| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
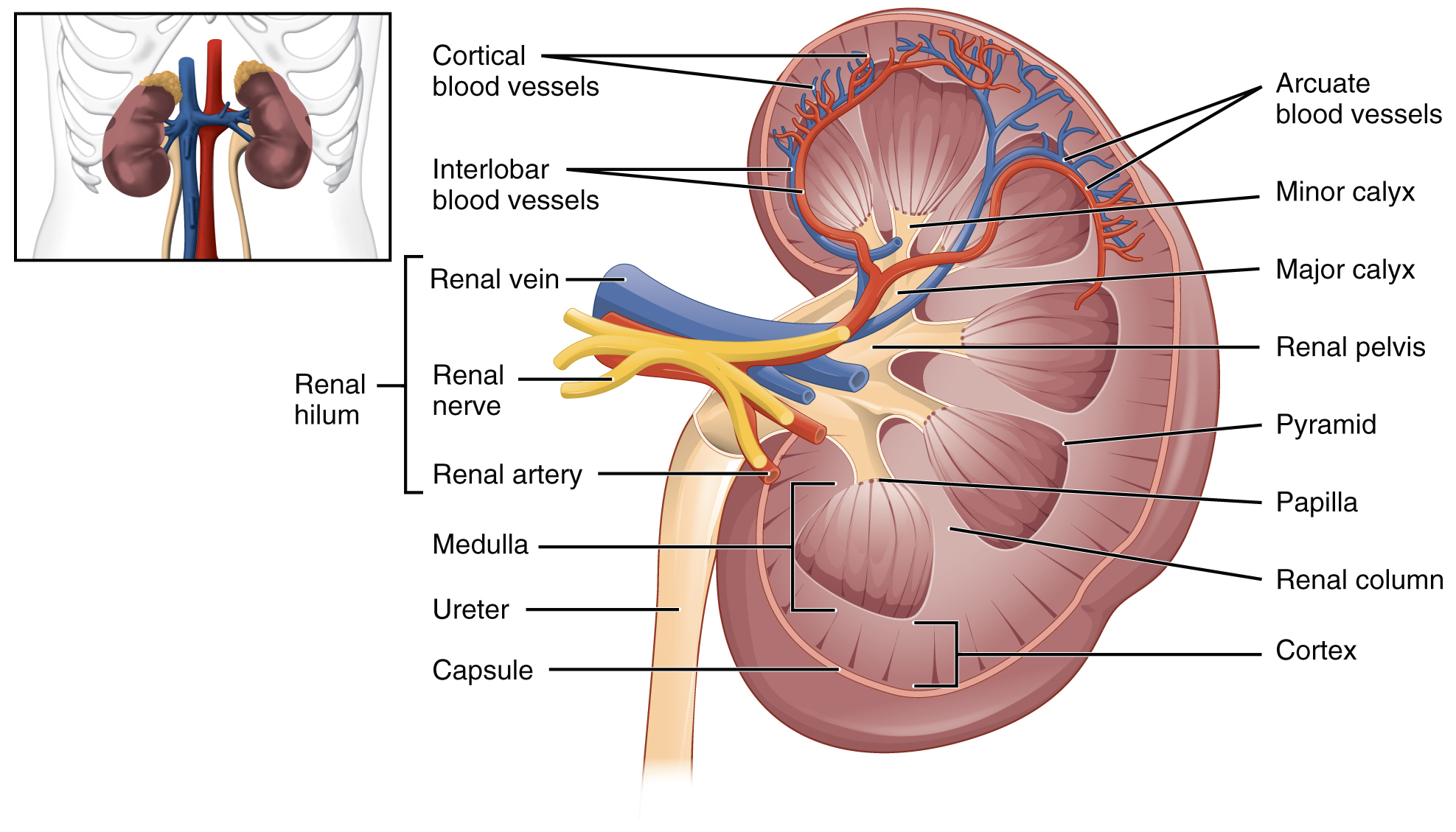
The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyxes in the kidney. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via peristalsis into the ureter. The renal arteries form directly from the descending aorta, whereas the renal veins return cleansed blood directly to the inferior vena cava. The artery, vein, and renal pelvis are arranged in an anterior-to-posterior order.
The renal artery first divides into segmental arteries, followed by further branching to form interlobar arteries that pass through the renal columns to reach the cortex ( [link] ). The interlobar arteries, in turn, branch into arcuate arteries, cortical radiate arteries, and then into afferent arterioles. The afferent arterioles service about 1.3 million nephrons in each kidney.
