| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
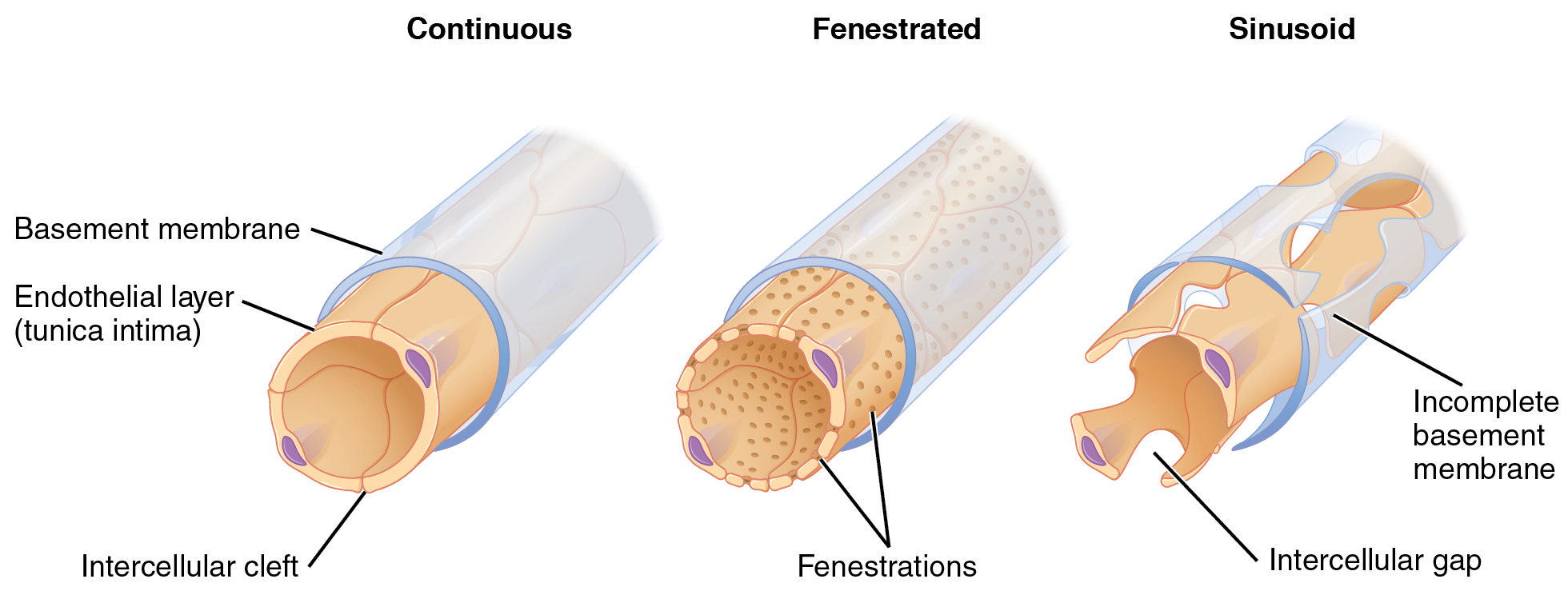
A fenestrated capillary is one that has pores (or fenestrations) in addition to tight junctions in the endothelial lining. These make the capillary permeable to larger molecules. The number of fenestrations and their degree of permeability vary, however, according to their location. Fenestrated capillaries are common in the small intestine, which is the primary site of nutrient absorption, as well as in the kidneys, which filter the blood. They are also found in the choroid plexus of the brain and many endocrine structures, including the hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, and thyroid glands.
A sinusoid capillary (or sinusoid) is the least common type of capillary. Sinusoid capillaries are flattened, and they have extensive intercellular gaps and incomplete basement membranes, in addition to intercellular clefts and fenestrations. This gives them an appearance not unlike Swiss cheese. These very large openings allow for the passage of the largest molecules, including plasma proteins and even cells. Blood flow through sinusoids is very slow, allowing more time for exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes. Sinusoids are found in the liver and spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes (where they carry lymph, not blood), and many endocrine glands including the pituitary and adrenal glands. Without these specialized capillaries, these organs would not be able to provide their myriad of functions. For example, when bone marrow forms new blood cells, the cells must enter the blood supply and can only do so through the large openings of a sinusoid capillary; they cannot pass through the small openings of continuous or fenestrated capillaries. The liver also requires extensive specialized sinusoid capillaries in order to process the materials brought to it by the hepatic portal vein from both the digestive tract and spleen, and to release plasma proteins into circulation.
A metarteriole is a type of vessel that has structural characteristics of both an arteriole and a capillary. Slightly larger than the typical capillary, the smooth muscle of the tunica media of the metarteriole is not continuous but forms rings of smooth muscle (sphincters) prior to the entrance to the capillaries. Each metarteriole arises from a terminal arteriole and branches to supply blood to a capillary bed that may consist of 10–100 capillaries.
The precapillary sphincters , circular smooth muscle cells that surround the capillary at its origin with the metarteriole, tightly regulate the flow of blood from a metarteriole to the capillaries it supplies. Their function is critical: If all of the capillary beds in the body were to open simultaneously, they would collectively hold every drop of blood in the body and there would be none in the arteries, arterioles, venules, veins, or the heart itself. Normally, the precapillary sphincters are closed. When the surrounding tissues need oxygen and have excess waste products, the precapillary sphincters open, allowing blood to flow through and exchange to occur before closing once more ( [link] ). If all of the precapillary sphincters in a capillary bed are closed, blood will flow from the metarteriole directly into a thoroughfare channel and then into the venous circulation, bypassing the capillary bed entirely. This creates what is known as a vascular shunt . In addition, an arteriovenous anastomosis may bypass the capillary bed and lead directly to the venous system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?