| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
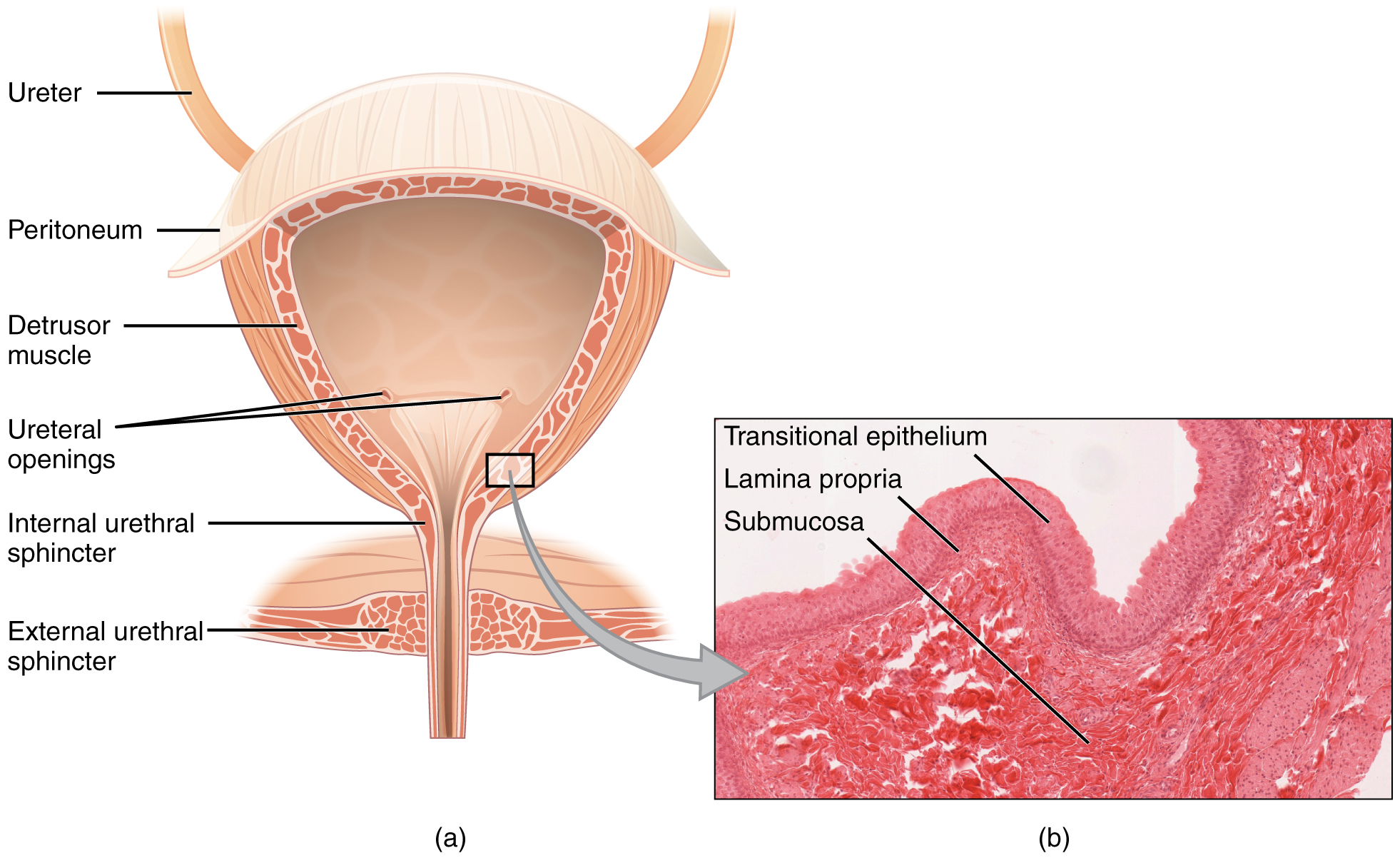
The urinary bladder collects urine from both ureters ( [link] ). The bladder lies anterior to the uterus in females, posterior to the pubic bone and anterior to the rectum. During late pregnancy, its capacity is reduced due to compression by the enlarging uterus, resulting in increased frequency of urination. In males, the anatomy is similar, minus the uterus, and with the addition of the prostate inferior to the bladder. The bladder is partially retroperitoneal (outside the peritoneal cavity) with its peritoneal-covered “dome” projecting into the abdomen when the bladder is distended with urine.
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail.
The bladder is a highly distensible organ comprised of irregular crisscrossing bands of smooth muscle collectively called the detrusor muscle . The interior surface is made of transitional cellular epithelium that is structurally suited for the large volume fluctuations of the bladder. When empty, it resembles columnar epithelia, but when stretched, it “transitions” (hence the name) to a squamous appearance (see [link] ). Volumes in adults can range from nearly zero to 500–600 mL.
The detrusor muscle contracts with significant force in the young. The bladder’s strength diminishes with age, but voluntary contractions of abdominal skeletal muscles can increase intra-abdominal pressure to promote more forceful bladder emptying. Such voluntary contraction is also used in forceful defecation and childbirth.
Micturition is a less-often used, but proper term for urination or voiding. It results from an interplay of involuntary and voluntary actions by the internal and external urethral sphincters. When bladder volume reaches about 150 mL, an urge to void is sensed but is easily overridden. Voluntary control of urination relies on consciously preventing relaxation of the external urethral sphincter to maintain urinary continence. As the bladder fills, subsequent urges become harder to ignore. Ultimately, voluntary constraint fails with resulting incontinence , which will occur as bladder volume approaches 300 to 400 mL.
Normal micturition is a result of stretch receptors in the bladder wall that transmit nerve impulses to the sacral region of the spinal cord to generate a spinal reflex. The resulting parasympathetic neural outflow causes contraction of the detrusor muscle and relaxation of the involuntary internal urethral sphincter. At the same time, the spinal cord inhibits somatic motor neurons, resulting in the relaxation of the skeletal muscle of the external urethral sphincter. The micturition reflex is active in infants but with maturity, children learn to override the reflex by asserting external sphincter control, thereby delaying voiding (potty training). This reflex may be preserved even in the face of spinal cord injury that results in paraplegia or quadriplegia. However, relaxation of the external sphincter may not be possible in all cases, and therefore, periodic catheterization may be necessary for bladder emptying.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?