| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The three lipases responsible for lipid digestion are lingual lipase, gastric lipase, and pancreatic lipase . However, because the pancreas is the only consequential source of lipase, virtually all lipid digestion occurs in the small intestine. Pancreatic lipase breaks down each triglyceride into two free fatty acids and a monoglyceride. The fatty acids include both short-chain (less than 10 to 12 carbons) and long-chain fatty acids.
The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are found in most of the foods you eat. Two types of pancreatic nuclease are responsible for their digestion: deoxyribonuclease , which digests DNA, and ribonuclease , which digests RNA. The nucleotides produced by this digestion are further broken down by two intestinal brush border enzymes ( nucleosidase and phosphatase ) into pentoses, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases, which can be absorbed through the alimentary canal wall. The large food molecules that must be broken down into subunits are summarized [link]
| Absorbable Food Substances | |
|---|---|
| Source | Substance |
| Carbohydrates | Monosaccharides: glucose, galactose, and fructose |
| Proteins | Single amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides |
| Triglycerides | Monoacylglycerides, glycerol, and free fatty acids |
| Nucleic acids | Pentose sugars, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases |
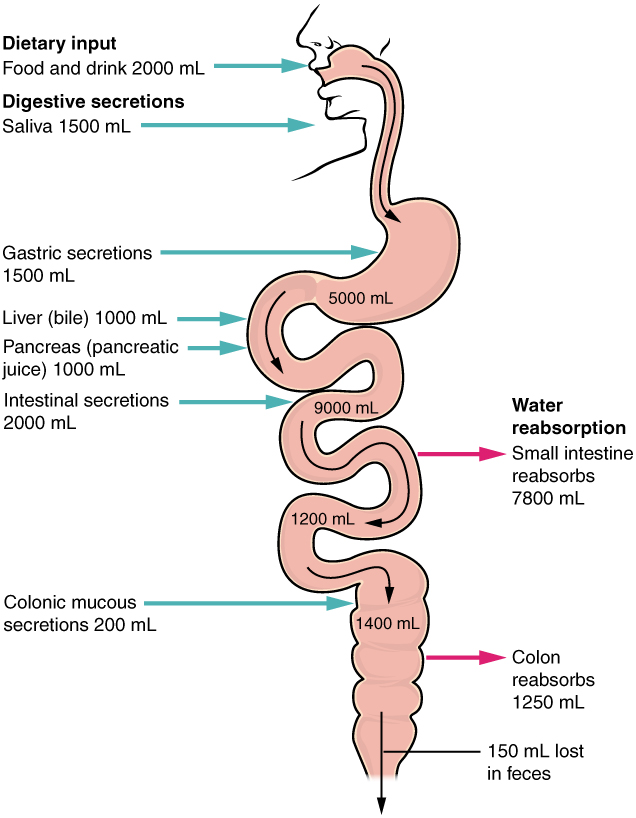
The mechanical and digestive processes have one goal: to convert food into molecules small enough to be absorbed by the epithelial cells of the intestinal villi. The absorptive capacity of the alimentary canal is almost endless. Each day, the alimentary canal processes up to 10 liters of food, liquids, and GI secretions, yet less than one liter enters the large intestine. Almost all ingested food, 80 percent of electrolytes, and 90 percent of water are absorbed in the small intestine. Although the entire small intestine is involved in the absorption of water and lipids, most absorption of carbohydrates and proteins occurs in the jejunum. Notably, bile salts and vitamin B 12 are absorbed in the terminal ileum. By the time chyme passes from the ileum into the large intestine, it is essentially indigestible food residue (mainly plant fibers like cellulose), some water, and millions of bacteria ( [link] ).
Absorption can occur through five mechanisms: (1) active transport, (2) passive diffusion, (3) facilitated diffusion, (4) co-transport (or secondary active transport), and (5) endocytosis. As you will recall from Chapter 3, active transport refers to the movement of a substance across a cell membrane going from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration (up the concentration gradient). In this type of transport, proteins within the cell membrane act as “pumps,” using cellular energy (ATP) to move the substance. Passive diffusion refers to the movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while facilitated diffusion refers to the movement of substances from an area of higher to an area of lower concentration using a carrier protein in the cell membrane. Co-transport uses the movement of one molecule through the membrane from higher to lower concentration to power the movement of another from lower to higher. Finally, endocytosis is a transportation process in which the cell membrane engulfs material. It requires energy, generally in the form of ATP.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?