| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

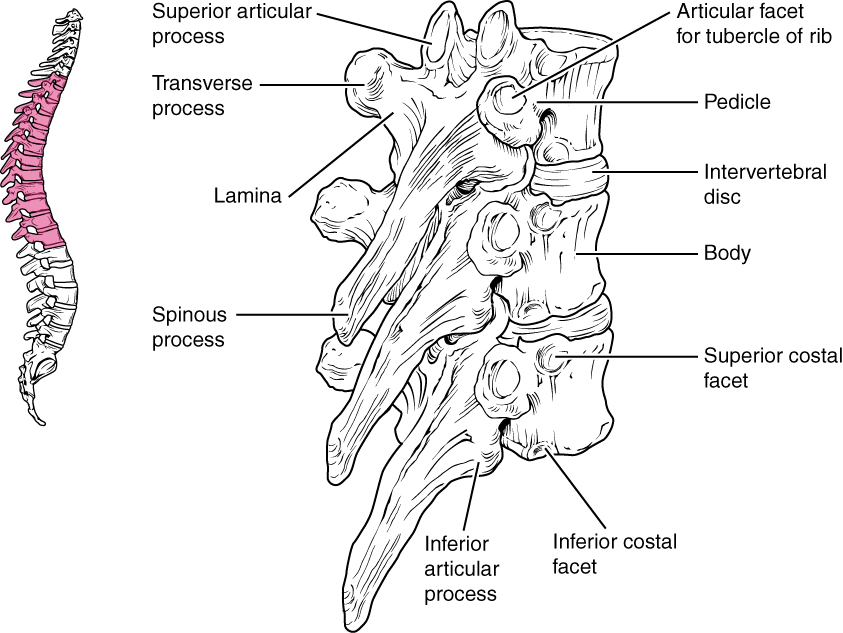
The bodies of the thoracic vertebrae are larger than those of cervical vertebrae ( [link] ). The characteristic feature for a typical midthoracic vertebra is the spinous process, which is long and has a pronounced downward angle that causes it to overlap the next inferior vertebra. The superior articular processes of thoracic vertebrae face anteriorly and the inferior processes face posteriorly. These orientations are important determinants for the type and range of movements available to the thoracic region of the vertebral column.
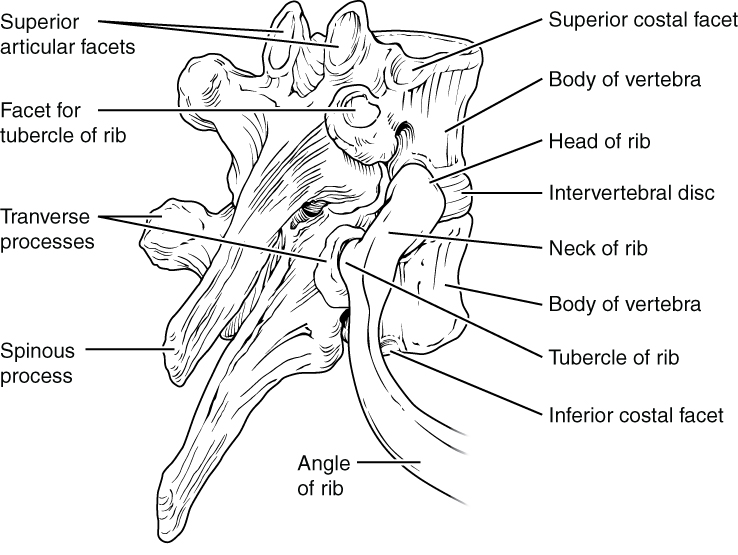
Thoracic vertebrae have several additional articulation sites, each of which is called a facet , where a rib is attached. Most thoracic vertebrae have two facets located on the lateral sides of the body, each of which is called a costal facet (costal = “rib”). These are for articulation with the head (end) of a rib. An additional facet is located on the transverse process for articulation with the tubercle of a rib.
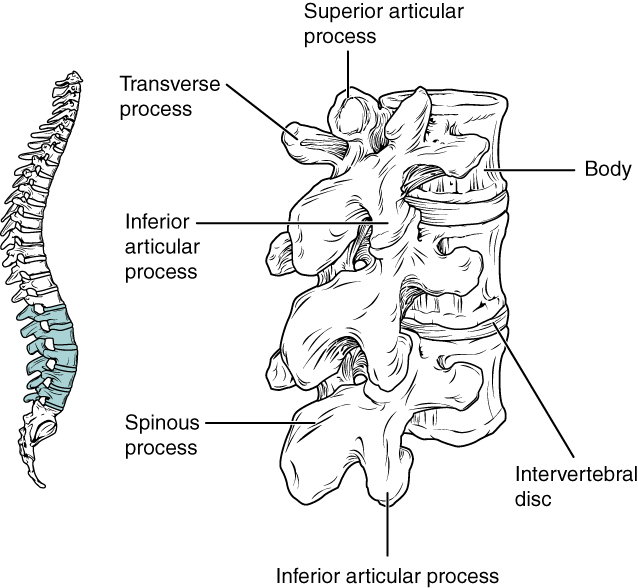
Lumbar vertebrae carry the greatest amount of body weight and are thus characterized by the large size and thickness of the vertebral body ( [link] ). They have short transverse processes and a short, blunt spinous process that projects posteriorly. The articular processes are large, with the superior process facing backward and the inferior facing forward.
The sacrum is a triangular-shaped bone that is thick and wide across its superior base where it is weight bearing and then tapers down to an inferior, non-weight bearing apex ( [link] ). It is formed by the fusion of five sacral vertebrae, a process that does not begin until after the age of 20. On the anterior surface of the older adult sacrum, the lines of vertebral fusion can be seen as four transverse ridges. On the posterior surface, running down the midline, is the median sacral crest , a bumpy ridge that is the remnant of the fused spinous processes (median = “midline”; while medial = “toward, but not necessarily at, the midline”). Similarly, the fused transverse processes of the sacral vertebrae form the lateral sacral crest .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?