| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
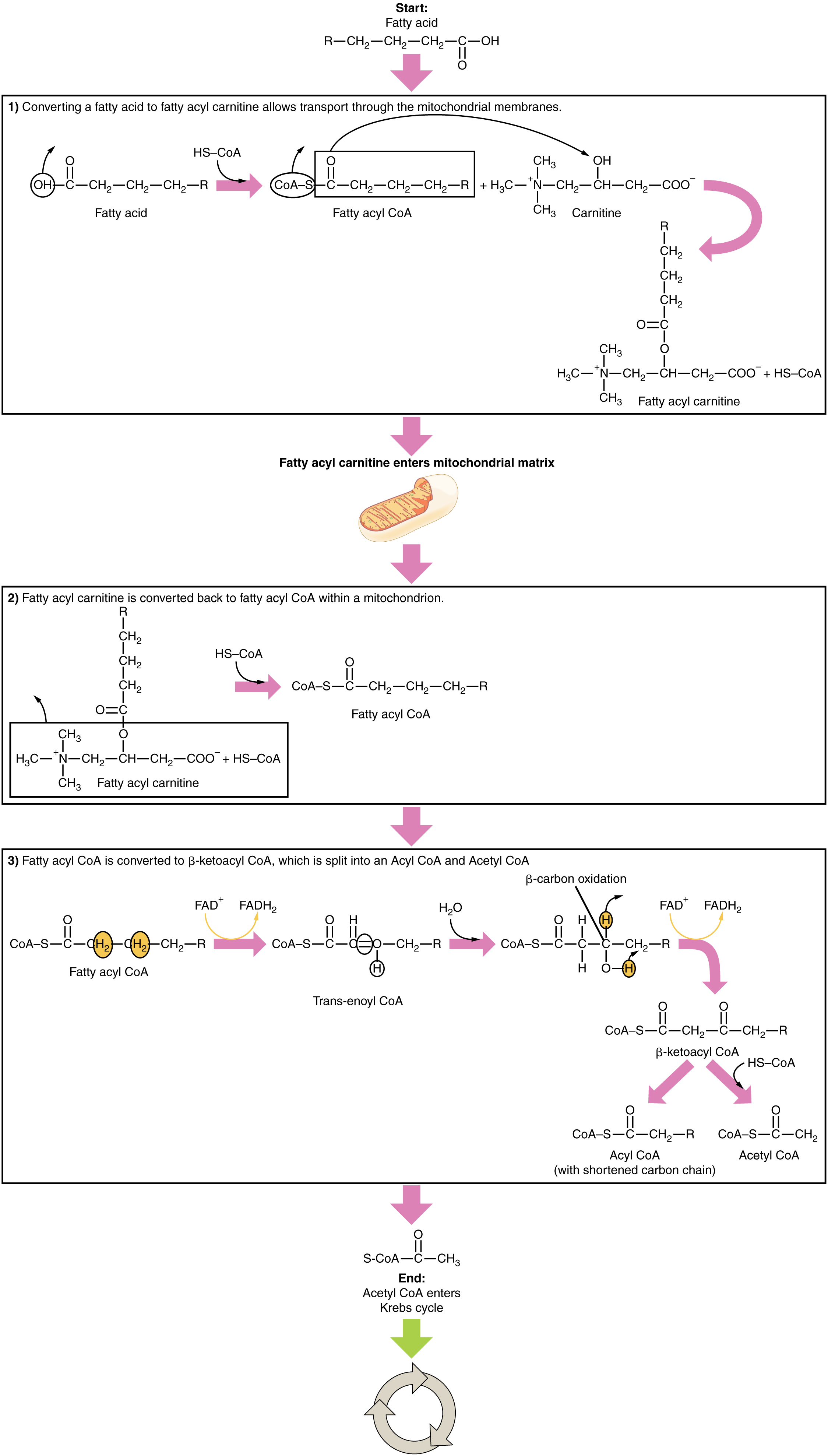
The breakdown of fatty acids, called fatty acid oxidation or beta (β)-oxidation , begins in the cytoplasm, where fatty acids are converted into fatty acyl CoA molecules. This fatty acyl CoA combines with carnitine to create a fatty acyl carnitine molecule, which helps to transport the fatty acid across the mitochondrial membrane. Once inside the mitochondrial matrix, the fatty acyl carnitine molecule is converted back into fatty acyl CoA and then into acetyl CoA ( [link] ). The newly formed acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and is used to produce ATP in the same way as acetyl CoA derived from pyruvate.
