| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Certain hormones, such as androgens, epinephrine, thyroid hormones, and growth hormone, can affect the oxygen–hemoglobin saturation/disassociation curve by stimulating the production of a compound called 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) by erythrocytes. BPG is a byproduct of glycolysis. Because erythrocytes do not contain mitochondria, glycolysis is the sole method by which these cells produce ATP. BPG promotes the disassociation of oxygen from hemoglobin. Therefore, the greater the concentration of BPG, the more readily oxygen dissociates from hemoglobin, despite its partial pressure.
The pH of the blood is another factor that influences the oxygen–hemoglobin saturation/dissociation curve (see [link] ). The Bohr effect is a phenomenon that arises from the relationship between pH and oxygen’s affinity for hemoglobin: A lower, more acidic pH promotes oxygen dissociation from hemoglobin. In contrast, a higher, or more basic, pH inhibits oxygen dissociation from hemoglobin. The greater the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood, the more molecules that must be converted, which in turn generates hydrogen ions and thus lowers blood pH. Furthermore, blood pH may become more acidic when certain byproducts of cell metabolism, such as lactic acid, carbonic acid, and carbon dioxide, are released into the bloodstream.
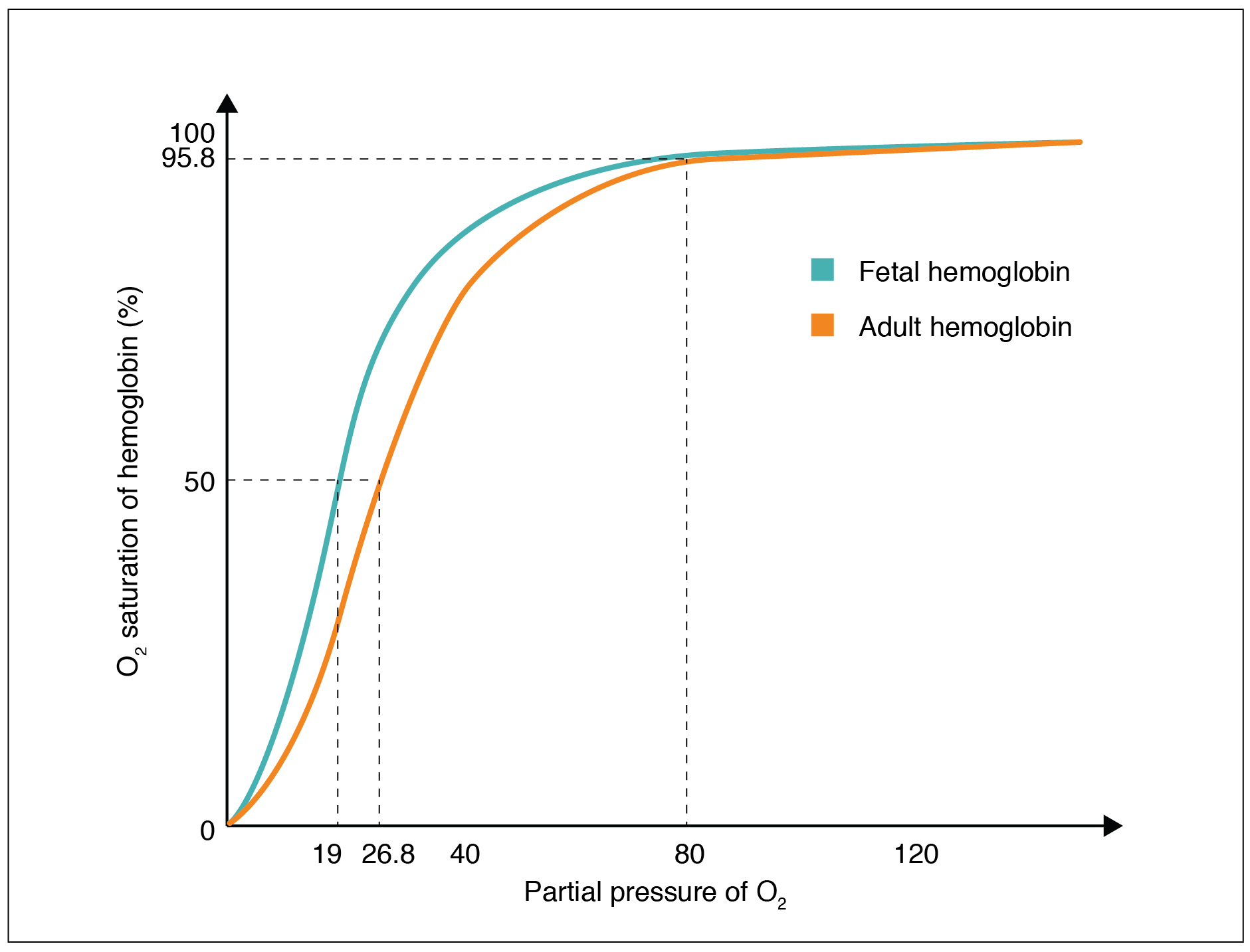
