| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although the masseter and temporalis are responsible for elevating and closing the jaw to break food into digestible pieces, the medial pterygoid and lateral pterygoid muscles provide assistance in chewing and moving food within the mouth.
Although the tongue is obviously important for tasting food, it is also necessary for mastication, deglutition (swallowing), and speech ( [link] and [link] ). Because it is so moveable, the tongue facilitates complex speech patterns and sounds.
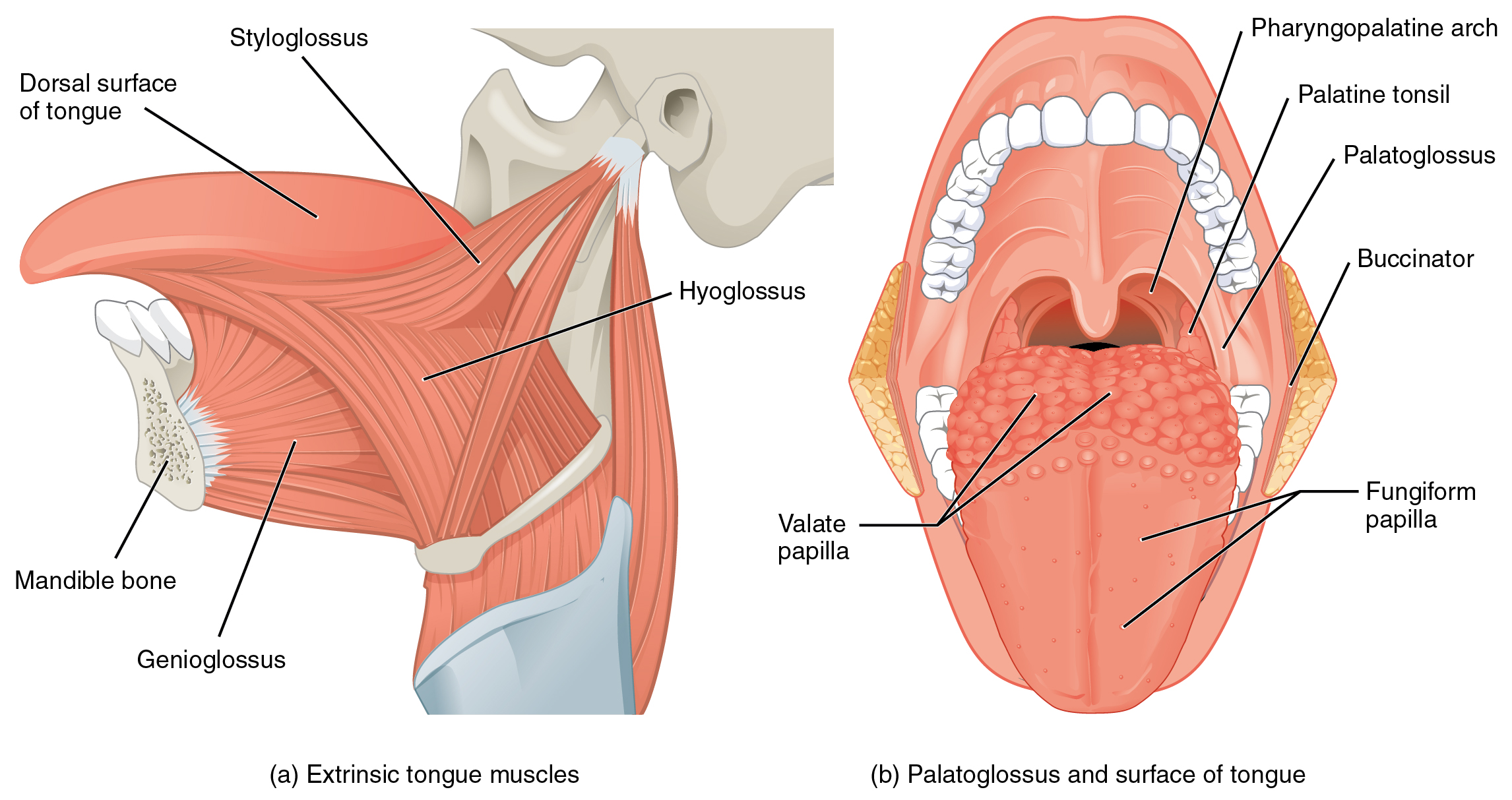
Tongue muscles can be extrinsic or intrinsic. Extrinsic tongue muscles insert into the tongue from outside origins, and the intrinsic tongue muscles insert into the tongue from origins within it. The extrinsic muscles move the whole tongue in different directions, whereas the intrinsic muscles allow the tongue to change its shape (such as, curling the tongue in a loop or flattening it).