If excessive acetyl CoA is created from the oxidation of fatty acids and the Krebs cycle is overloaded and cannot handle it, the acetyl CoA is diverted to create ketone bodies . These ketone bodies can serve as a fuel source if glucose levels are too low in the body. Ketones serve as fuel in times of prolonged starvation or when patients suffer from uncontrolled diabetes and cannot utilize most of the circulating glucose. In both cases, fat stores are liberated to generate energy through the Krebs cycle and will generate ketone bodies when too much acetyl CoA accumulates.
In this ketone synthesis reaction, excess acetyl CoA is converted into hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA (HMG CoA) . HMG CoA is a precursor of cholesterol and is an intermediate that is subsequently converted into β-hydroxybutyrate, the primary ketone body in the blood ( [link] ).
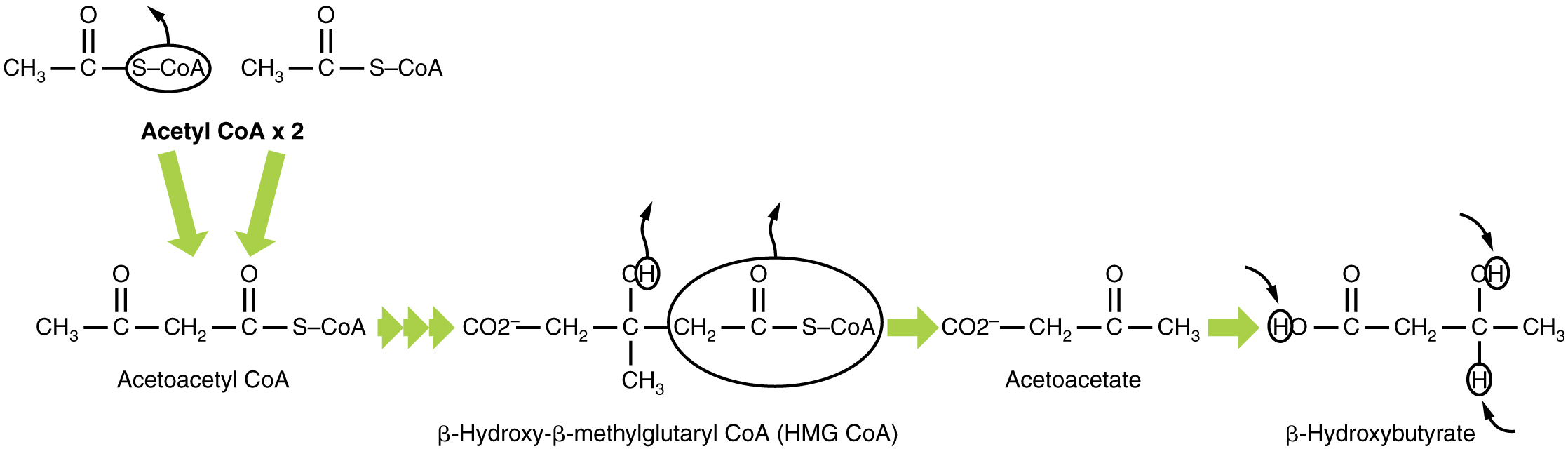
Organs that have classically been thought to be dependent solely on glucose, such as the brain, can actually use ketones as an alternative energy source. This keeps the brain functioning when glucose is limited. When ketones are produced faster than they can be used, they can be broken down into CO 2 and acetone. The acetone is removed by exhalation. One symptom of ketogenesis is that the patient’s breath smells sweet like alcohol. This effect provides one way of telling if a diabetic is properly controlling the disease. The carbon dioxide produced can acidify the blood, leading to diabetic ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition in diabetics.
Ketones oxidize to produce energy for the brain. beta (β)-hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to acetoacetate and NADH is released. An HS-CoA molecule is added to acetoacetate, forming acetoacetyl CoA. The carbon within the acetoacetyl CoA that is not bonded to the CoA then detaches, splitting the molecule in two. This carbon then attaches to another free HS-CoA, resulting in two acetyl CoA molecules. These two acetyl CoA molecules are then processed through the Krebs cycle to generate energy ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?