The fetus has its own circulation with its own erythrocytes; however, it is dependent on the mother for oxygen. Blood is supplied to the fetus by way of the umbilical cord, which is connected to the placenta and separated from maternal blood by the chorion. The mechanism of gas exchange at the chorion is similar to gas exchange at the respiratory membrane. However, the partial pressure of oxygen is lower in the maternal blood in the placenta, at about 35 to 50 mm Hg, than it is in maternal arterial blood. The difference in partial pressures between maternal and fetal blood is not large, as the partial pressure of oxygen in fetal blood at the placenta is about 20 mm Hg. Therefore, there is not as much diffusion of oxygen into the fetal blood supply. The fetus’ hemoglobin overcomes this problem by having a greater affinity for oxygen than maternal hemoglobin ( [link] ). Both fetal and adult hemoglobin have four subunits, but two of the subunits of fetal hemoglobin have a different structure that causes fetal hemoglobin to have a greater affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
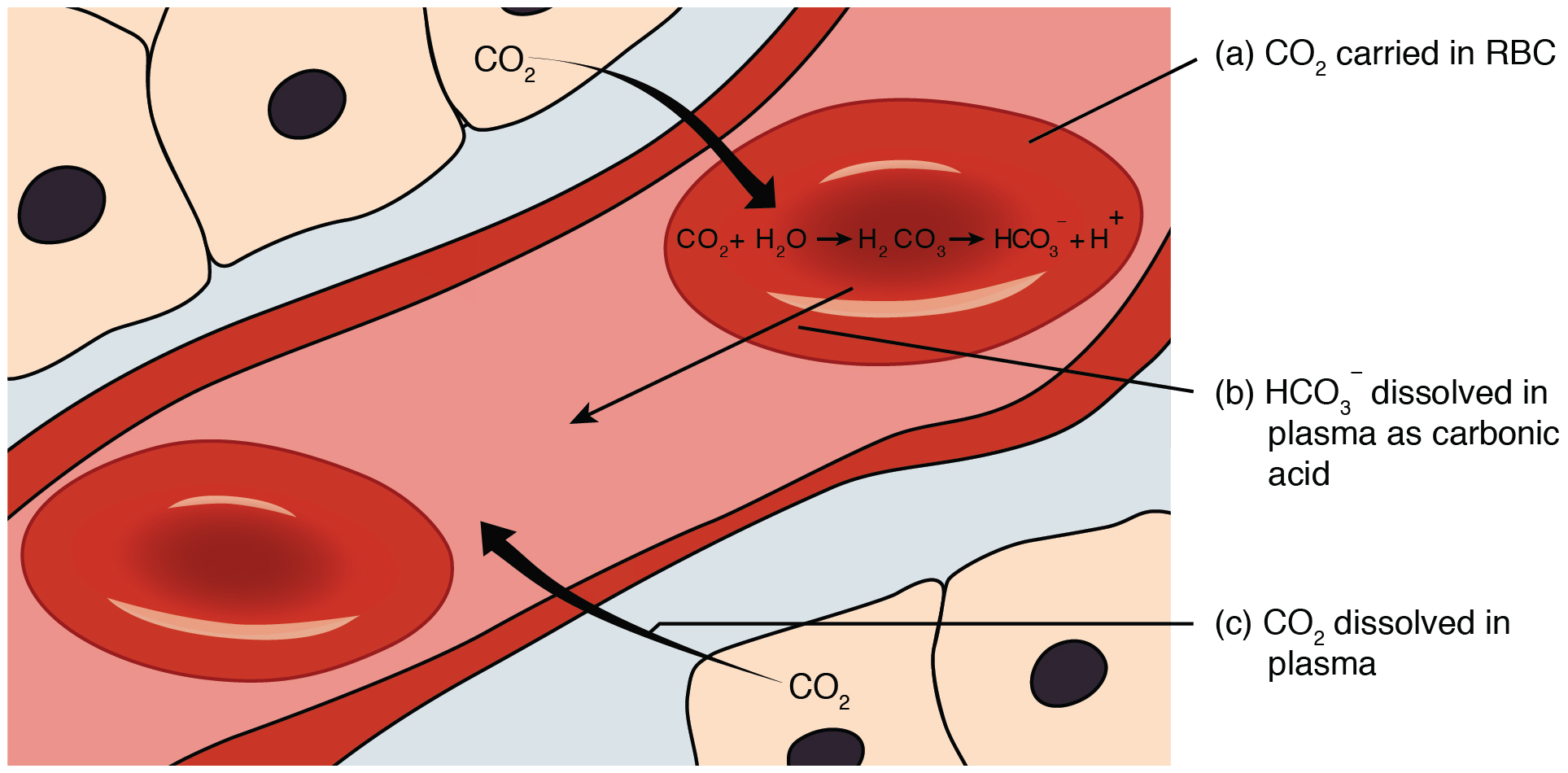
Carbon dioxide is transported by three major mechanisms. The first mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is by blood plasma, as some carbon dioxide molecules dissolve in the blood. The second mechanism is transport in the form of bicarbonate (HCO 3 – ), which also dissolves in plasma. The third mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is similar to the transport of oxygen by erythrocytes ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?