| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
At a plane joint (gliding joint), the articulating surfaces of the bones are flat or slightly curved and of approximately the same size, which allows the bones to slide against each other (see [link] d ). The motion at this type of joint is usually small and tightly constrained by surrounding ligaments. Based only on their shape, plane joints can allow multiple movements, including rotation. Thus plane joints can be functionally classified as a multiaxial joint. However, not all of these movements are available to every plane joint due to limitations placed on it by ligaments or neighboring bones. Thus, depending upon the specific joint of the body, a plane joint may exhibit only a single type of movement or several movements. Plane joints are found between the carpal bones (intercarpal joints) of the wrist or tarsal bones (intertarsal joints) of the foot, between the clavicle and acromion of the scapula (acromioclavicular joint), and between the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae (zygapophysial joints).
The joint with the greatest range of motion is the ball-and-socket joint . At these joints, the rounded head of one bone (the ball) fits into the concave articulation (the socket) of the adjacent bone (see [link] f ). The hip joint and the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint are the only ball-and-socket joints of the body. At the hip joint, the head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the hip bone, and at the shoulder joint, the head of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Ball-and-socket joints are classified functionally as multiaxial joints. The femur and the humerus are able to move in both anterior-posterior and medial-lateral directions and they can also rotate around their long axis. The shallow socket formed by the glenoid cavity allows the shoulder joint an extensive range of motion. In contrast, the deep socket of the acetabulum and the strong supporting ligaments of the hip joint serve to constrain movements of the femur, reflecting the need for stability and weight-bearing ability at the hip.
Watch this video to see an animation of synovial joints in action. Synovial joints are places where bones articulate with each other inside of a joint cavity. The different types of synovial joints are the ball-and-socket joint (shoulder joint), hinge joint (knee), pivot joint (atlantoaxial joint, between C1 and C2 vertebrae of the neck), condyloid joint (radiocarpal joint of the wrist), saddle joint (first carpometacarpal joint, between the trapezium carpal bone and the first metacarpal bone, at the base of the thumb), and plane joint (facet joints of vertebral column, between superior and inferior articular processes). Which type of synovial joint allows for the widest range of motion?
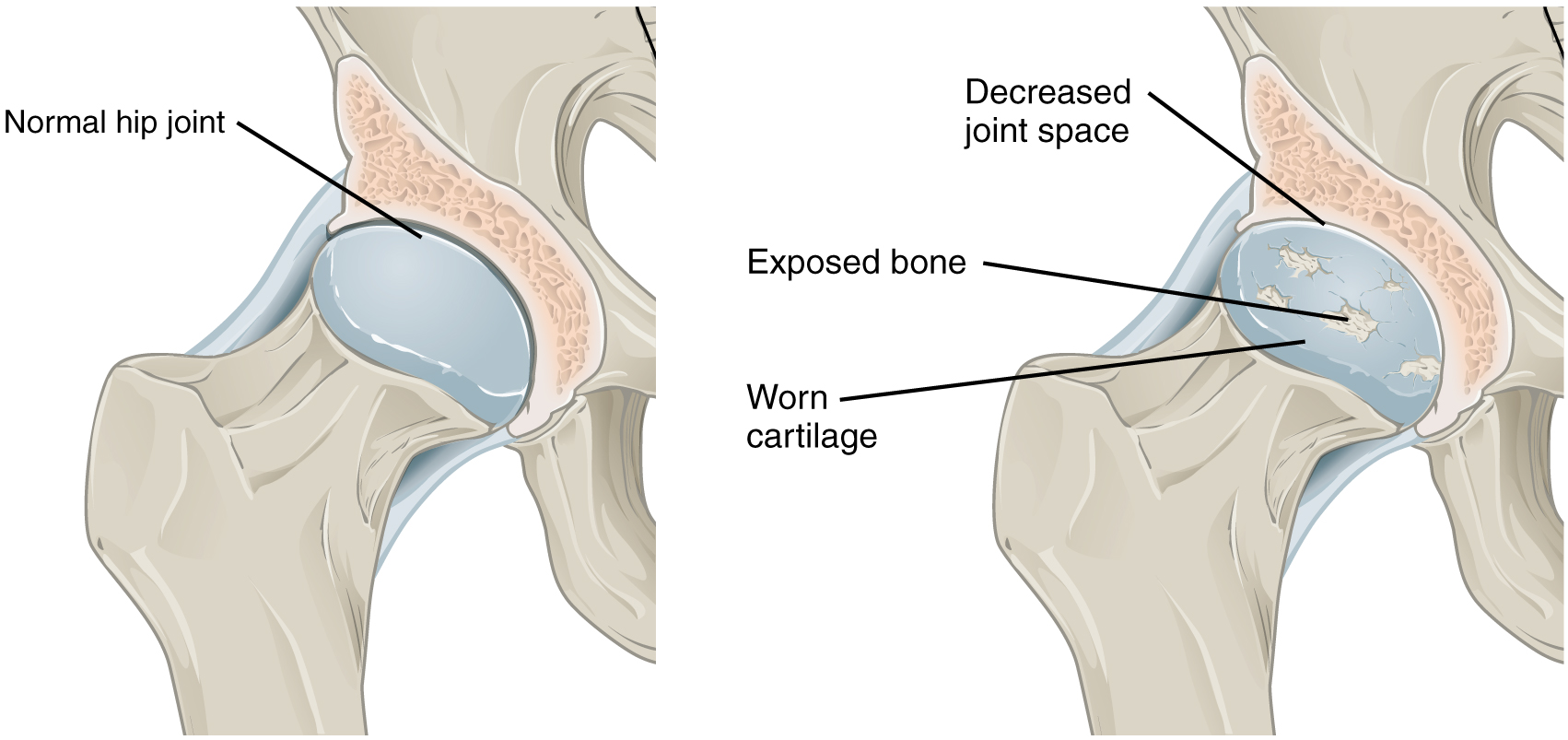
The most common type of arthritis is osteoarthritis, which is associated with aging and “wear and tear” of the articular cartilage ( [link] ). Risk factors that may lead to osteoarthritis later in life include injury to a joint; jobs that involve physical labor; sports with running, twisting, or throwing actions; and being overweight. These factors put stress on the articular cartilage that covers the surfaces of bones at synovial joints, causing the cartilage to gradually become thinner. As the articular cartilage layer wears down, more pressure is placed on the bones. The joint responds by increasing production of the lubricating synovial fluid, but this can lead to swelling of the joint