| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inflammation of the peritoneum is called peritonitis. Chemical peritonitis can develop any time the wall of the alimentary canal is breached, allowing the contents of the lumen entry into the peritoneal cavity. For example, when an ulcer perforates the stomach wall, gastric juices spill into the peritoneal cavity. Hemorrhagic peritonitis occurs after a ruptured tubal pregnancy or traumatic injury to the liver or spleen fills the peritoneal cavity with blood. Even more severe peritonitis is associated with bacterial infections seen with appendicitis, colonic diverticulitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (infection of uterine tubes, usually by sexually transmitted bacteria). Peritonitis is life threatening and often results in emergency surgery to correct the underlying problem and intensive antibiotic therapy. When your great grandparents and even your parents were young, the mortality from peritonitis was high. Aggressive surgery, improvements in anesthesia safety, the advance of critical care expertise, and antibiotics have greatly improved the mortality rate from this condition. Even so, the mortality rate still ranges from 30 to 40 percent.
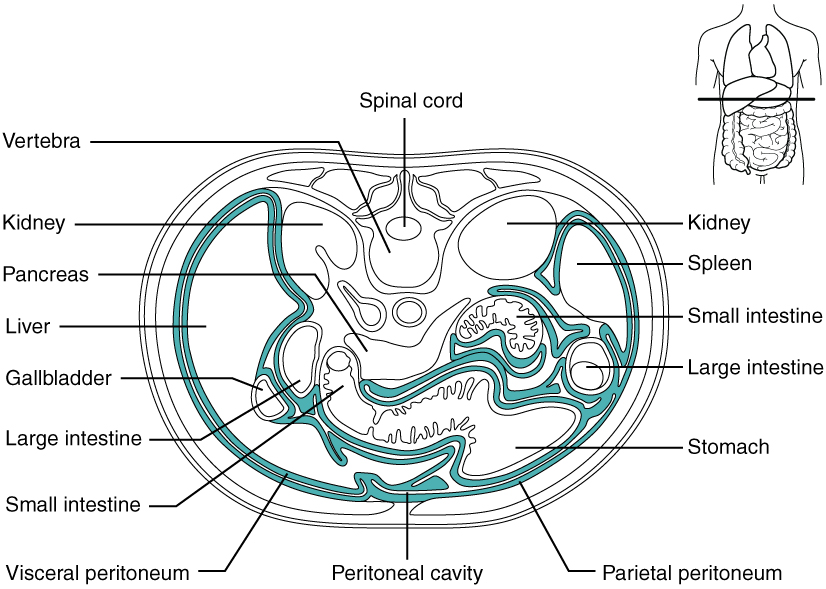
The visceral peritoneum includes multiple large folds that envelope various abdominal organs, holding them to the dorsal surface of the body wall. Within these folds are blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves that innervate the organs with which they are in contact, supplying their adjacent organs. The five major peritoneal folds are described in [link] . Note that during fetal development, certain digestive structures, including the first portion of the small intestine (called the duodenum), the pancreas, and portions of the large intestine (the ascending and descending colon, and the rectum) remain completely or partially posterior to the peritoneum. Thus, the location of these organs is described as retroperitoneal .
| The Five Major Peritoneal Folds | |
|---|---|
| Fold | Description |
| Greater omentum | Apron-like structure that lies superficial to the small intestine and transverse colon; a site of fat deposition in people who are overweight |
| Falciform ligament | Anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and inferior border of the diaphragm |
| Lesser omentum | Suspends the stomach from the inferior border of the liver; provides a pathway for structures connecting to the liver |
| Mesentery | Vertical band of tissue anterior to the lumbar vertebrae and anchoring all of the small intestine except the initial portion (the duodenum) |
| Mesocolon | Attaches two portions of the large intestine (the transverse and sigmoid colon) to the posterior abdominal wall |

By clicking on this link you can watch a short video of what happens to the food you eat, as it passes from your mouth to your intestine. Along the way, note how the food changes consistency and form. How does this change in consistency facilitate your gaining nutrients from food?
The digestive system includes the organs of the alimentary canal and accessory structures. The alimentary canal forms a continuous tube that is open to the outside environment at both ends. The organs of the alimentary canal are the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The accessory digestive structures include the teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The wall of the alimentary canal is composed of four basic tissue layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa. The enteric nervous system provides intrinsic innervation, and the autonomic nervous system provides extrinsic innervation.
By clicking on this link , you can watch a short video of what happens to the food you eat as it passes from your mouth to your intestine. Along the way, note how the food changes consistency and form. How does this change in consistency facilitate your gaining nutrients from food?
Answers may vary.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?