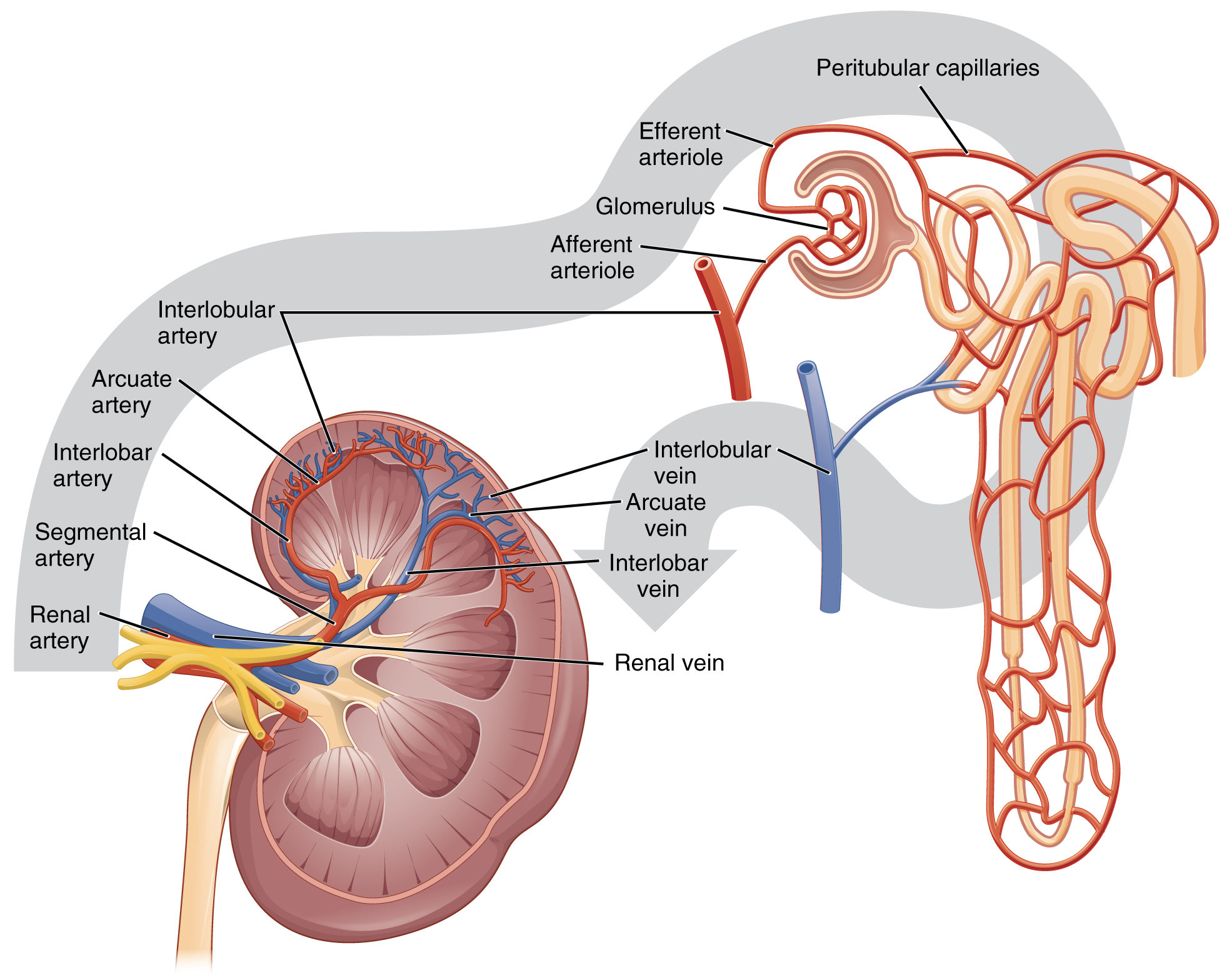
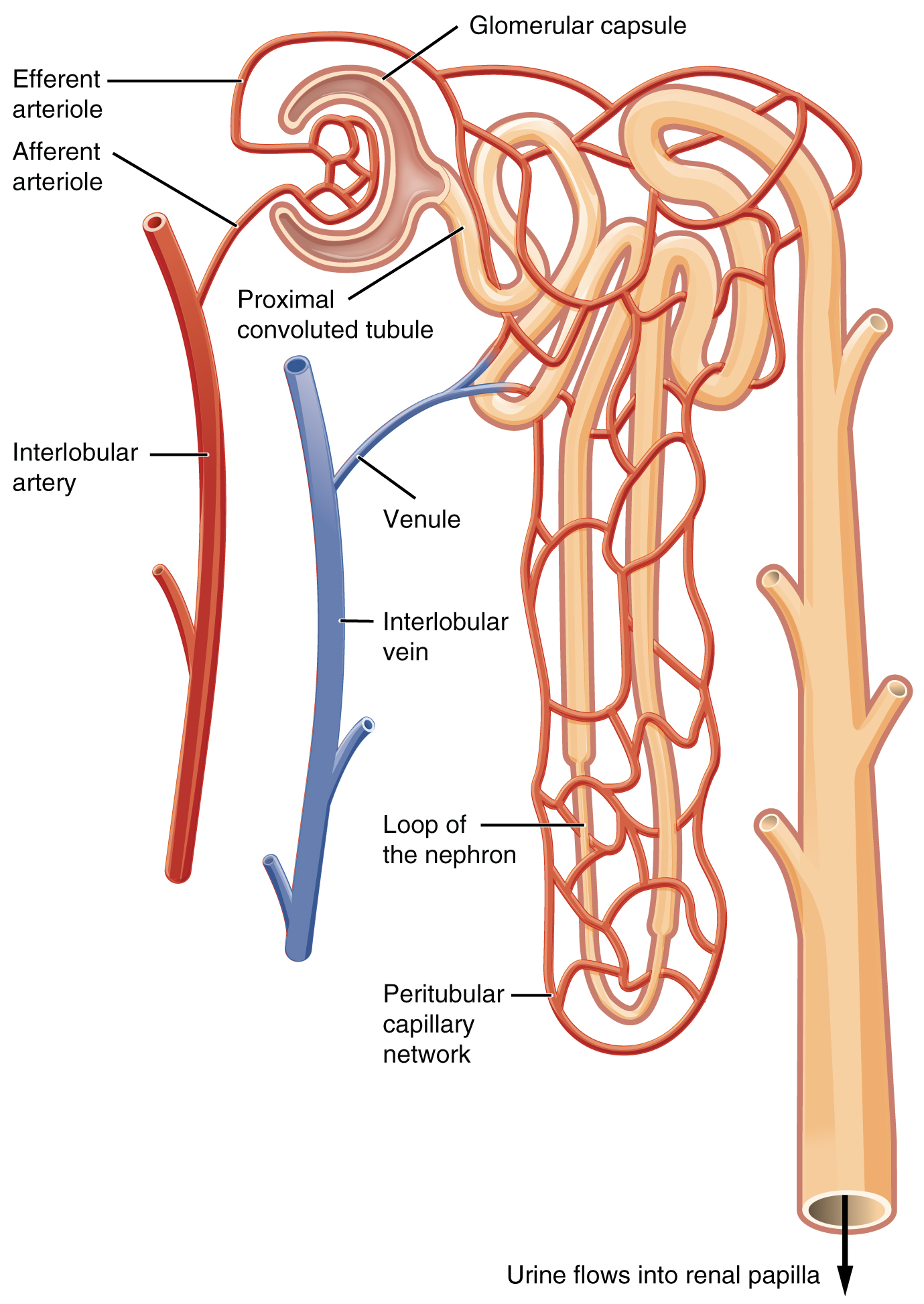
Nephrons are the “functional units” of the kidney; they cleanse the blood and balance the constituents of the circulation. The afferent arterioles form a tuft of high-pressure capillaries about 200 µm in diameter, the glomerulus . The rest of the nephron consists of a continuous sophisticated tubule whose proximal end surrounds the glomerulus in an intimate embrace—this is Bowman’s capsule . The glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule together form the renal corpuscle . As mentioned earlier, these glomerular capillaries filter the blood based on particle size. After passing through the renal corpuscle, the capillaries form a second arteriole, the efferent arteriole ( [link] ). These will next form a capillary network around the more distal portions of the nephron tubule, the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta , before returning to the venous system. As the glomerular filtrate progresses through the nephron, these capillary networks recover most of the solutes and water, and return them to the circulation. Since a capillary bed (the glomerulus) drains into a vessel that in turn forms a second capillary bed, the definition of a portal system is met. This is the only portal system in which an arteriole is found between the first and second capillary beds. (Portal systems also link the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary, and the blood vessels of the digestive viscera to the liver.)
Visit this link to view an interactive tutorial of the flow of blood through the kidney.
