| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A gland is a structure made up of one or more cells modified to synthesize and secrete chemical substances. Most glands consist of groups of epithelial cells. A gland can be classified as an endocrine gland , a ductless gland that releases secretions directly into surrounding tissues and fluids (endo- = “inside”), or an exocrine gland whose secretions leave through a duct that opens directly, or indirectly, to the external environment (exo- = “outside”).
The secretions of endocrine glands are called hormones. Hormones are released into the interstitial fluid, diffused into the bloodstream, and delivered to targets, in other words, cells that have receptors to bind the hormones. The endocrine system is part of a major regulatory system coordinating the regulation and integration of body responses. A few examples of endocrine glands include the anterior pituitary, thymus, adrenal cortex, and gonads.
Exocrine glands release their contents through a duct that leads to the epithelial surface. Mucous, sweat, saliva, and breast milk are all examples of secretions from exocrine glands. They are all discharged through tubular ducts. Secretions into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, technically outside of the body, are of the exocrine category.
Exocrine glands are classified as either unicellular or multicellular. The unicellular glands are scattered single cells, such as goblet cells, found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine.
The multicellular exocrine glands known as serous glands develop from simple epithelium to form a secretory surface that secretes directly into an inner cavity. These glands line the internal cavities of the abdomen and chest and release their secretions directly into the cavities. Other multicellular exocrine glands release their contents through a tubular duct. The duct is single in a simple gland but in compound glands is divided into one or more branches ( [link] ). In tubular glands, the ducts can be straight or coiled, whereas tubes that form pockets are alveolar (acinar), such as the exocrine portion of the pancreas. Combinations of tubes and pockets are known as tubuloalveolar (tubuloacinar) compound glands. In a branched gland, a duct is connected to more than one secretory group of cells.
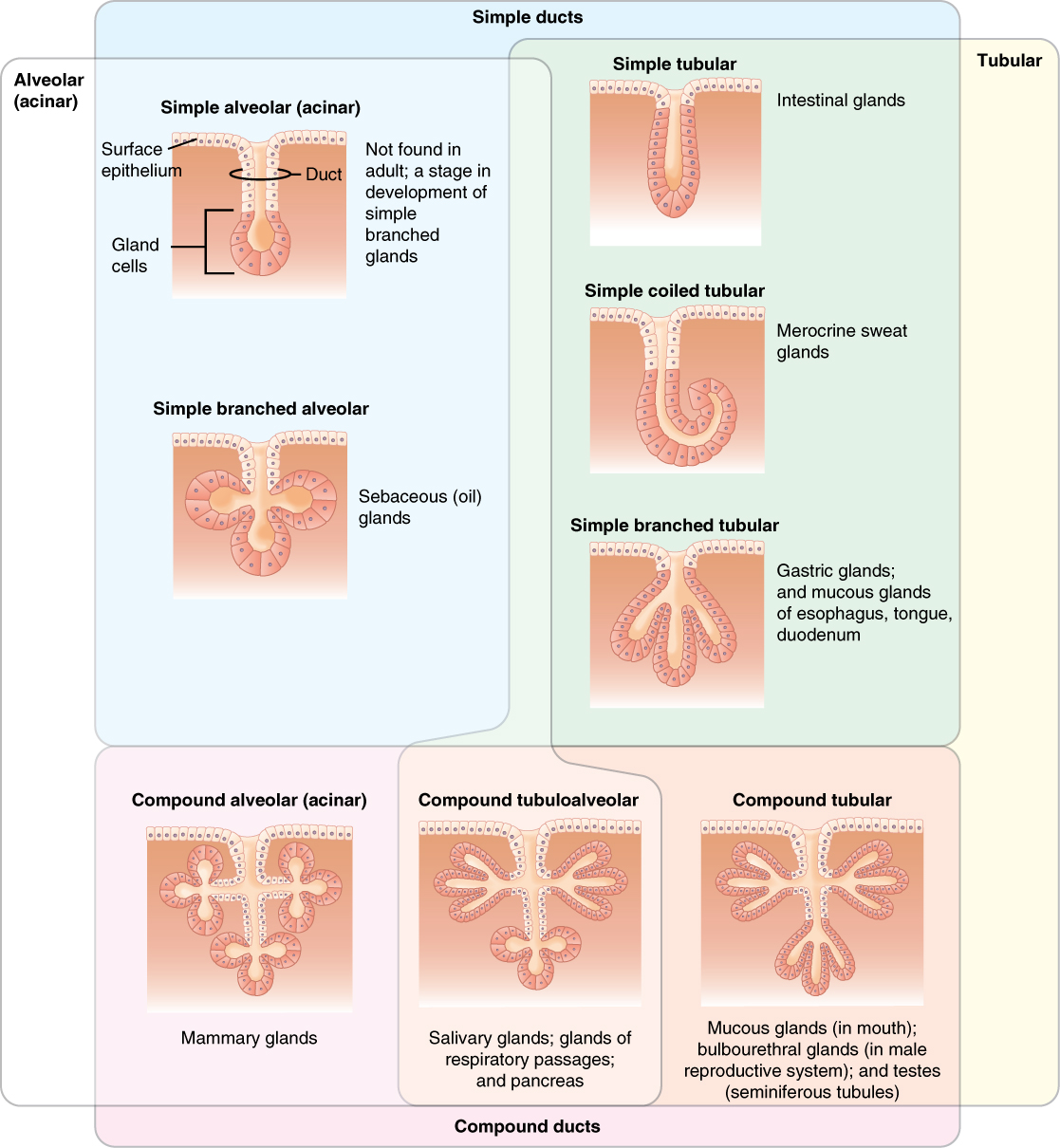
Exocrine glands can be classified by their mode of secretion and the nature of the substances released, as well as by the structure of the glands and shape of ducts ( [link] ). Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion. The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the contents are released by exocytosis. For example, watery mucous containing the glycoprotein mucin, a lubricant that offers some pathogen protection is a merocrine secretion. The eccrine glands that produce and secrete sweat are another example.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?