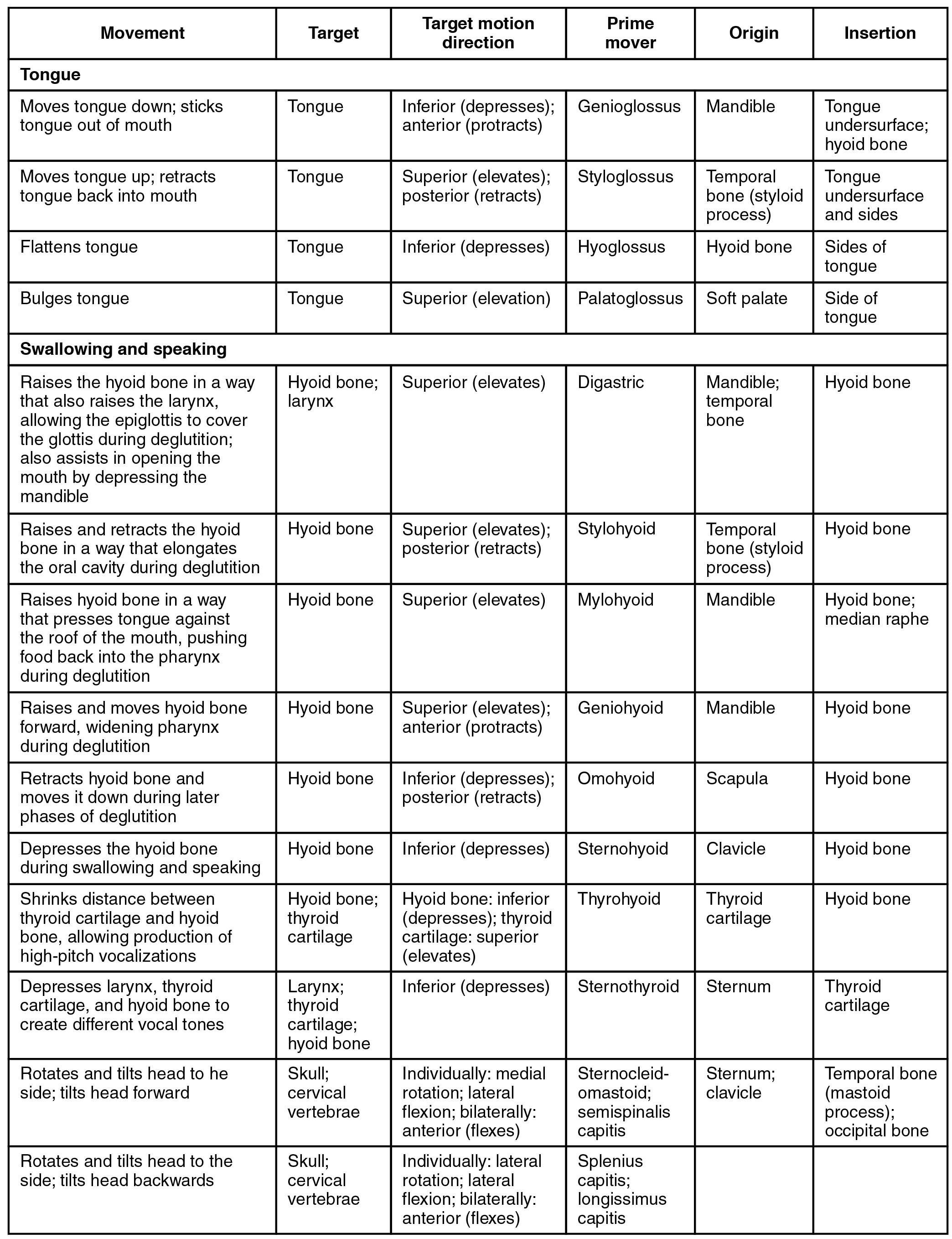
The extrinsic muscles all include the word root glossus (glossus = “tongue”), and the muscle names are derived from where the muscle originates. The genioglossus (genio = “chin”) originates on the mandible and allows the tongue to move downward and forward. The styloglossus originates on the styloid bone, and allows upward and backward motion. The palatoglossus originates on the soft palate to elevate the back of the tongue, and the hyoglossus originates on the hyoid bone to move the tongue downward and flatten it.
Among the muscles affected during general anesthesia are those that are necessary for breathing and moving the tongue. Under anesthesia, the tongue can relax and partially or fully block the airway, and the muscles of respiration may not move the diaphragm or chest wall. To avoid possible complications, the safest procedure to use on a patient is called endotracheal intubation. Placing a tube into the trachea allows the doctors to maintain a patient’s (open) airway to the lungs and seal the airway off from the oropharynx. Post-surgery, the anesthesiologist gradually changes the mixture of the gases that keep the patient unconscious, and when the muscles of respiration begin to function, the tube is removed. It still takes about 30 minutes for a patient to wake up, and for breathing muscles to regain control of respiration. After surgery, most people have a sore or scratchy throat for a few days.
The muscles of the anterior neck assist in deglutition (swallowing) and speech by controlling the positions of the larynx (voice box), and the hyoid bone, a horseshoe-shaped bone that functions as a solid foundation on which the tongue can move. The muscles of the neck are categorized according to their position relative to the hyoid bone ( [link] ). Suprahyoid muscles are superior to it, and the infrahyoid muscles are located inferiorly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?