| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cardiac muscle cells branch freely. A junction between two adjoining cells is marked by a critical structure called an intercalated disc , which helps support the synchronized contraction of the muscle ( [link] b ). The sarcolemmas from adjacent cells bind together at the intercalated discs. They consist of desmosomes, specialized linking proteoglycans, tight junctions, and large numbers of gap junctions that allow the passage of ions between the cells and help to synchronize the contraction ( [link] c ). Intercellular connective tissue also helps to bind the cells together. The importance of strongly binding these cells together is necessitated by the forces exerted by contraction.
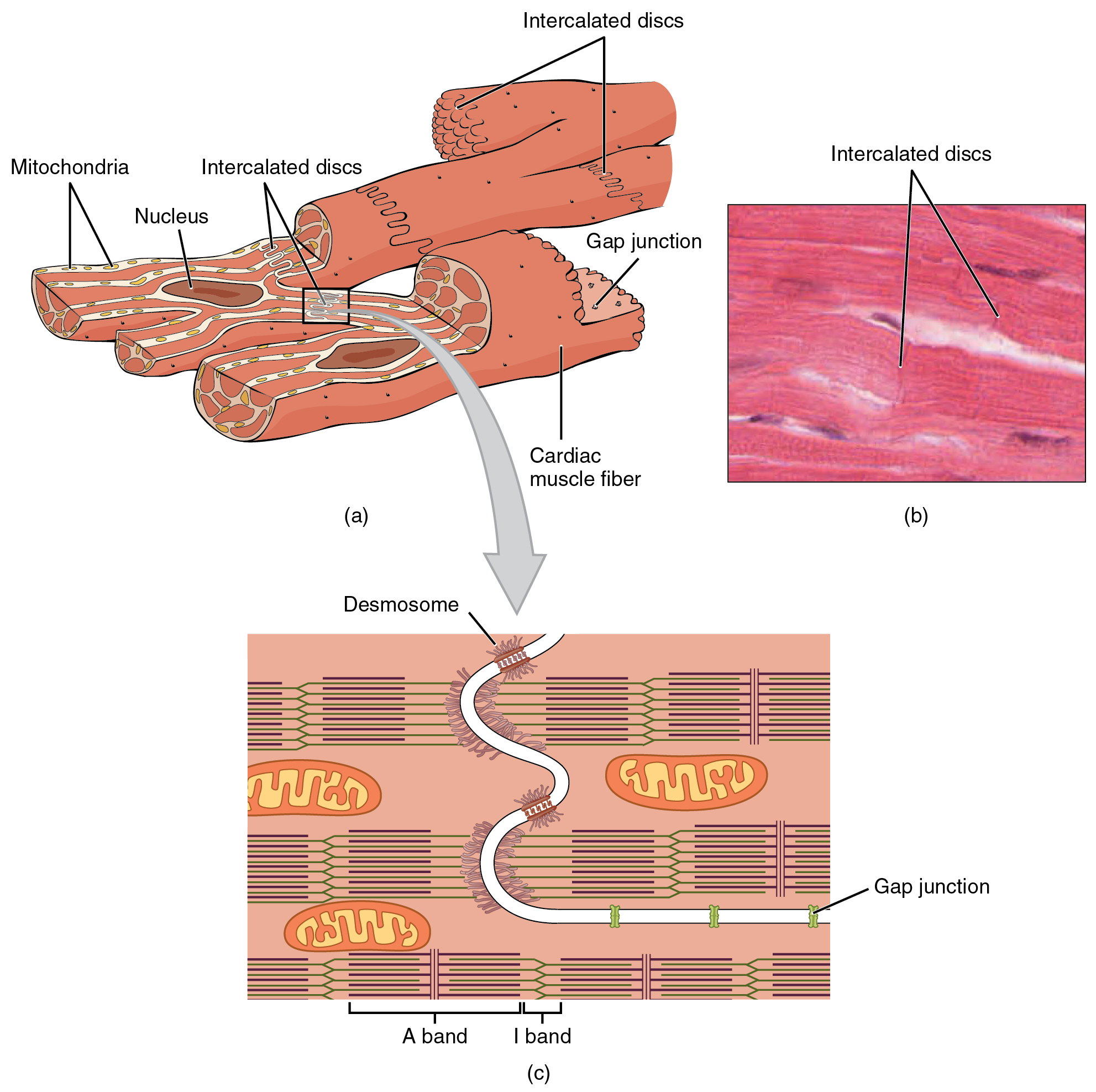
Cardiac muscle undergoes aerobic respiration patterns, primarily metabolizing lipids and carbohydrates. Myoglobin, lipids, and glycogen are all stored within the cytoplasm. Cardiac muscle cells undergo twitch-type contractions with long refractory periods followed by brief relaxation periods. The relaxation is essential so the heart can fill with blood for the next cycle. The refractory period is very long to prevent the possibility of tetany, a condition in which muscle remains involuntarily contracted. In the heart, tetany is not compatible with life, since it would prevent the heart from pumping blood.
If embryonic heart cells are separated into a Petri dish and kept alive, each is capable of generating its own electrical impulse followed by contraction. When two independently beating embryonic cardiac muscle cells are placed together, the cell with the higher inherent rate sets the pace, and the impulse spreads from the faster to the slower cell to trigger a contraction. As more cells are joined together, the fastest cell continues to assume control of the rate. A fully developed adult heart maintains the capability of generating its own electrical impulse, triggered by the fastest cells, as part of the cardiac conduction system. The components of the cardiac conduction system include the sinoatrial node, the atrioventricular node, the atrioventricular bundle, the atrioventricular bundle branches, and the Purkinje cells ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?