| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
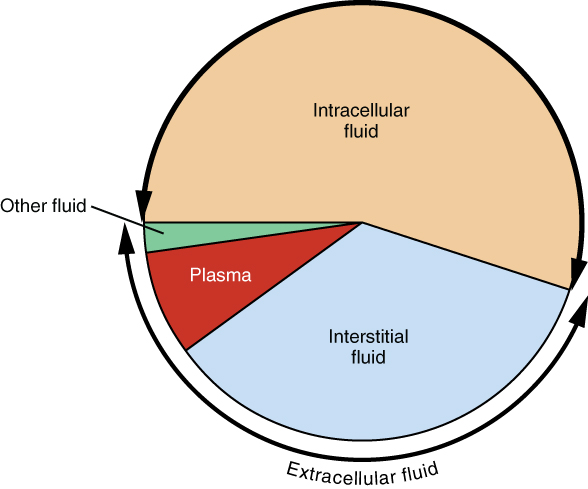
The ECF accounts for the other one-third of the body’s water content. Approximately 20 percent of the ECF is found in plasma. Plasma travels through the body in blood vessels and transports a range of materials, including blood cells, proteins (including clotting factors and antibodies), electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and wastes. Gases, nutrients, and waste materials travel between capillaries and cells through the IF. Cells are separated from the IF by a selectively permeable cell membrane that helps regulate the passage of materials between the IF and the interior of the cell.
The body has other water-based ECF. These include the cerebrospinal fluid that bathes the brain and spinal cord, lymph, the synovial fluid in joints, the pleural fluid in the pleural cavities, the pericardial fluid in the cardiac sac, the peritoneal fluid in the peritoneal cavity, and the aqueous humor of the eye. Because these fluids are outside of cells, these fluids are also considered components of the ECF compartment.
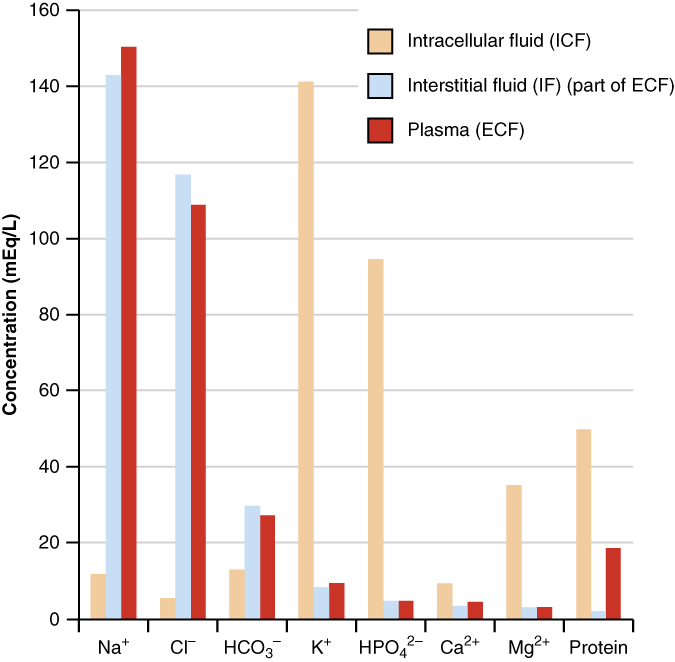
The compositions of the two components of the ECF—plasma and IF—are more similar to each other than either is to the ICF ( [link] ). Blood plasma has high concentrations of sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, and protein. The IF has high concentrations of sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate, but a relatively lower concentration of protein. In contrast, the ICF has elevated amounts of potassium, phosphate, magnesium, and protein. Overall, the ICF contains high concentrations of potassium and phosphate ( ), whereas both plasma and the ECF contain high concentrations of sodium and chloride.

Watch this video to learn more about body fluids, fluid compartments, and electrolytes. When blood volume decreases due to sweating, from what source is water taken in by the blood?
Most body fluids are neutral in charge. Thus, cations, or positively charged ions, and anions, or negatively charged ions, are balanced in fluids. As seen in the previous graph, sodium (Na + ) ions and chloride (Cl - ) ions are concentrated in the ECF of the body, whereas potassium (K + ) ions are concentrated inside cells. Although sodium and potassium can “leak” through “pores” into and out of cells, respectively, the high levels of potassium and low levels of sodium in the ICF are maintained by sodium-potassium pumps in the cell membranes. These pumps use the energy supplied by ATP to pump sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?