In a dissected kidney, it is easy to identify the cortex; it appears lighter in color compared to the rest of the kidney. All of the renal corpuscles as well as both the proximal convoluted tubules (PCTs) and distal convoluted tubules are found here. Some nephrons have a short loop of Henle that does not dip beyond the cortex. These nephrons are called cortical nephrons . About 15 percent of nephrons have long loops of Henle that extend deep into the medulla and are called juxtamedullary nephrons .
As noted previously, the structure of the kidney is divided into two principle regions—the peripheral rim of cortex and the central medulla. The two kidneys receive about 25 percent of cardiac output. They are protected in the retroperitoneal space by the renal fat pad and overlying ribs and muscle. Ureters, blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves enter and leave at the renal hilum. The renal arteries arise directly from the aorta, and the renal veins drain directly into the inferior vena cava. Kidney function is derived from the actions of about 1.3 million nephrons per kidney; these are the “functional units.” A capillary bed, the glomerulus, filters blood and the filtrate is captured by Bowman’s capsule. A portal system is formed when the blood flows through a second capillary bed surrounding the proximal and distal convoluted tubules and the loop of Henle. Most water and solutes are recovered by this second capillary bed. This filtrate is processed and finally gathered by collecting ducts that drain into the minor calyces, which merge to form major calyces; the filtrate then proceeds to the renal pelvis and finally the ureters.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?