| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

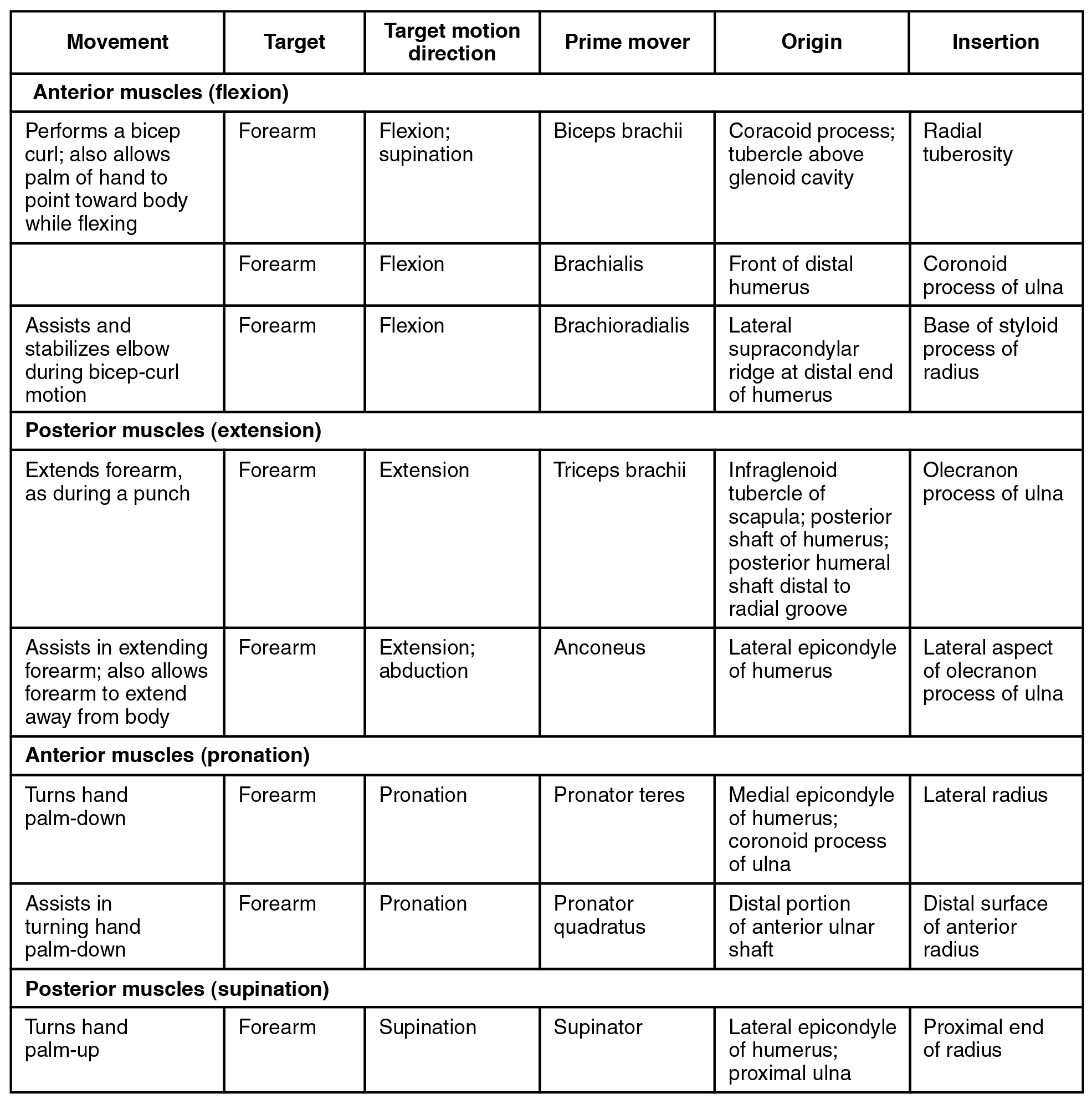
Wrist, hand, and finger movements are facilitated by two groups of muscles. The forearm is the origin of the extrinsic muscles of the hand . The palm is the origin of the intrinsic muscles of the hand.
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (anterior flexor compartment of the forearm) originate on the humerus and insert onto different parts of the hand. These make up the bulk of the forearm. From lateral to medial, the superficial anterior compartment of the forearm includes the flexor carpi radialis , palmaris longus , flexor carpi ulnaris , and flexor digitorum superficialis . The flexor digitorum superficialis flexes the hand as well as the digits at the knuckles, which allows for rapid finger movements, as in typing or playing a musical instrument (see [link] and [link] ). However, poor ergonomics can irritate the tendons of these muscles as they slide back and forth with the carpal tunnel of the anterior wrist and pinch the median nerve, which also travels through the tunnel, causing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. The deep anterior compartment produces flexion and bends fingers to make a fist. These are the flexor pollicis longus and the flexor digitorum profundus .
The muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the forearm (superficial posterior extensor compartment of the forearm) originate on the humerus. These are the extensor radialis longus , extensor carpi radialis brevis , extensor digitorum , extensor digiti minimi , and the extensor carpi ulnaris .
The muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the forearm (deep posterior extensor compartment of the forearm) originate on the radius and ulna. These include the abductor pollicis longus , extensor pollicis brevis , extensor pollicis longus , and extensor indicis (see [link] ).
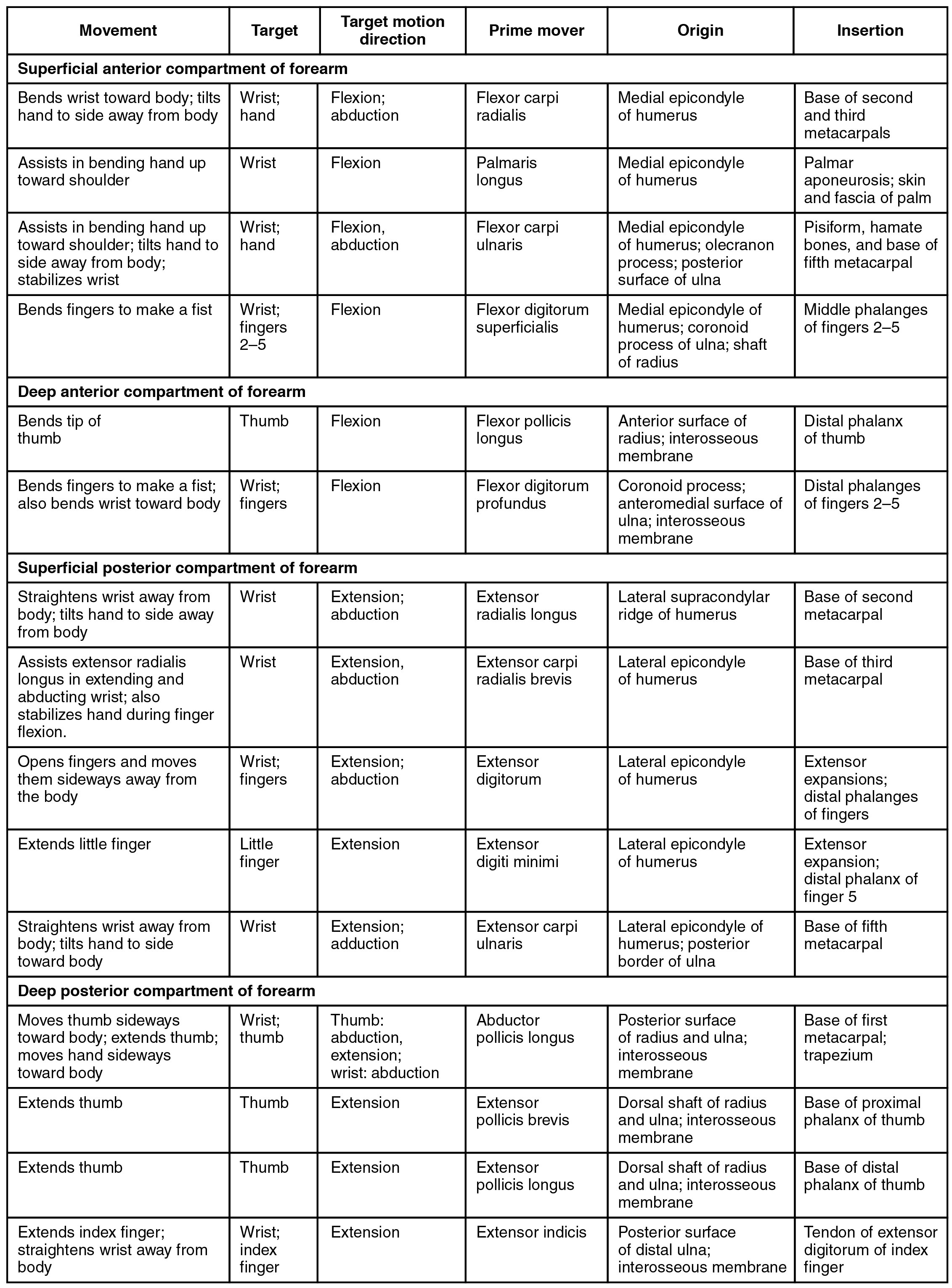
The tendons of the forearm muscles attach to the wrist and extend into the hand. Fibrous bands called retinacula sheath the tendons at the wrist. The flexor retinaculum extends over the palmar surface of the hand while the extensor retinaculum extends over the dorsal surface of the hand.
The intrinsic muscles of the hand both originate and insert within it ( [link] ). These muscles allow your fingers to also make precise movements for actions, such as typing or writing. These muscles are divided into three groups. The thenar muscles are on the radial aspect of the palm. The hypothenar muscles are on the medial aspect of the palm, and the intermediate muscles are midpalmar.
The thenar muscles include the abductor pollicis brevis , opponens pollicis , flexor pollicis brevis , and the adductor pollicis . These muscles form the thenar eminence , the rounded contour of the base of the thumb, and all act on the thumb. The movements of the thumb play an integral role in most precise movements of the hand.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?