| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
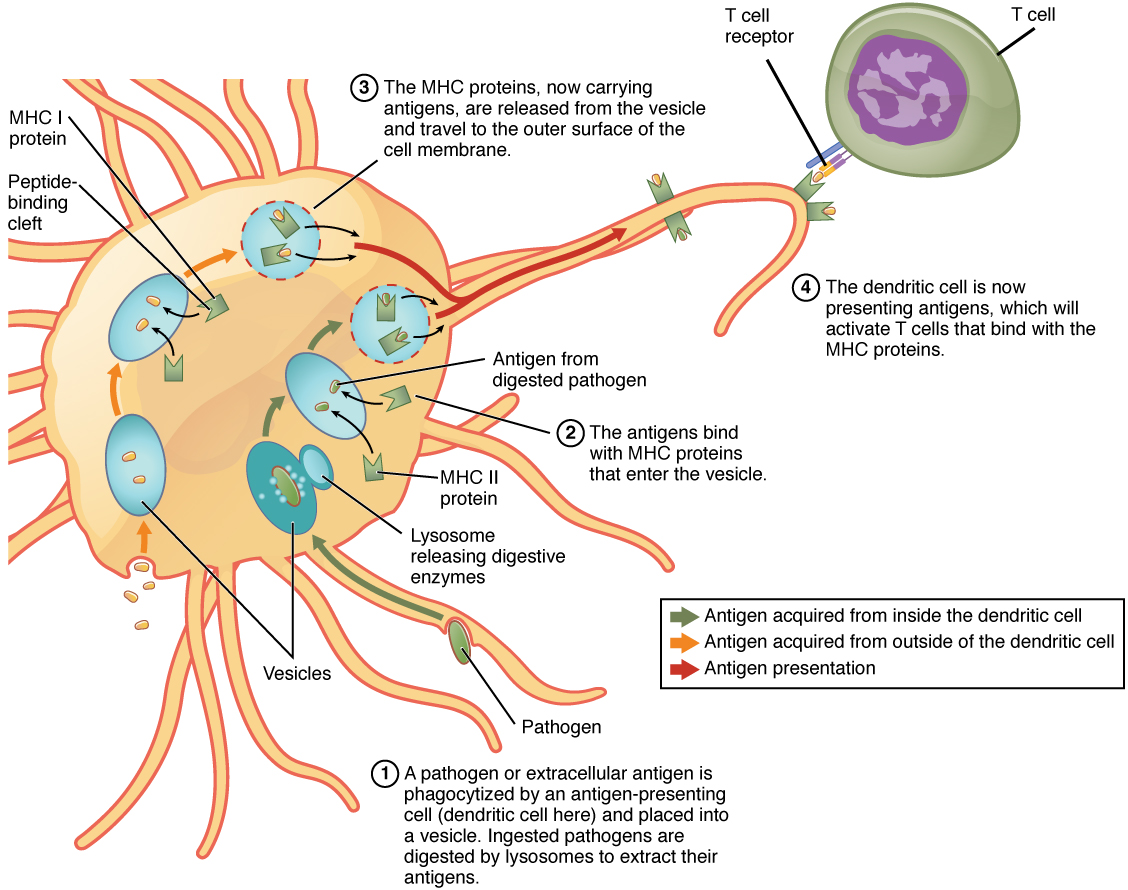
Two distinct types of MHC molecules, MHC class I and MHC class II , play roles in antigen presentation. Although produced from different genes, they both have similar functions. They bring processed antigen to the surface of the cell via a transport vesicle and present the antigen to the T cell and its receptor. Antigens from different classes of pathogens, however, use different MHC classes and take different routes through the cell to get to the surface for presentation. The basic mechanism, though, is the same. Antigens are processed by digestion, are brought into the endomembrane system of the cell, and then are expressed on the surface of the antigen-presenting cell for antigen recognition by a T cell. Intracellular antigens are typical of viruses, which replicate inside the cell, and certain other intracellular parasites and bacteria. These antigens are processed in the cytosol by an enzyme complex known as the proteasome and are then brought into the endoplasmic reticulum by the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) system, where they interact with class I MHC molecules and are eventually transported to the cell surface by a transport vesicle.
Extracellular antigens, characteristic of many bacteria, parasites, and fungi that do not replicate inside the cell’s cytoplasm, are brought into the endomembrane system of the cell by receptor-mediated endocytosis. The resulting vesicle fuses with vesicles from the Golgi complex, which contain pre-formed MHC class II molecules. After fusion of these two vesicles and the association of antigen and MHC, the new vesicle makes its way to the cell surface.
Many cell types express class I molecules for the presentation of intracellular antigens. These MHC molecules may then stimulate a cytotoxic T cell immune response, eventually destroying the cell and the pathogen within. This is especially important when it comes to the most common class of intracellular pathogens, the virus. Viruses infect nearly every tissue of the body, so all these tissues must necessarily be able to express class I MHC or no T cell response can be made.
On the other hand, class II MHC molecules are expressed only on the cells of the immune system, specifically cells that affect other arms of the immune response. Thus, these cells are called “professional” antigen-presenting cells to distinguish them from those that bear class I MHC. The three types of professional antigen presenters are macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells ( [link] ).
Macrophages stimulate T cells to release cytokines that enhance phagocytosis. Dendritic cells also kill pathogens by phagocytosis (see [link] ), but their major function is to bring antigens to regional draining lymph nodes. The lymph nodes are the locations in which most T cell responses against pathogens of the interstitial tissues are mounted. Macrophages are found in the skin and in the lining of mucosal surfaces, such as the nasopharynx, stomach, lungs, and intestines. B cells may also present antigens to T cells, which are necessary for certain types of antibody responses, to be covered later in this chapter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?