cavity, causing pain and joint stiffness as the articular capsule is stretched. The bone tissue underlying the damaged articular cartilage also responds by thickening, producing irregularities and causing the articulating surface of the bone to become rough or bumpy. Joint movement then results in pain and inflammation. In its early stages, symptoms of osteoarthritis may be reduced by mild activity that “warms up” the joint, but the symptoms may worsen following exercise. In individuals with more advanced osteoarthritis, the affected joints can become more painful and therefore are difficult to use effectively, resulting in increased immobility. There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but several treatments can help alleviate the pain. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and low-impact exercise, and over-the-counter or prescription medications that help to alleviate the pain and inflammation. For severe cases, joint replacement surgery (arthroplasty) may be required.
Joint replacement is a very invasive procedure, so other treatments are always tried before surgery. However arthroplasty can provide relief from chronic pain and can enhance mobility within a few months following the surgery. This type of surgery involves replacing the articular surfaces of the bones with prosthesis (artificial components). For example, in hip arthroplasty, the worn or damaged parts of the hip joint, including the head and neck of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis, are removed and replaced with artificial joint components. The replacement head for the femur consists of a rounded ball attached to the end of a shaft that is inserted inside the diaphysis of the femur. The acetabulum of the pelvis is reshaped and a replacement socket is fitted into its place. The parts, which are always built in advance of the surgery, are sometimes custom made to produce the best possible fit for a patient.
Gout is a form of arthritis that results from the deposition of uric acid crystals within a body joint. Usually only one or a few joints are affected, such as the big toe, knee, or ankle. The attack may only last a few days, but may return to the same or another joint. Gout occurs when the body makes too much uric acid or the kidneys do not properly excrete it. A diet with excessive fructose has been implicated in raising the chances of a susceptible individual developing gout.
Other forms of arthritis are associated with various autoimmune diseases, bacterial infections of the joint, or unknown genetic causes. Autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, or systemic lupus erythematosus, produce arthritis because the immune system of the body attacks the body joints. In rheumatoid arthritis, the joint capsule and synovial membrane become inflamed. As the disease progresses, the articular cartilage is severely damaged or destroyed, resulting in joint deformation, loss of movement, and severe disability. The most commonly involved joints are the hands, feet, and cervical spine, with corresponding joints on both sides of the body usually affected, though not always to the same extent. Rheumatoid arthritis is also associated with lung fibrosis, vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels), coronary heart disease, and premature mortality. With no known cure, treatments are aimed at alleviating symptoms. Exercise, anti-inflammatory and pain medications, various specific disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, or surgery are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?