| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
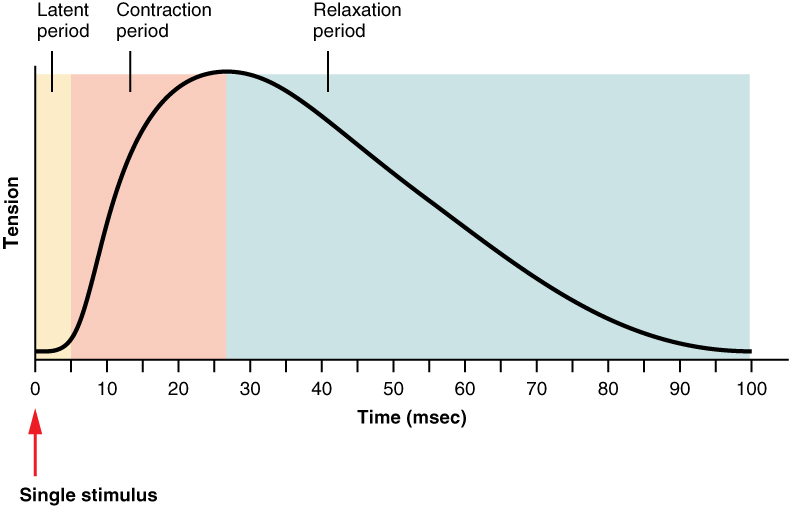
Although a person can experience a muscle “twitch,” a single twitch does not produce any significant muscle activity in a living body. A series of action potentials to the muscle fibers is necessary to produce a muscle contraction that can produce work. Normal muscle contraction is more sustained, and it can be modified by input from the nervous system to produce varying amounts of force; this is called a graded muscle response . The frequency of action potentials (nerve impulses) from a motor neuron and the number of motor neurons transmitting action potentials both affect the tension produced in skeletal muscle.
The rate at which a motor neuron fires action potentials affects the tension produced in the skeletal muscle. If the fibers are stimulated while a previous twitch is still occurring, the second twitch will be stronger. This response is called wave summation , because the excitation-contraction coupling effects of successive motor neuron signaling is summed, or added together ( [link] a ). At the molecular level, summation occurs because the second stimulus triggers the release of more Ca ++ ions, which become available to activate additional sarcomeres while the muscle is still contracting from the first stimulus. Summation results in greater contraction of the motor unit.

If the frequency of motor neuron signaling increases, summation and subsequent muscle tension in the motor unit continues to rise until it reaches a peak point. The tension at this point is about three to four times greater than the tension of a single twitch, a state referred to as incomplete tetanus. During incomplete tetanus, the muscle goes through quick cycles of contraction with a short relaxation phase for each. If the stimulus frequency is so high that the relaxation phase disappears completely, contractions become continuous in a process called complete tetanus ( [link] b ).
During tetanus, the concentration of Ca ++ ions in the sarcoplasm allows virtually all of the sarcomeres to form cross-bridges and shorten, so that a contraction can continue uninterrupted (until the muscle fatigues and can no longer produce tension).
When a skeletal muscle has been dormant for an extended period and then activated to contract, with all other things being equal, the initial contractions generate about one-half the force of later contractions. The muscle tension increases in a graded manner that to some looks like a set of stairs. This tension increase is called treppe , a condition where muscle contractions become more efficient. It’s also known as the “staircase effect” ( [link] ).
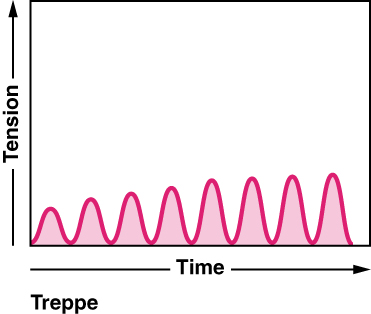
It is believed that treppe results from a higher concentration of Ca ++ in the sarcoplasm resulting from the steady stream of signals from the motor neuron. It can only be maintained with adequate ATP.
Skeletal muscles are rarely completely relaxed, or flaccid. Even if a muscle is not producing movement, it is contracted a small amount to maintain its contractile proteins and produce muscle tone . The tension produced by muscle tone allows muscles to continually stabilize joints and maintain posture.
Muscle tone is accomplished by a complex interaction between the nervous system and skeletal muscles that results in the activation of a few motor units at a time, most likely in a cyclical manner. In this manner, muscles never fatigue completely, as some motor units can recover while others are active.
The absence of the low-level contractions that lead to muscle tone is referred to as hypotonia or atrophy, and can result from damage to parts of the central nervous system (CNS), such as the cerebellum, or from loss of innervations to a skeletal muscle, as in poliomyelitis. Hypotonic muscles have a flaccid appearance and display functional impairments, such as weak reflexes. Conversely, excessive muscle tone is referred to as hypertonia , accompanied by hyperreflexia (excessive reflex responses), often the result of damage to upper motor neurons in the CNS. Hypertonia can present with muscle rigidity (as seen in Parkinson’s disease) or spasticity, a phasic change in muscle tone, where a limb will “snap” back from passive stretching (as seen in some strokes).
The number of cross-bridges formed between actin and myosin determines the amount of tension produced by a muscle. The length of a sarcomere is optimal when the zone of overlap between thin and thick filaments is greatest. Muscles that are stretched or compressed too greatly do not produce maximal amounts of power. A motor unit is formed by a motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers that are innervated by that same motor neuron. A single contraction is called a twitch. A muscle twitch has a latent period, a contraction phase, and a relaxation phase. A graded muscle response allows variation in muscle tension. Summation occurs as successive stimuli are added together to produce a stronger muscle contraction. Tetanus is the fusion of contractions to produce a continuous contraction. Increasing the number of motor neurons involved increases the amount of motor units activated in a muscle, which is called recruitment. Muscle tone is the constant low-level contractions that allow for posture and stability.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?