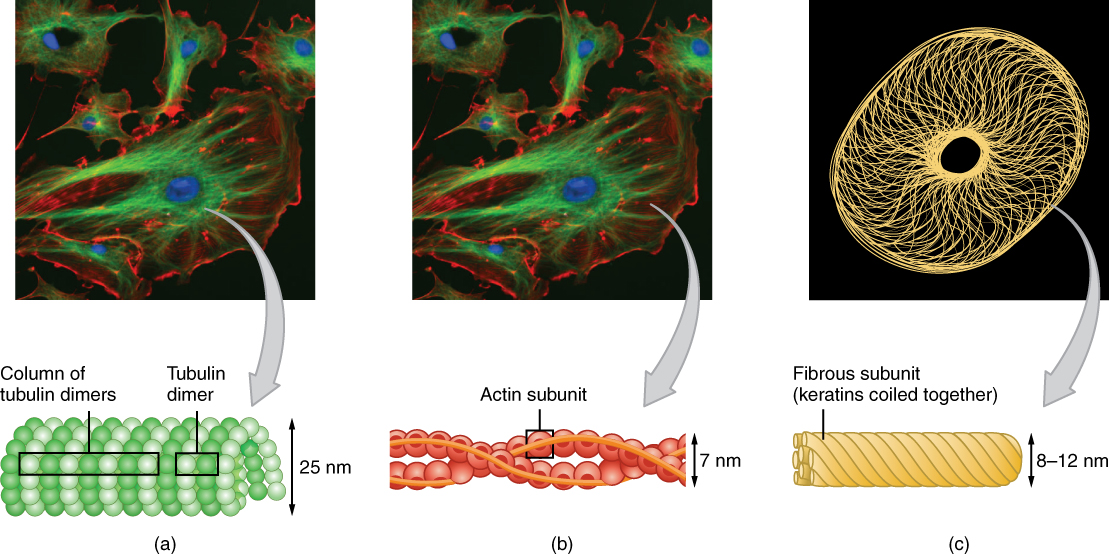
A very important function of microtubules is to set the paths (somewhat like railroad tracks) along which the genetic material can be pulled (a process requiring ATP) during cell division, so that each new daughter cell receives the appropriate set of chromosomes. Two short, identical microtubule structures called centrioles are found near the nucleus of cells. A centriole can serve as the cellular origin point for microtubules extending outward as cilia or flagella or can assist with the separation of DNA during cell division. Microtubules grow out from the centrioles by adding more tubulin subunits, like adding additional links to a chain.
In contrast with microtubules, the microfilament is a thinner type of cytoskeletal filament (see [link] b ). Actin, a protein that forms chains, is the primary component of these microfilaments. Actin fibers, twisted chains of actin filaments, constitute a large component of muscle tissue and, along with the protein myosin, are responsible for muscle contraction. Like microtubules, actin filaments are long chains of single subunits (called actin subunits). In muscle cells, these long actin strands, called thin filaments, are “pulled” by thick filaments of the myosin protein to contract the cell.
Actin also has an important role during cell division. When a cell is about to split in half during cell division, actin filaments work with myosin to create a cleavage furrow that eventually splits the cell down the middle, forming two new cells from the original cell.
The final cytoskeletal filament is the intermediate filament. As its name would suggest, an intermediate filament is a filament intermediate in thickness between the microtubules and microfilaments (see [link] c ). Intermediate filaments are made up of long fibrous subunits of a protein called keratin that are wound together like the threads that compose a rope. Intermediate filaments, in concert with the microtubules, are important for maintaining cell shape and structure. Unlike the microtubules, which resist compression, intermediate filaments resist tension—the forces that pull apart cells. There are many cases in which cells are prone to tension, such as when epithelial cells of the skin are compressed, tugging them in different directions. Intermediate filaments help anchor organelles together within a cell and also link cells to other cells by forming special cell-to-cell junctions.
The internal environmental of a living cell is made up of a fluid, jelly-like substance called cytosol, which consists mainly of water, but also contains various dissolved nutrients and other molecules. The cell contains an array of cellular organelles, each one performing a unique function and helping to maintain the health and activity of the cell. The cytosol and organelles together compose the cell’s cytoplasm. Most organelles are surrounded by a lipid membrane similar to the cell membrane of the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes share a functional connectivity and are collectively referred to as the endomembrane system. There are two types of ER: smooth and rough. While the smooth ER performs many functions, including lipid synthesis and ion storage, the rough ER is mainly responsible for protein synthesis using its associated ribosomes. The rough ER sends newly made proteins to the Golgi apparatus where they are modified and packaged for delivery to various locations within or outside of the cell. Some of these protein products are enzymes destined to break down unwanted material and are packaged as lysosomes for use inside the cell.
Cells also contain mitochondria and peroxisomes, which are the organelles responsible for producing the cell’s energy supply and detoxifying certain chemicals, respectively. Biochemical reactions within mitochondria transform energy-carrying molecules into the usable form of cellular energy known as ATP. Peroxisomes contain enzymes that transform harmful substances such as free radicals into oxygen and water. Cells also contain a miniaturized “skeleton” of protein filaments that extend throughout its interior. Three different kinds of filaments compose this cytoskeleton (in order of increasing thickness): microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Each cytoskeletal component performs unique functions as well as provides a supportive framework for the cell.
Watch this video to learn about the endomembrane system, which includes the rough and smooth ER and the Golgi body as well as lysosomes and vesicles. What is the primary role of the endomembrane system?
Processing, packaging, and moving materials manufactured by the cell.
Kolata, G. Severe diet doesn’t prolong life, at least in monkeys. New York Times [Internet]. 2012 Aug. 29 [cited 2013 Jan 21]; Available from:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?