| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
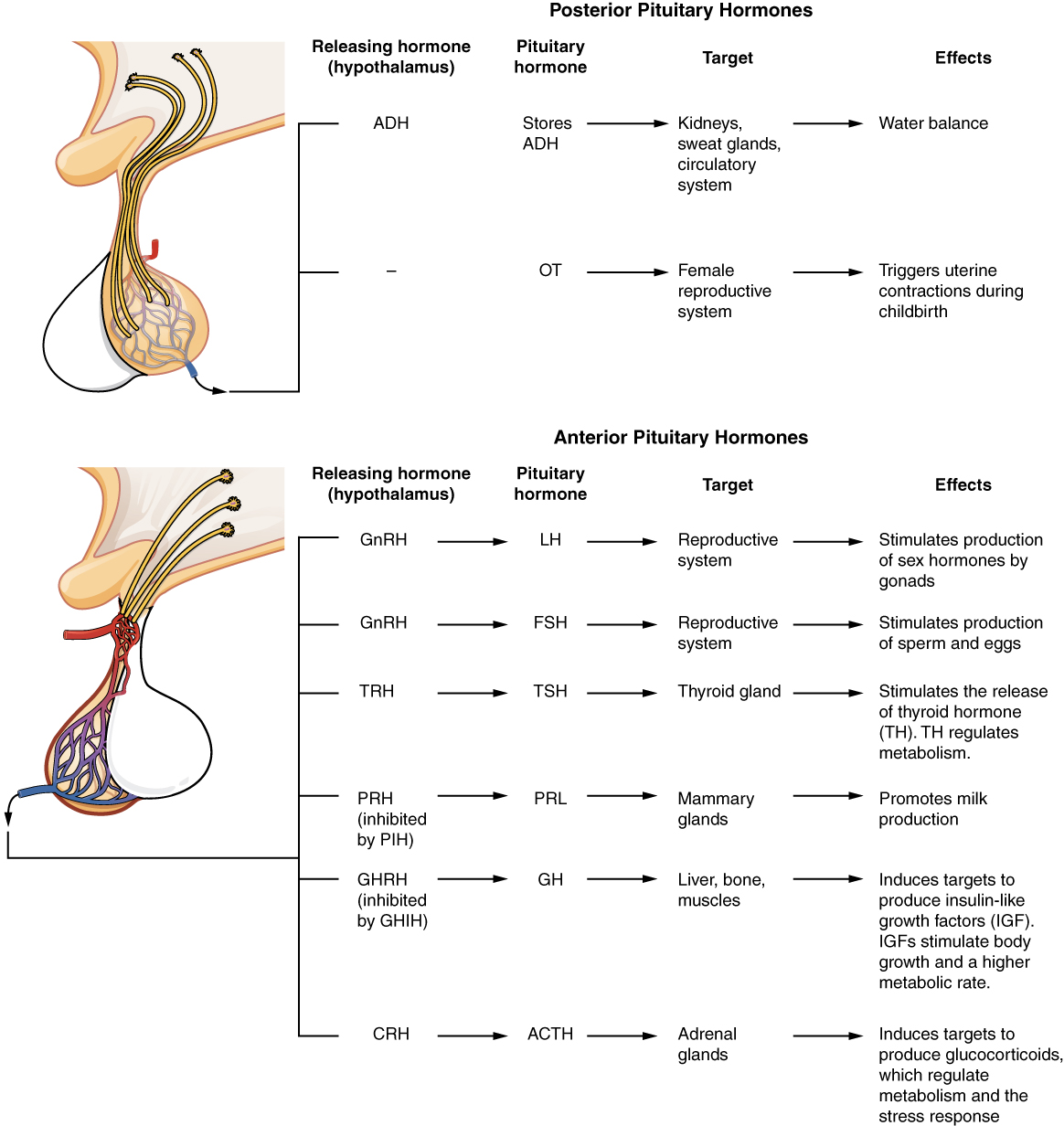
The activity of the thyroid gland is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) , also called thyrotropin. TSH is released from the anterior pituitary in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus. As discussed shortly, it triggers the secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. In a classic negative feedback loop, elevated levels of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream then trigger a drop in production of TRH and subsequently TSH.
The adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) , also called corticotropin, stimulates the adrenal cortex (the more superficial “bark” of the adrenal glands) to secrete corticosteroid hormones such as cortisol. ACTH come from a precursor molecule known as pro-opiomelanotropin (POMC) which produces several biologically active molecules when cleaved, including ACTH, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, and the brain opioid peptides known as endorphins.
The release of ACTH is regulated by the corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus in response to normal physiologic rhythms. A variety of stressors can also influence its release, and the role of ACTH in the stress response is discussed later in this chapter.
The endocrine glands secrete a variety of hormones that control the development and regulation of the reproductive system (these glands include the anterior pituitary, the adrenal cortex, and the gonads—the testes in males and the ovaries in females). Much of the development of the reproductive system occurs during puberty and is marked by the development of sex-specific characteristics in both male and female adolescents. Puberty is initiated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a hormone produced and secreted by the hypothalamus. GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete gonadotropins —hormones that regulate the function of the gonads. The levels of GnRH are regulated through a negative feedback loop; high levels of reproductive hormones inhibit the release of GnRH. Throughout life, gonadotropins regulate reproductive function and, in the case of women, the onset and cessation of reproductive capacity.
The gonadotropins include two glycoprotein hormones: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the production and maturation of sex cells, or gametes, including ova in women and sperm in men. FSH also promotes follicular growth; these follicles then release estrogens in the female ovaries. Luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation in women, as well as the production of estrogens and progesterone by the ovaries. LH stimulates production of testosterone by the male testes.
As its name implies, prolactin (PRL) promotes lactation (milk production) in women. During pregnancy, it contributes to development of the mammary glands, and after birth, it stimulates the mammary glands to produce breast milk. However, the effects of prolactin depend heavily upon the permissive effects of estrogens, progesterone, and other hormones. And as noted earlier, the let-down of milk occurs in response to stimulation from oxytocin.
In a non-pregnant woman, prolactin secretion is inhibited by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH), which is actually the neurotransmitter dopamine, and is released from neurons in the hypothalamus. Only during pregnancy do prolactin levels rise in response to prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH) from the hypothalamus.
The cells in the zone between the pituitary lobes secrete a hormone known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) that is formed by cleavage of the pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) precursor protein. Local production of MSH in the skin is responsible for melanin production in response to UV light exposure. The role of MSH made by the pituitary is more complicated. For instance, people with lighter skin generally have the same amount of MSH as people with darker skin. Nevertheless, this hormone is capable of darkening of the skin by inducing melanin production in the skin’s melanocytes. Women also show increased MSH production during pregnancy; in combination with estrogens, it can lead to darker skin pigmentation, especially the skin of the areolas and labia minora. [link] is a summary of the pituitary hormones and their principal effects.
Visit this link to watch an animation showing the role of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. Which hormone is released by the pituitary to stimulate the thyroid gland?
The hypothalamus–pituitary complex is located in the diencephalon of the brain. The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland are connected by a structure called the infundibulum, which contains vasculature and nerve axons. The pituitary gland is divided into two distinct structures with different embryonic origins. The posterior lobe houses the axon terminals of hypothalamic neurons. It stores and releases into the bloodstream two hypothalamic hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH). The anterior lobe is connected to the hypothalamus by vasculature in the infundibulum and produces and secretes six hormones. Their secretion is regulated, however, by releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus. The six anterior pituitary hormones are: growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and prolactin (PRL).
Visit this link to watch an animation showing the role of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. Which hormone is released by the pituitary to stimulate the thyroid gland?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?