| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The control of ventilation is a complex interplay of multiple regions in the brain that signal the muscles used in pulmonary ventilation to contract ( [link] ). The result is typically a rhythmic, consistent ventilation rate that provides the body with sufficient amounts of oxygen, while adequately removing carbon dioxide.
| Summary of Ventilation Regulation | |
|---|---|
| System component | Function |
| Medullary respiratory renter | Sets the basic rhythm of breathing |
| Ventral respiratory group (VRG) | Generates the breathing rhythm and integrates data coming into the medulla |
| Dorsal respiratory group (DRG) | Integrates input from the stretch receptors and the chemoreceptors in the periphery |
| Pontine respiratory group (PRG) | Influences and modifies the medulla oblongata’s functions |
| Aortic body | Monitors blood PCO 2 , PO 2 , and pH |
| Carotid body | Monitors blood PCO 2 , PO 2 , and pH |
| Hypothalamus | Monitors emotional state and body temperature |
| Cortical areas of the brain | Control voluntary breathing |
| Proprioceptors | Send impulses regarding joint and muscle movements |
| Pulmonary irritant reflexes | Protect the respiratory zones of the system from foreign material |
| Inflation reflex | Protects the lungs from over-inflating |
Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group ( [link] ).
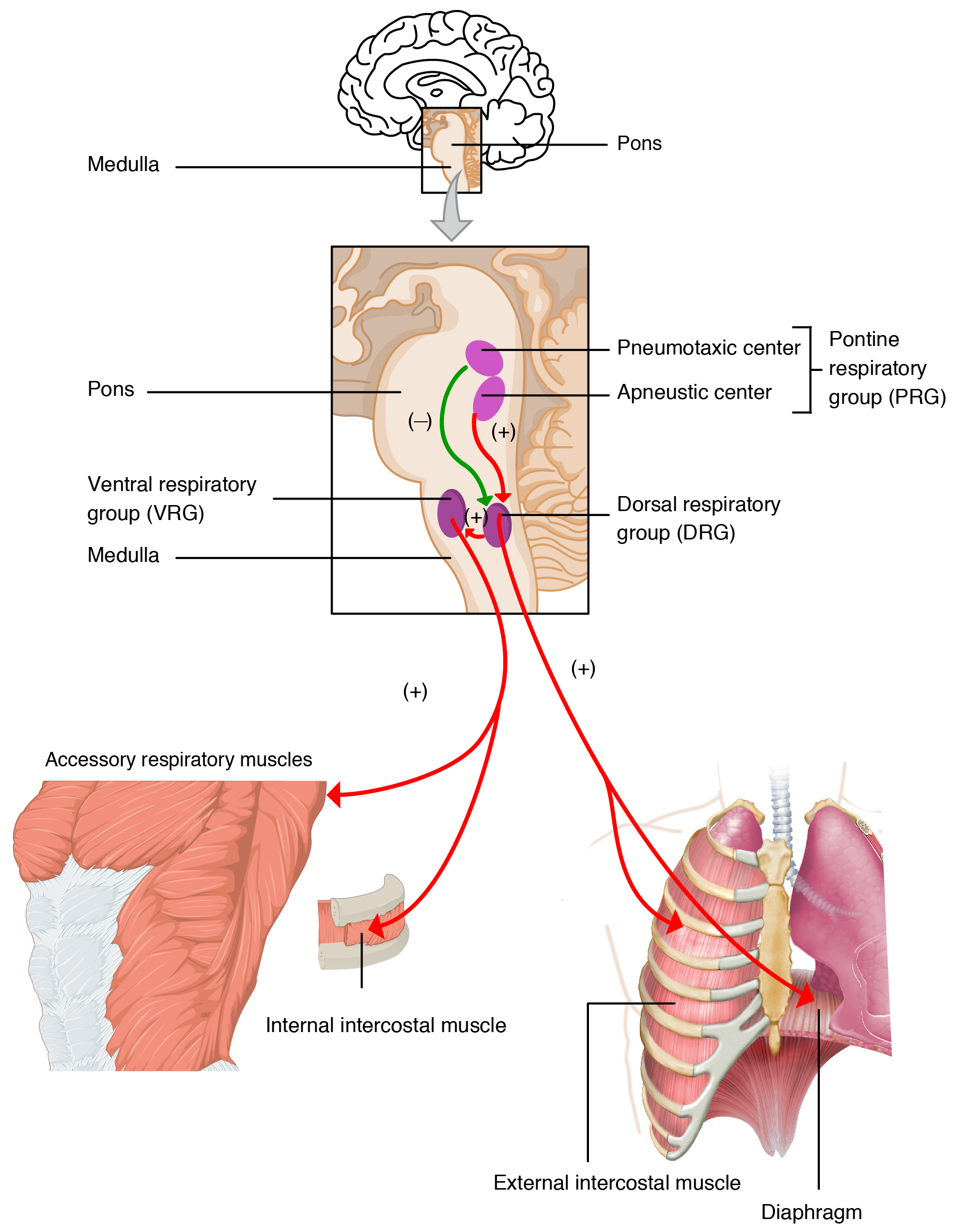
The medulla oblongata contains the dorsal respiratory group (DRG) and the ventral respiratory group (VRG) . The DRG is involved in maintaining a constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration. When activity in the DRG ceases, it no longer stimulates the diaphragm and intercostals to contract, allowing them to relax, resulting in expiration. The VRG is involved in forced breathing, as the neurons in the VRG stimulate the accessory muscles involved in forced breathing to contract, resulting in forced inspiration. The VRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract.
The second respiratory center of the brain is located within the pons, called the pontine respiratory group, and consists of the apneustic and pneumotaxic centers. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. The pneumotaxic center is a network of neurons that inhibits the activity of neurons in the DRG, allowing relaxation after inspiration, and thus controlling the overall rate.
The respiratory rate and the depth of inspiration are regulated by the medulla oblongata and pons; however, these regions of the brain do so in response to systemic stimuli. It is a dose-response, positive-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Thus, increasing stimuli results in forced breathing. Multiple systemic factors are involved in stimulating the brain to produce pulmonary ventilation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?