| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
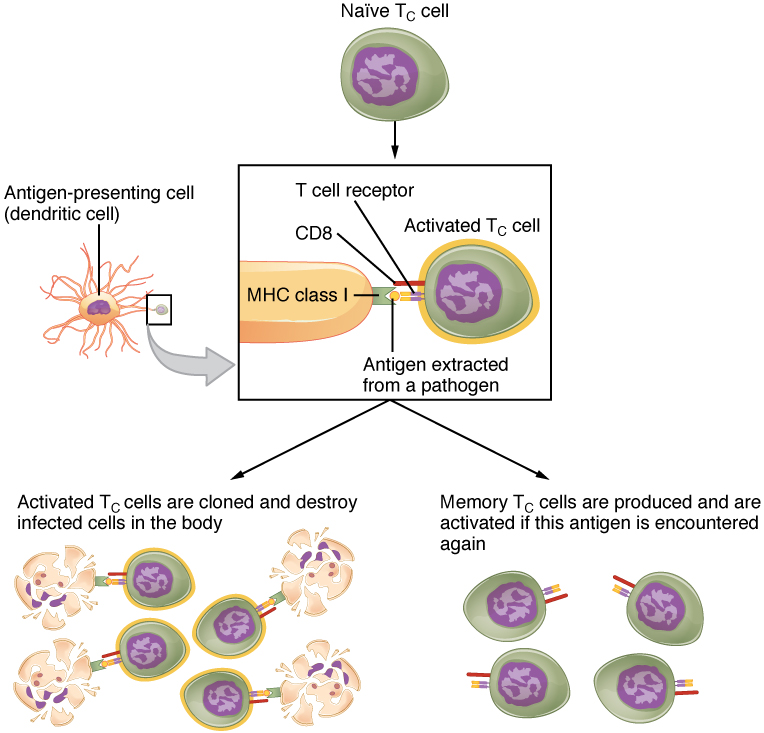
The clonal selection theory was proposed by Frank Burnet in the 1950s. However, the term clonal selection is not a complete description of the theory, as clonal expansion goes hand in glove with the selection process. The main tenet of the theory is that a typical individual has a multitude (10 11 ) of different types of T cell clones based on their receptors. In this use, a clone is a group of lymphocytes that share the same antigen receptor . Each clone is necessarily present in the body in low numbers. Otherwise, the body would not have room for lymphocytes with so many specificities.
Only those clones of lymphocytes whose receptors are activated by the antigen are stimulated to proliferate. Keep in mind that most antigens have multiple antigenic determinants, so a T cell response to a typical antigen involves a polyclonal response. A polyclonal response is the stimulation of multiple T cell clones. Once activated, the selected clones increase in number and make many copies of each cell type, each clone with its unique receptor. By the time this process is complete, the body will have large numbers of specific lymphocytes available to fight the infection (see [link] ).
As already discussed, one of the major features of an adaptive immune response is the development of immunological memory.
During a primary adaptive immune response, both memory T cells and effector T cells are generated. Memory T cells are long-lived and can even persist for a lifetime. Memory cells are primed to act rapidly. Thus, any subsequent exposure to the pathogen will elicit a very rapid T cell response. This rapid, secondary adaptive response generates large numbers of effector T cells so fast that the pathogen is often overwhelmed before it can cause any symptoms of disease. This is what is meant by immunity to a disease. The same pattern of primary and secondary immune responses occurs in B cells and the antibody response, as will be discussed later in the chapter.
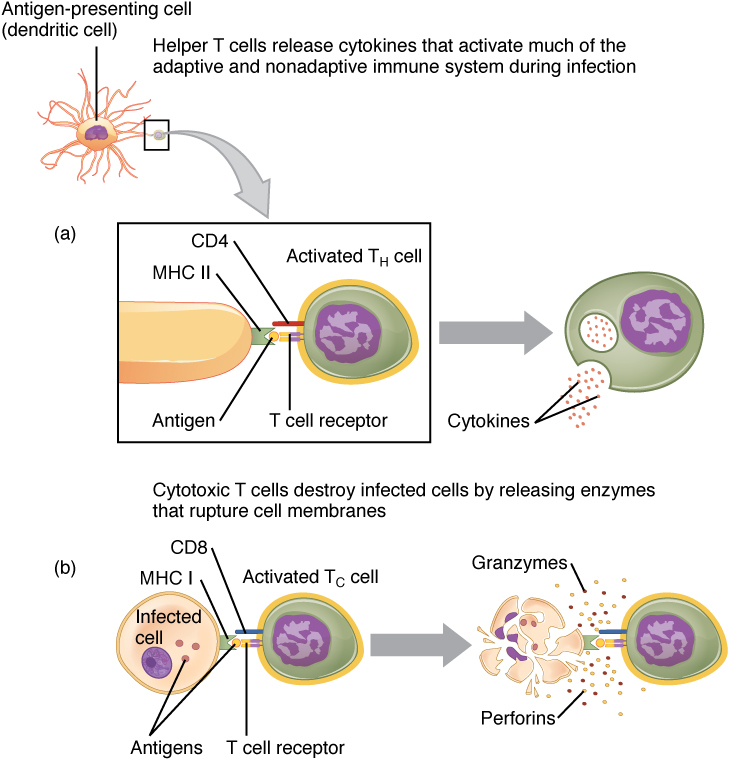
In the discussion of T cell development, you saw that mature T cells express either the CD4 marker or the CD8 marker, but not both. These markers are cell adhesion molecules that keep the T cell in close contact with the antigen-presenting cell by directly binding to the MHC molecule (to a different part of the molecule than does the antigen). Thus, T cells and antigen-presenting cells are held together in two ways: by CD4 or CD8 attaching to MHC and by the T cell receptor binding to antigen ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?