| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
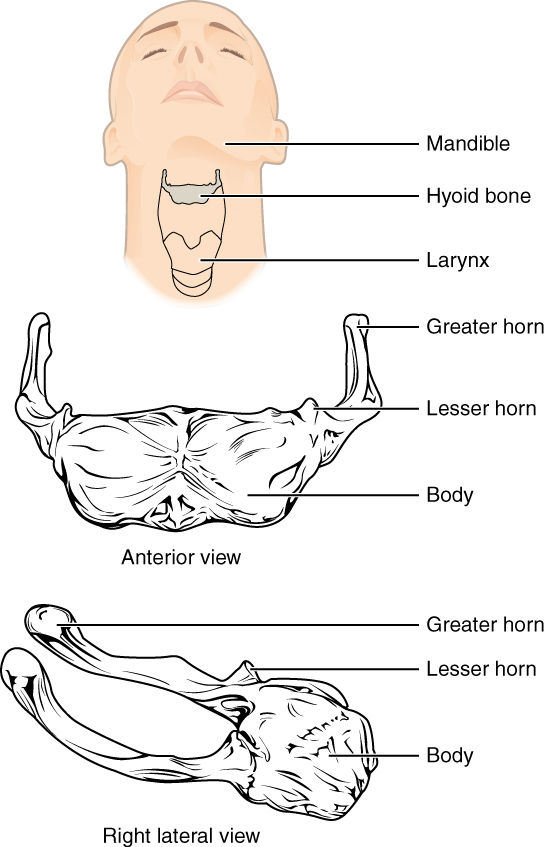
The hyoid bone is an independent bone that does not contact any other bone and thus is not part of the skull ( [link] ). It is a small U-shaped bone located in the upper neck near the level of the inferior mandible, with the tips of the “U” pointing posteriorly. The hyoid serves as the base for the tongue above, and is attached to the larynx below and the pharynx posteriorly. The hyoid is held in position by a series of small muscles that attach to it either from above or below. These muscles act to move the hyoid up/down or forward/back. Movements of the hyoid are coordinated with movements of the tongue, larynx, and pharynx during swallowing and speaking.
The skull consists of the brain case and the facial bones. The brain case surrounds and protects the brain, which occupies the cranial cavity inside the skull. It consists of the rounded calvaria and a complex base. The brain case is formed by eight bones, the paired parietal and temporal bones plus the unpaired frontal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. The narrow gap between the bones is filled with dense, fibrous connective tissue that unites the bones. The sagittal suture joins the right and left parietal bones. The coronal suture joins the parietal bones to the frontal bone, the lamboid suture joins them to the occipital bone, and the squamous suture joins them to the temporal bone.
The facial bones support the facial structures and form the upper and lower jaws. These consist of 14 bones, with the paired maxillary, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior conchae bones and the unpaired vomer and mandible bones. The ethmoid bone also contributes to the formation of facial structures. The maxilla forms the upper jaw and the mandible forms the lower jaw. The maxilla also forms the larger anterior portion of the hard palate, which is completed by the smaller palatine bones that form the posterior portion of the hard palate.
The floor of the cranial cavity increases in depth from front to back and is divided into three cranial fossae. The anterior cranial fossa is located between the frontal bone and lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. A small area of the ethmoid bone, consisting of the crista galli and cribriform plates, is located at the midline of this fossa. The middle cranial fossa extends from the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone to the petrous ridge (petrous portion of temporal bone). The right and left sides are separated at the midline by the sella turcica, which surrounds the shallow hypophyseal fossa. Openings through the skull in the floor of the middle fossa include the optic canal and superior orbital fissure, which open into the posterior orbit, the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale, and foramen spinosum, and the exit of the carotid canal with its underlying foramen lacerum. The deep posterior cranial fossa extends from the petrous ridge to the occipital bone. Openings here include the large foramen magnum, plus the internal acoustic meatus, jugular foramina, and hypoglossal canals. Additional openings located on the external base of the skull include the stylomastoid foramen and the entrance to the carotid canal.
The anterior skull has the orbits that house the eyeballs and associated muscles. The walls of the orbit are formed by contributions from seven bones: the frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, palatine, ethmoid, lacrimal, and sphenoid. Located at the superior margin of the orbit is the supraorbital foramen, and below the orbit is the infraorbital foramen. The mandible has two openings, the mandibular foramen on its inner surface and the mental foramen on its external surface near the chin. The nasal conchae are bony projections from the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. The large inferior nasal concha is an independent bone, while the middle and superior conchae are parts of the ethmoid bone. The nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, the vomer bone, and the septal cartilage. The paranasal sinuses are air-filled spaces located within the frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
On the lateral skull, the zygomatic arch consists of two parts, the temporal process of the zygomatic bone anteriorly and the zygomatic process of the temporal bone posteriorly. The temporal fossa is the shallow space located on the lateral skull above the level of the zygomatic arch. The infratemporal fossa is located below the zygomatic arch and deep to the ramus of the mandible.
The hyoid bone is located in the upper neck and does not join with any other bone. It is held in position by muscles and serves to support the tongue above, the larynx below, and the pharynx posteriorly.
Watch this video to view a rotating and exploded skull with color-coded bones. Which bone (yellow) is centrally located and joins with most of the other bones of the skull?
The sphenoid bone joins with most other bones of the skull. It is centrally located, where it forms portions of the rounded brain case and cranial base.
View this animation to see how a blow to the head may produce a contrecoup (counterblow) fracture of the basilar portion of the occipital bone on the base of the skull. Why may a basilar fracture be life threatening?
A basilar fracture may damage an artery entering the skull, causing bleeding in the brain.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). Injury prevention and control: traumatic brain injury [Internet]. Atlanta, GA; [cited 2013 Mar 18]. Available from: (External Link) .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?